Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets for risk-free gains. Both strategies enhance market efficiency but require distinct skill sets and risk management approaches. Explore the nuances of market making and arbitrage to optimize your trading strategy.
Why it is important
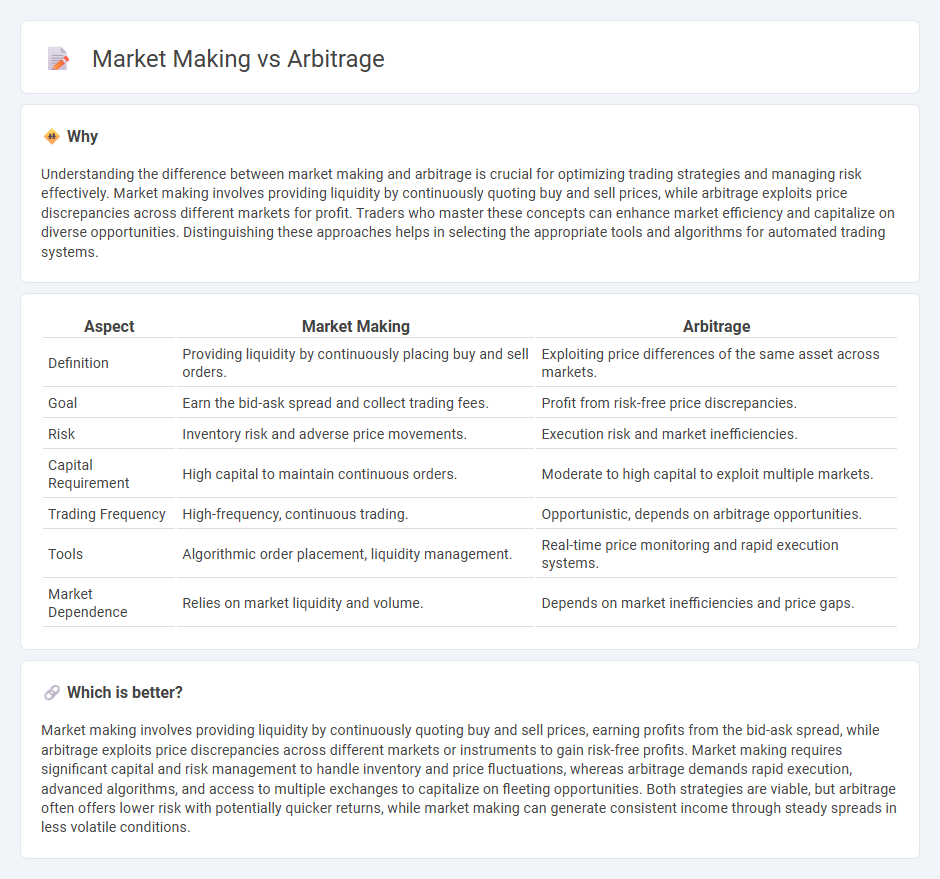
Understanding the difference between market making and arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets for profit. Traders who master these concepts can enhance market efficiency and capitalize on diverse opportunities. Distinguishing these approaches helps in selecting the appropriate tools and algorithms for automated trading systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Making | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing liquidity by continuously placing buy and sell orders. | Exploiting price differences of the same asset across markets. |
| Goal | Earn the bid-ask spread and collect trading fees. | Profit from risk-free price discrepancies. |
| Risk | Inventory risk and adverse price movements. | Execution risk and market inefficiencies. |
| Capital Requirement | High capital to maintain continuous orders. | Moderate to high capital to exploit multiple markets. |
| Trading Frequency | High-frequency, continuous trading. | Opportunistic, depends on arbitrage opportunities. |
| Tools | Algorithmic order placement, liquidity management. | Real-time price monitoring and rapid execution systems. |
| Market Dependence | Relies on market liquidity and volume. | Depends on market inefficiencies and price gaps. |
Which is better?
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, earning profits from the bid-ask spread, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to gain risk-free profits. Market making requires significant capital and risk management to handle inventory and price fluctuations, whereas arbitrage demands rapid execution, advanced algorithms, and access to multiple exchanges to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. Both strategies are viable, but arbitrage often offers lower risk with potentially quicker returns, while market making can generate consistent income through steady spreads in less volatile conditions.
Connection
Market making and arbitrage are interconnected through their reliance on price discrepancies in financial markets. Market makers provide liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, enabling arbitrageurs to exploit price differences across various exchanges or related assets. This dynamic enhances market efficiency by narrowing spreads and aligning prices across platforms.
Key Terms
Arbitrage:
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets, enabling traders to buy low in one exchange and sell high in another for risk-free profit. This strategy requires swift execution and access to multiple trading platforms to capitalize on transient inefficiencies before they vanish. Explore deeper insights into arbitrage techniques and tools to enhance your trading success.
Price Discrepancy
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of identical assets across different markets, buying low in one and selling high in another to earn risk-free profits. Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread rather than price differences. Explore the nuances between arbitrage and market making strategies to deepen your understanding.
Simultaneous Buy/Sell
Arbitrage involves simultaneously buying and selling assets in different markets to exploit price discrepancies for profit, relying on speed and market inefficiencies. Market making, on the other hand, entails providing liquidity by posting both buy and sell orders simultaneously, profiting primarily from the bid-ask spread. Explore more to understand the strategic nuances and risk profiles of both trading approaches.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of simultaneously buying and selling an asset in different markets to profit from price differences, usually involving risk-free profit opportunities in theory but some risk in practice, mainly used in financial fields by arbitrageurs.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Arbitrage is an investment strategy where investors buy and sell assets simultaneously in different markets to exploit price differences with key types including pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, and convertible arbitrage.
What is arbitrage and how does it work in financial markets | StoneX - Arbitrage involves exploiting minor price differences of the same asset across markets, including forms such as merger arbitrage, triangular arbitrage in Forex, and pure arbitrage through simultaneous purchases and sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com