Execution algorithms automate order placement to minimize market impact and achieve optimal trade prices, using strategies like TWAP, POV, and implementation shortfall. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) algorithms aim to match or better the average market price by distributing trades proportionally throughout the trading day according to volume patterns. Explore the nuances between execution algorithms and VWAP to enhance your trading strategy and execution efficiency.
Why it is important
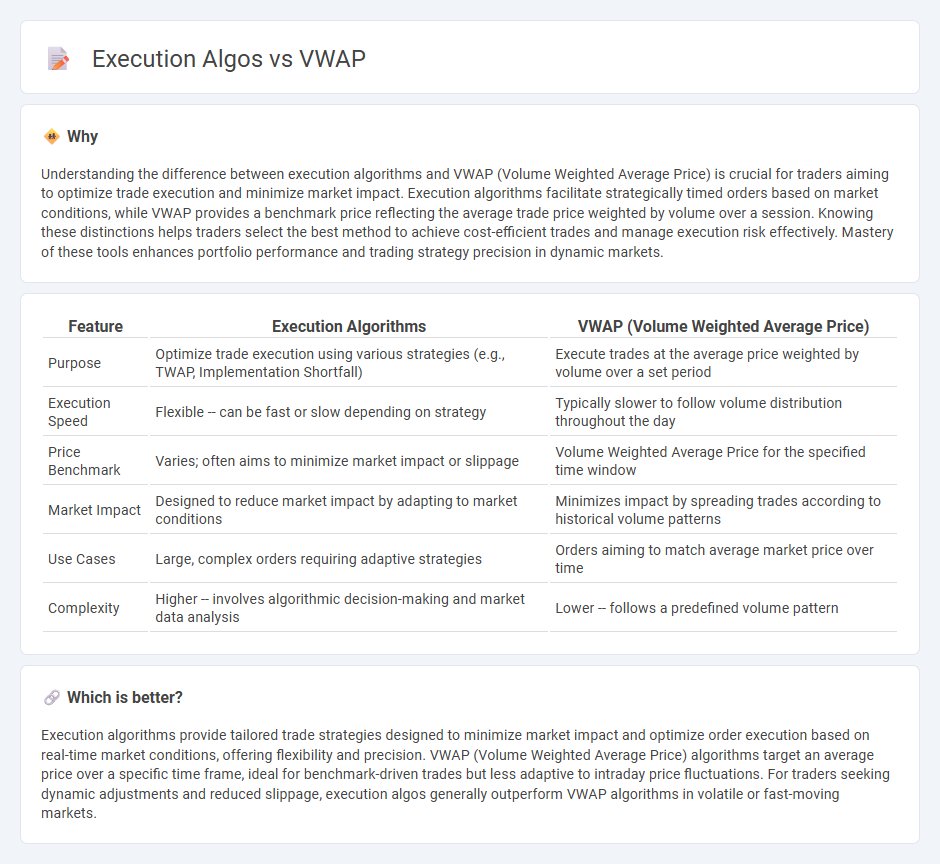
Understanding the difference between execution algorithms and VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) is crucial for traders aiming to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Execution algorithms facilitate strategically timed orders based on market conditions, while VWAP provides a benchmark price reflecting the average trade price weighted by volume over a session. Knowing these distinctions helps traders select the best method to achieve cost-efficient trades and manage execution risk effectively. Mastery of these tools enhances portfolio performance and trading strategy precision in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Execution Algorithms | VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Optimize trade execution using various strategies (e.g., TWAP, Implementation Shortfall) | Execute trades at the average price weighted by volume over a set period |
| Execution Speed | Flexible -- can be fast or slow depending on strategy | Typically slower to follow volume distribution throughout the day |
| Price Benchmark | Varies; often aims to minimize market impact or slippage | Volume Weighted Average Price for the specified time window |
| Market Impact | Designed to reduce market impact by adapting to market conditions | Minimizes impact by spreading trades according to historical volume patterns |
| Use Cases | Large, complex orders requiring adaptive strategies | Orders aiming to match average market price over time |
| Complexity | Higher -- involves algorithmic decision-making and market data analysis | Lower -- follows a predefined volume pattern |
Which is better?
Execution algorithms provide tailored trade strategies designed to minimize market impact and optimize order execution based on real-time market conditions, offering flexibility and precision. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) algorithms target an average price over a specific time frame, ideal for benchmark-driven trades but less adaptive to intraday price fluctuations. For traders seeking dynamic adjustments and reduced slippage, execution algos generally outperform VWAP algorithms in volatile or fast-moving markets.
Connection
Execution algorithms optimize trade orders by breaking them into smaller chunks to minimize market impact and achieve better pricing, often using Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) as a benchmark. VWAP provides a measure of the average price at which a security has traded throughout the day, weighted by volume, serving as a key reference for execution algos aiming to match or outperform market prices. By aligning order execution with VWAP trends, algorithms improve trade efficiency and reduce slippage in electronic trading environments.
Key Terms
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) calculates the average price of a security by weighting each transaction price with its corresponding volume over a trading period, providing a benchmark for trade execution quality. Execution algorithms utilize VWAP to distribute large orders strategically throughout the day, minimizing market impact and achieving price efficiency. Explore advanced strategies and real-world applications of VWAP-driven execution algos to enhance trading performance.
Implementation Shortfall
Implementation Shortfall measures the difference between the decision price and the final execution price, quantifying the cost of timing and market impact in trading. VWAP execution algorithms aim to minimize this cost by spreading trades evenly over a trading horizon to achieve an average price close to the volume-weighted average price. Explore detailed strategies to optimize Implementation Shortfall and improve execution quality.
TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price)
TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) is an execution algorithm designed to execute orders evenly over a specified time period, minimizing market impact by distributing trades uniformly. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) focuses on trading in line with market volume patterns, aiming to achieve an average price weighted by volume rather than time. Explore deeper insights into how TWAP and VWAP algorithms optimize trade execution strategies for different market conditions.
Source and External Links
Volume-weighted average price - VWAP is the ratio of the total value traded of a security to the total volume, calculated as the sum of each trade price times its volume divided by total volume, commonly used by traders to assess market sentiment and by institutions to execute large orders without price disturbance.
VWAP Indicator - What it Is and How to Trade With It - VWAP is an intraday moving average indicator weighted by volume used to identify trends, benchmark trade execution quality, and guide trading strategies by tracking average price per volume throughout the day.
VWAP: Technical Indicator - VWAP combines price and volume to indicate market trends, support and resistance levels, and timing for entry or exit points by showing bullish conditions when price is above VWAP and bearish when below.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com