Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals to profit from market fluctuations, offering a systematic approach suitable for ranging markets. Scalping focuses on rapid, small trades to capitalize on minor price changes, demanding quick decision-making and high-frequency execution. Explore the nuances and strategies of grid trading versus scalping to enhance your trading skills.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between grid trading and scalping is crucial as grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals to profit from market fluctuations over time, while scalping focuses on very short-term trades aiming for small, quick profits. Grid trading suits ranging markets and requires less constant monitoring, whereas scalping demands intense focus and rapid execution in volatile conditions. Choosing the right strategy impacts risk management, trading frequency, and potential profitability. Mastery of these distinctions helps traders align methods with their goals and market environments for optimal results.
Comparison Table
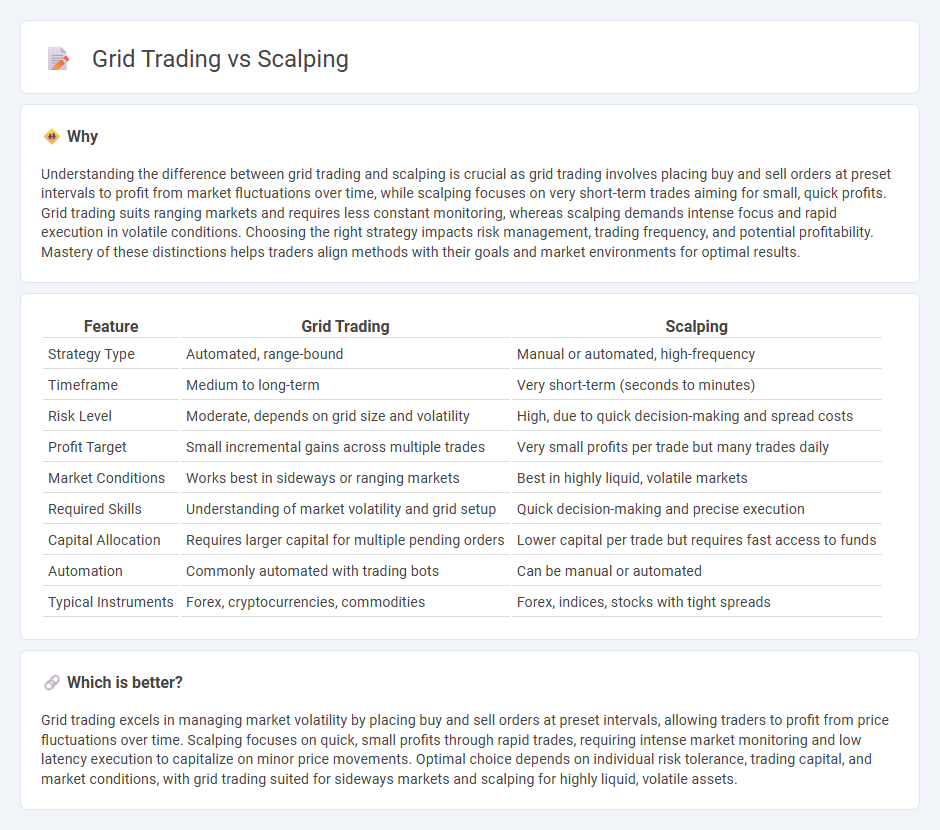
| Feature | Grid Trading | Scalping |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Automated, range-bound | Manual or automated, high-frequency |
| Timeframe | Medium to long-term | Very short-term (seconds to minutes) |
| Risk Level | Moderate, depends on grid size and volatility | High, due to quick decision-making and spread costs |
| Profit Target | Small incremental gains across multiple trades | Very small profits per trade but many trades daily |
| Market Conditions | Works best in sideways or ranging markets | Best in highly liquid, volatile markets |
| Required Skills | Understanding of market volatility and grid setup | Quick decision-making and precise execution |
| Capital Allocation | Requires larger capital for multiple pending orders | Lower capital per trade but requires fast access to funds |
| Automation | Commonly automated with trading bots | Can be manual or automated |
| Typical Instruments | Forex, cryptocurrencies, commodities | Forex, indices, stocks with tight spreads |
Which is better?
Grid trading excels in managing market volatility by placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals, allowing traders to profit from price fluctuations over time. Scalping focuses on quick, small profits through rapid trades, requiring intense market monitoring and low latency execution to capitalize on minor price movements. Optimal choice depends on individual risk tolerance, trading capital, and market conditions, with grid trading suited for sideways markets and scalping for highly liquid, volatile assets.
Connection
Grid trading and scalping both capitalize on small price fluctuations to generate consistent profits, with grid trading placing multiple buy and sell orders at predefined intervals and scalping focusing on rapid, short-term trades. Both strategies require precise market analysis and risk management to maximize gains from high-frequency trading environments. By leveraging volatility and tight spreads, traders can effectively combine elements of grid trading and scalping for enhanced market opportunities.
Key Terms
Timeframe
Scalping and grid trading differ significantly in their approach to timeframes, with scalping targeting very short-term trades often lasting seconds to minutes, aiming for quick profits from small price movements. Grid trading operates on longer timeframes, placing orders at regular intervals above and below a set price to capture gains over extended market fluctuations. Explore further to understand which timeframe aligns best with your trading strategy and risk tolerance.
Order Execution
Scalping involves rapid order execution to capitalize on small price movements within seconds or minutes, requiring high-speed trading platforms and minimal latency. Grid trading places multiple buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals, aiming to profit from market fluctuations over a broader price range and necessitating precise order management to maintain the grid structure. Explore detailed strategies and platform recommendations to enhance your order execution efficiency in both scalping and grid trading.
Position Sizing
Position sizing in scalping involves executing quick trades with small position sizes to minimize risk and capitalize on minor price fluctuations, emphasizing rapid entry and exit strategies. In grid trading, position sizing is strategically managed across multiple price levels within the grid, allowing traders to systematically accumulate or reduce positions based on market movements, which helps in maximizing profit potential over a wider range. Explore detailed strategies on optimizing position sizing in scalping and grid trading to enhance your trading performance.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Scalping is a day trading strategy where an investor buys and sells a stock multiple times within the same day aiming to make many small profits rather than large gains from each trade.
Scalping (trading) - Scalping in trading refers either to a legitimate arbitrage method exploiting small price gaps or to fraudulent market manipulation, with scalpers quickly opening and closing positions to gain tiny profits mostly in seconds or minutes.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how ... - Scalping relies heavily on technical indicators like Stochastic Oscillator, Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD to execute fast trades and capitalize on small price movements throughout the trading day.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com