Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously buying and selling assets at quoted prices, profiting from bid-ask spreads and market fluctuations. Value investing focuses on analyzing a company's fundamentals to identify undervalued stocks with long-term growth potential, emphasizing patience and disciplined capital allocation. Explore the detailed strategies and benefits of market making versus value investing to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
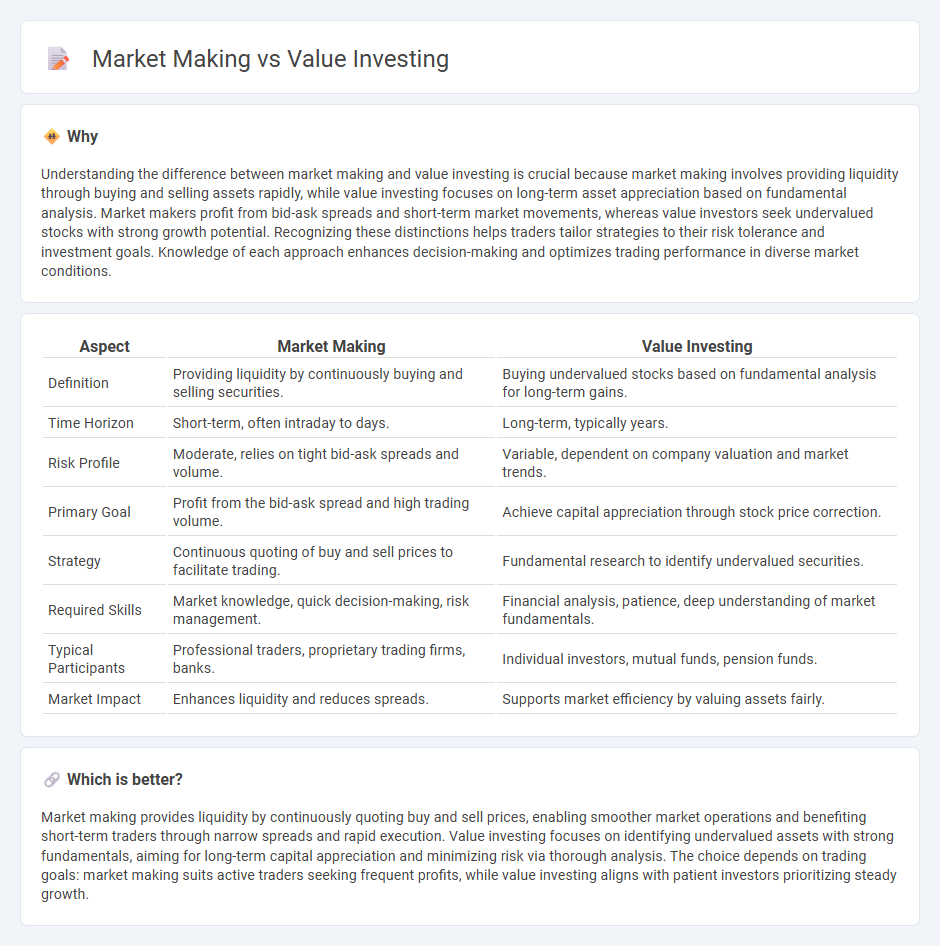
Understanding the difference between market making and value investing is crucial because market making involves providing liquidity through buying and selling assets rapidly, while value investing focuses on long-term asset appreciation based on fundamental analysis. Market makers profit from bid-ask spreads and short-term market movements, whereas value investors seek undervalued stocks with strong growth potential. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders tailor strategies to their risk tolerance and investment goals. Knowledge of each approach enhances decision-making and optimizes trading performance in diverse market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Making | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity by continuously buying and selling securities. | Buying undervalued stocks based on fundamental analysis for long-term gains. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term, often intraday to days. | Long-term, typically years. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate, relies on tight bid-ask spreads and volume. | Variable, dependent on company valuation and market trends. |
| Primary Goal | Profit from the bid-ask spread and high trading volume. | Achieve capital appreciation through stock price correction. |
| Strategy | Continuous quoting of buy and sell prices to facilitate trading. | Fundamental research to identify undervalued securities. |
| Required Skills | Market knowledge, quick decision-making, risk management. | Financial analysis, patience, deep understanding of market fundamentals. |
| Typical Participants | Professional traders, proprietary trading firms, banks. | Individual investors, mutual funds, pension funds. |
| Market Impact | Enhances liquidity and reduces spreads. | Supports market efficiency by valuing assets fairly. |
Which is better?
Market making provides liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, enabling smoother market operations and benefiting short-term traders through narrow spreads and rapid execution. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued assets with strong fundamentals, aiming for long-term capital appreciation and minimizing risk via thorough analysis. The choice depends on trading goals: market making suits active traders seeking frequent profits, while value investing aligns with patient investors prioritizing steady growth.
Connection
Market making and value investing intersect through their shared focus on liquidity and intrinsic asset valuation; market makers provide continuous bid-ask quotes that enhance market liquidity, enabling value investors to acquire undervalued stocks efficiently. Both strategies rely on deep analysis of asset prices and market behavior, with value investing targeting long-term gains from assets priced below their intrinsic value, while market making profits from short-term spreads and price efficiency. This symbiotic relationship supports market stability and price discovery, as market makers facilitate trades that help value investors capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Key Terms
**Value Investing:**
Value investing involves identifying undervalued stocks by analyzing financial statements, intrinsic value, and long-term growth potential, aiming for capital appreciation as market prices correct over time. Key metrics include price-to-earnings ratio, book value, and dividend yield, emphasizing patience and margin of safety to mitigate risk. Discover deeper insights into how value investing can enhance your portfolio's resilience and returns.
Intrinsic Value
Value investing centers on identifying stocks trading below their intrinsic value by analyzing fundamental factors such as earnings, cash flow, and asset quality to secure long-term growth. Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously buying and selling securities, profiting from bid-ask spreads rather than intrinsic value assessment. Discover how these distinct approaches impact portfolio strategies and risk management in the financial markets.
Margin of Safety
Value investing emphasizes the Margin of Safety by purchasing undervalued stocks with a significant discount to their intrinsic value, minimizing downside risk and enhancing long-term returns. Market making involves providing liquidity through bid-ask spreads, relying on volume and price stability rather than intrinsic valuation or Margin of Safety. Explore further to understand how Margin of Safety distinctly impacts investment strategies and risk management.
Source and External Links
Value investing - Value investing is a strategy of buying securities that appear underpriced by fundamental analysis, originally developed by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd in the 1920s, focusing on purchasing stocks at prices below their intrinsic value with a margin of safety. Prominent proponents include Warren Buffett, who emphasizes quality companies bought at sensible prices.
What is value investing? | iShares - BlackRock - Value investing targets companies that are cheap compared to their peers based on financial metrics like price-to-book and price-to-earnings ratios, enabling investors to identify undervalued stocks. Modern technology allows easy access to value investing via ETFs like the iShares MSCI World ex Australia Value ETF, which uses a sector-neutral approach to diversify risk.
Value Investing History | Columbia Business School - Developed by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd in the 1920s at Columbia Business School, value investing emphasizes estimating the intrinsic value of stocks and purchasing them when they trade below that value, avoiding efforts to predict price movements and relying on the convergence of intrinsic and market values over time.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com