Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting a portfolio's positions to maintain a delta-neutral stance, minimizing risk from price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Static hedging relies on setting a fixed hedge ratio at initiation, without frequent rebalancing, often suited for stable market conditions. Explore the nuances of delta hedging versus static hedging to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between delta hedging and static hedging is crucial for effective risk management in trading. Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting positions to maintain a neutral delta exposure, minimizing price movement risks in options portfolios. Static hedging uses fixed positions without frequent adjustments, providing simpler but less flexible risk control. Mastery of both strategies allows traders to optimize hedging efficiency and protect against market volatility.
Comparison Table
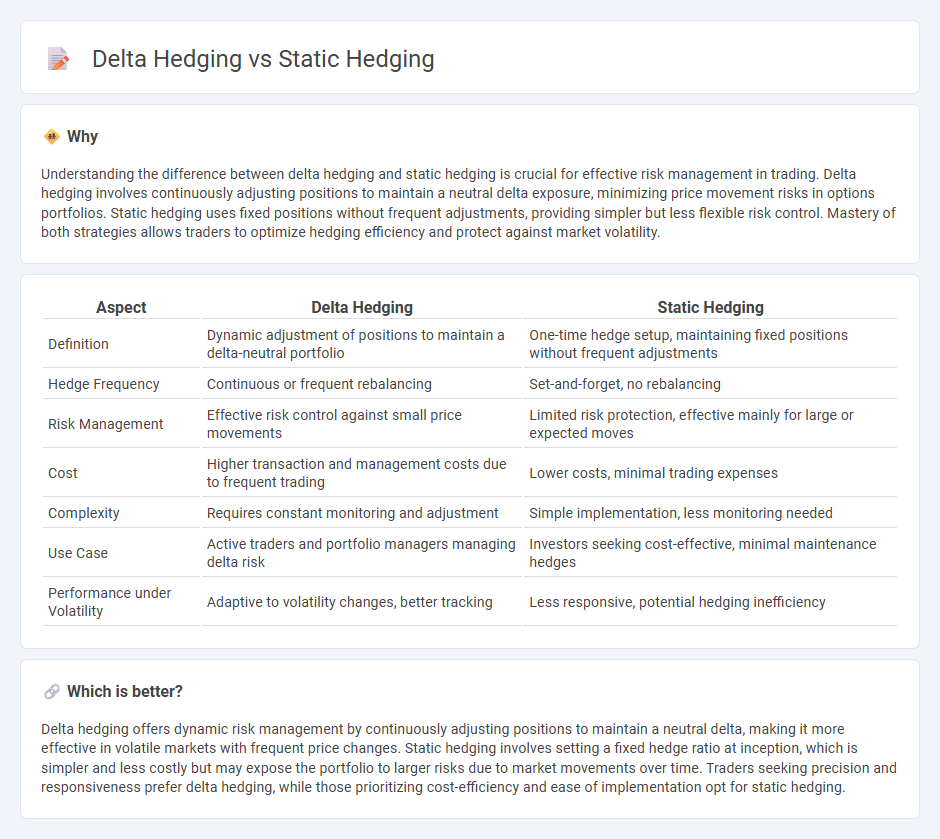
| Aspect | Delta Hedging | Static Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic adjustment of positions to maintain a delta-neutral portfolio | One-time hedge setup, maintaining fixed positions without frequent adjustments |
| Hedge Frequency | Continuous or frequent rebalancing | Set-and-forget, no rebalancing |
| Risk Management | Effective risk control against small price movements | Limited risk protection, effective mainly for large or expected moves |
| Cost | Higher transaction and management costs due to frequent trading | Lower costs, minimal trading expenses |
| Complexity | Requires constant monitoring and adjustment | Simple implementation, less monitoring needed |
| Use Case | Active traders and portfolio managers managing delta risk | Investors seeking cost-effective, minimal maintenance hedges |
| Performance under Volatility | Adaptive to volatility changes, better tracking | Less responsive, potential hedging inefficiency |
Which is better?
Delta hedging offers dynamic risk management by continuously adjusting positions to maintain a neutral delta, making it more effective in volatile markets with frequent price changes. Static hedging involves setting a fixed hedge ratio at inception, which is simpler and less costly but may expose the portfolio to larger risks due to market movements over time. Traders seeking precision and responsiveness prefer delta hedging, while those prioritizing cost-efficiency and ease of implementation opt for static hedging.
Connection
Delta hedging and static hedging are connected through their roles in risk management strategies for options trading. Delta hedging involves continuously adjusting positions to maintain a delta-neutral portfolio, minimizing exposure to small price movements, while static hedging establishes fixed positions to offset risk without frequent rebalancing. Both aim to protect against price fluctuations but differ in execution and responsiveness to market changes.
Key Terms
Options Contracts
Static hedging in options contracts involves creating a fixed hedge position held throughout the life of the option, minimizing transaction costs and simplifying risk management. Delta hedging continuously adjusts the hedge ratio to maintain a neutral delta exposure as underlying asset prices fluctuate, requiring frequent rebalancing to manage directional risk effectively. Explore in-depth insights on how static and delta hedging strategies impact options portfolio performance and risk.
Risk Management
Static hedging involves establishing a fixed hedge position that remains unchanged over a certain period, effectively minimizing exposure to price fluctuations without frequent adjustments. Delta hedging continuously adjusts the hedge by buying or selling underlying assets to maintain a delta-neutral position, offering dynamic risk management against small price movements. Explore how these strategies impact portfolio risk and optimize hedging efficiency for tailored risk management solutions.
Rebalancing Frequency
Static hedging involves establishing a fixed hedge position that remains unchanged over the investment horizon, resulting in minimal rebalancing frequency. Delta hedging requires continuous or frequent rebalancing to maintain a delta-neutral position as underlying asset prices fluctuate. Explore the nuances and efficiency of both strategies to optimize your portfolio's risk management.
Source and External Links
Static hedge - Investment strategies - Moneyterms - A static hedge is a hedging strategy that does not require rebalancing as market factors change, contrasting with dynamic hedging which needs constant adjustments; an example is using futures to hedge foreign exchange risk which can eliminate it entirely without needing continual changes.
Static Hedging - DiVA portal - Static hedging involves constructing a hedge portfolio that only requires a finite number of rebalancing actions, offering an alternative to continuous rebalancing in delta hedging, commonly applied to options like digital or barrier options for risk management.
Static Hedging of Standard Options - Static hedging with a limited number of options can outperform dynamic strategies by avoiding restrictions like short sales and leverage constraints, reducing transaction and monitoring costs, making it attractive for hedging options especially when frequent rebalancing is impractical.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com