Gamma scalping involves actively managing options positions to capitalize on changes in an asset's volatility and delta, aiming to maintain a neutral risk profile. Risk reversal is a strategy combining a long call and short put to hedge or speculate on directional moves while limiting downside risk. Discover how these distinct approaches can optimize your trading strategy and risk management.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between gamma scalping and risk reversal is crucial for traders to effectively manage options risk and optimize profit strategies. Gamma scalping focuses on adjusting hedge positions to capitalize on volatility and minimize directional risk, enhancing delta-neutral portfolios. Risk reversal involves buying calls and selling puts, or vice versa, to hedge or speculate on directional market moves and implied volatility skew. Mastering both strategies enables informed decision-making in option trading, tailored to market outlook and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
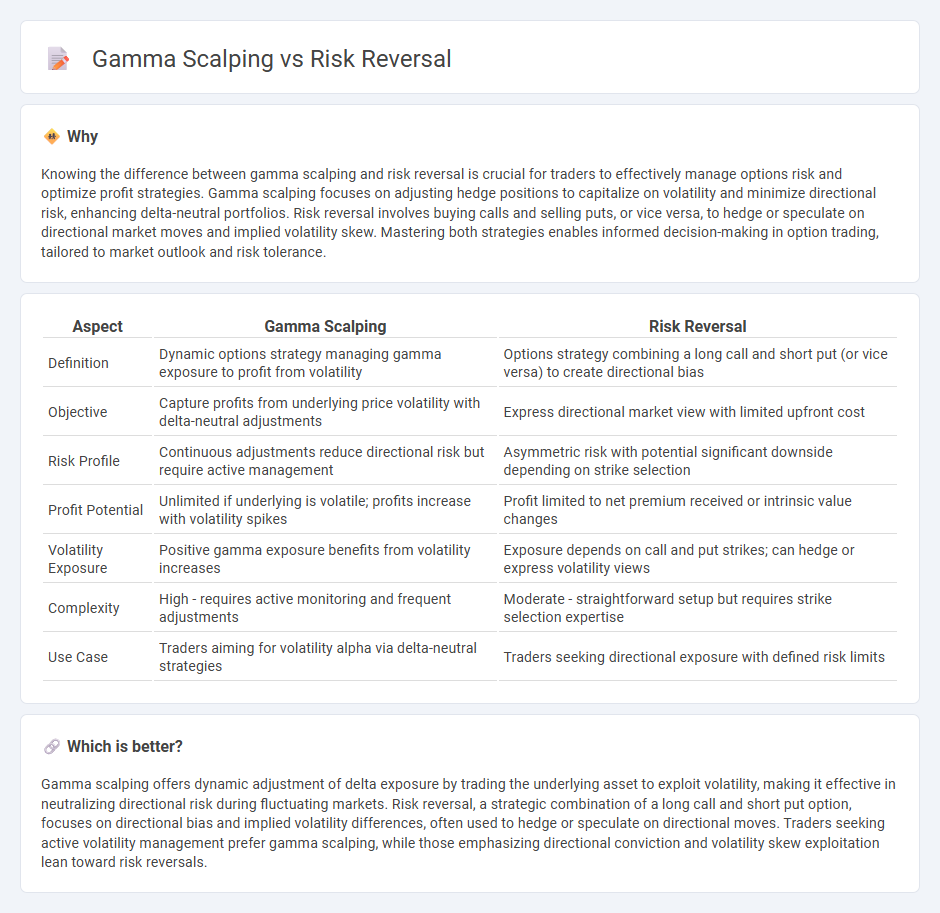
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Risk Reversal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic options strategy managing gamma exposure to profit from volatility | Options strategy combining a long call and short put (or vice versa) to create directional bias |
| Objective | Capture profits from underlying price volatility with delta-neutral adjustments | Express directional market view with limited upfront cost |
| Risk Profile | Continuous adjustments reduce directional risk but require active management | Asymmetric risk with potential significant downside depending on strike selection |
| Profit Potential | Unlimited if underlying is volatile; profits increase with volatility spikes | Profit limited to net premium received or intrinsic value changes |
| Volatility Exposure | Positive gamma exposure benefits from volatility increases | Exposure depends on call and put strikes; can hedge or express volatility views |
| Complexity | High - requires active monitoring and frequent adjustments | Moderate - straightforward setup but requires strike selection expertise |
| Use Case | Traders aiming for volatility alpha via delta-neutral strategies | Traders seeking directional exposure with defined risk limits |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers dynamic adjustment of delta exposure by trading the underlying asset to exploit volatility, making it effective in neutralizing directional risk during fluctuating markets. Risk reversal, a strategic combination of a long call and short put option, focuses on directional bias and implied volatility differences, often used to hedge or speculate on directional moves. Traders seeking active volatility management prefer gamma scalping, while those emphasizing directional conviction and volatility skew exploitation lean toward risk reversals.
Connection
Gamma scalping and risk reversal are connected through their focus on managing options portfolio risk and capitalizing on volatility changes. Gamma scalping involves dynamically adjusting a delta-neutral position to profit from fluctuations in the underlying asset's price, while risk reversal strategies use options combinations to hedge against directional market moves and implied volatility shifts. Both techniques rely on understanding and exploiting the Greeks, particularly gamma and delta, to optimize trading outcomes in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Delta
Risk reversal involves creating directional exposure by simultaneously buying out-of-the-money calls and selling out-of-the-money puts, deliberately targeting Delta to profit from anticipated price movements. Gamma scalping, on the other hand, emphasizes maintaining a Delta-neutral position by continuously adjusting option holdings to capture gains from changes in underlying volatility. Explore these strategies in-depth to master Delta risk management and optimize options trading performance.
Volatility
Risk reversal strategies involve buying out-of-the-money calls and selling out-of-the-money puts to benefit from directional volatility shifts, often used to hedge or speculate on market direction. Gamma scalping exploits the changing gamma of an options position to manage risk and capture profits by adjusting the hedge dynamically as volatility fluctuates. Explore deeper insights into how these volatility-focused techniques can optimize your trading strategies.
Hedging
Risk reversal hedging involves simultaneously buying a call option and selling a put option to offset potential losses while positioning for directional movement. Gamma scalping, on the other hand, focuses on managing delta exposure dynamically by adjusting the underlying asset holdings to profit from volatility and maintain a neutral position. Discover more about the nuances and practical applications of these hedging strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Risk Reversal Strategy in Options Trading: An Essential Guide - Risk reversal is an options trading strategy involving buying a call and selling a put for bullish views (or the opposite for bearish), allowing traders to manage risk while capitalizing on market direction through precise option selection and position management.
How a Risk Reversal Options Strategy Works | Charles Schwab - A risk reversal is a multi-leg options strategy using both a call and a put option simultaneously, often structured to generate a net credit while providing upside potential and downside protection with defined maximum gain and loss scenarios.
Risk Reversal - Deutsche Bank - In FX markets, a risk reversal is a two-legged option strategy combining buying calls and selling puts (or vice versa) to hedge foreign currency liabilities or assets, allowing participation in upside movements while protecting against downside risk beyond the bought option strike.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com