Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask) in market transactions, emphasizing liquidity provision and order execution efficiency. Statistical arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies and patterns through quantitative models and automated trading strategies across multiple assets or markets. Explore further to understand how these distinct trading techniques can optimize portfolio returns and manage risk effectively.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and statistical arbitrage is crucial because bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from liquidity provision by exploiting the price difference between buying and selling quotes, while statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models to identify mispricings in correlated securities. Traders focusing on bid-ask spread capture need precise timing and control over execution costs, whereas statistical arbitrage requires robust data analysis and risk management to exploit market inefficiencies. Mastery of both strategies enhances portfolio diversification and optimizes risk-adjusted returns. Knowing these distinctions helps tailor trading approaches to specific market conditions and trader expertise.
Comparison Table
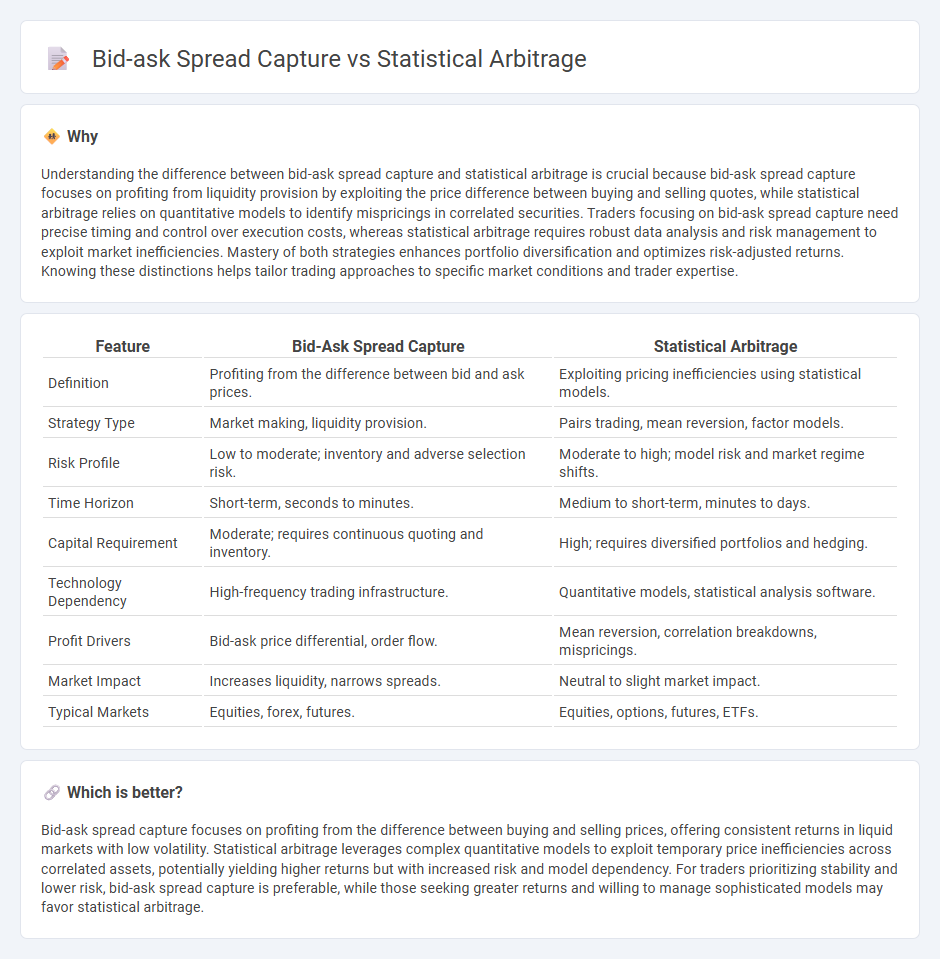
| Feature | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from the difference between bid and ask prices. | Exploiting pricing inefficiencies using statistical models. |
| Strategy Type | Market making, liquidity provision. | Pairs trading, mean reversion, factor models. |
| Risk Profile | Low to moderate; inventory and adverse selection risk. | Moderate to high; model risk and market regime shifts. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term, seconds to minutes. | Medium to short-term, minutes to days. |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate; requires continuous quoting and inventory. | High; requires diversified portfolios and hedging. |
| Technology Dependency | High-frequency trading infrastructure. | Quantitative models, statistical analysis software. |
| Profit Drivers | Bid-ask price differential, order flow. | Mean reversion, correlation breakdowns, mispricings. |
| Market Impact | Increases liquidity, narrows spreads. | Neutral to slight market impact. |
| Typical Markets | Equities, forex, futures. | Equities, options, futures, ETFs. |
Which is better?
Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices, offering consistent returns in liquid markets with low volatility. Statistical arbitrage leverages complex quantitative models to exploit temporary price inefficiencies across correlated assets, potentially yielding higher returns but with increased risk and model dependency. For traders prioritizing stability and lower risk, bid-ask spread capture is preferable, while those seeking greater returns and willing to manage sophisticated models may favor statistical arbitrage.
Connection
Trading strategies involving bid-ask spread capture focus on profiting from the difference between buy and sell prices in the market. Statistical arbitrage complements this approach by using quantitative models to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies between correlated securities. Both techniques rely on rapid execution and precise market data analysis to maximize gains while minimizing risk exposure.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies in correlated securities by using quantitative models to identify and execute trades with expected mean-reverting returns, often involving large volumes and high-frequency strategies to capitalize on transient mispricings. This approach contrasts with bid-ask spread capture, which profits from narrow differences between buying and selling prices, typically requiring lower capital and simpler execution but offering smaller, more consistent gains. Explore deeper insights into implementing statistical arbitrage strategies and optimizing their algorithmic frameworks.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage strategies leverage mean reversion by identifying temporary price deviations in correlated assets and executing trades to profit from their expected return to equilibrium. Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices, often requiring high-frequency execution but not necessarily relying on price reversal patterns. Explore detailed comparisons and practical applications of mean reversion in these trading approaches to enhance your quantitative trading strategies.
Cointegration
Statistical arbitrage leverages cointegration to identify pairs of assets whose prices move together over time, enabling traders to exploit temporary deviations from their equilibrium relationship. In contrast, bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices without relying on long-term price relationships. Explore the nuances of cointegration in these strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - WunderTrading - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral, quantitative trading strategy that exploits pricing discrepancies between correlated securities using complex algorithms and statistical models to achieve consistent returns while managing risk.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage is a short-term trading strategy applying mean reversion models on broadly diversified portfolios, using beta-neutral, bottom-up approaches and automated trading systems to exploit subtle pricing inefficiencies across many stocks.
Statistical Arbitrage in High Frequency Trading Based on Limit Order ... - A more academic perspective defines statistical arbitrage as spreading risk across thousands to millions of very short-term trades, aiming to profit from small mispricings using high-frequency and data-driven techniques.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com