Execution algorithms enhance trading efficiency by dynamically adjusting order placement based on real-time market conditions. Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) algorithms execute trades evenly over a specified period to minimize market impact and reduce price slippage. Explore the differences and benefits of execution algorithms versus TWAP to optimize trading strategies effectively.
Why it is important
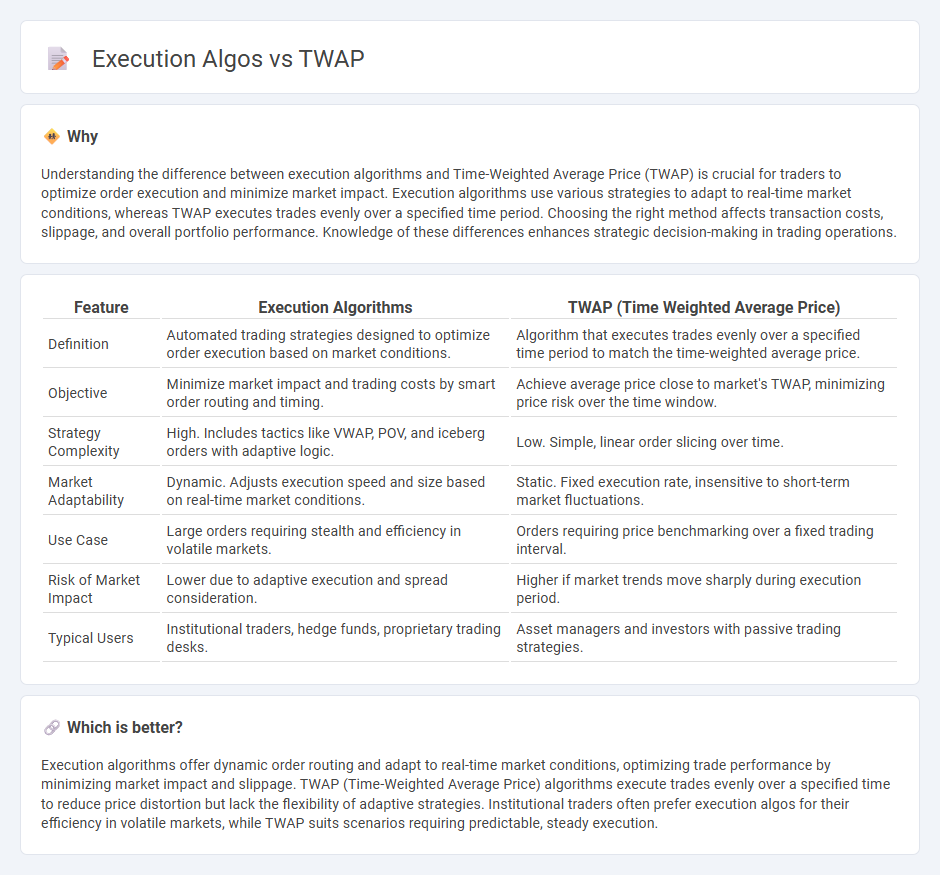
Understanding the difference between execution algorithms and Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is crucial for traders to optimize order execution and minimize market impact. Execution algorithms use various strategies to adapt to real-time market conditions, whereas TWAP executes trades evenly over a specified time period. Choosing the right method affects transaction costs, slippage, and overall portfolio performance. Knowledge of these differences enhances strategic decision-making in trading operations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Execution Algorithms | TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading strategies designed to optimize order execution based on market conditions. | Algorithm that executes trades evenly over a specified time period to match the time-weighted average price. |
| Objective | Minimize market impact and trading costs by smart order routing and timing. | Achieve average price close to market's TWAP, minimizing price risk over the time window. |
| Strategy Complexity | High. Includes tactics like VWAP, POV, and iceberg orders with adaptive logic. | Low. Simple, linear order slicing over time. |
| Market Adaptability | Dynamic. Adjusts execution speed and size based on real-time market conditions. | Static. Fixed execution rate, insensitive to short-term market fluctuations. |
| Use Case | Large orders requiring stealth and efficiency in volatile markets. | Orders requiring price benchmarking over a fixed trading interval. |
| Risk of Market Impact | Lower due to adaptive execution and spread consideration. | Higher if market trends move sharply during execution period. |
| Typical Users | Institutional traders, hedge funds, proprietary trading desks. | Asset managers and investors with passive trading strategies. |
Which is better?
Execution algorithms offer dynamic order routing and adapt to real-time market conditions, optimizing trade performance by minimizing market impact and slippage. TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) algorithms execute trades evenly over a specified time to reduce price distortion but lack the flexibility of adaptive strategies. Institutional traders often prefer execution algos for their efficiency in volatile markets, while TWAP suits scenarios requiring predictable, steady execution.
Connection
Execution algorithms enhance trading efficiency by automating order placement to minimize market impact, with TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) as a specific strategy designed to execute orders evenly over a set time period. TWAP algorithms break large trades into smaller segments, distributing them uniformly to achieve an average price close to the market's time-weighted average, reducing the risk of price slippage. This connection between execution algos and TWAP enables traders to optimize trade execution by balancing market impact and timing flexibility.
Key Terms
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP)
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) is an execution algorithm designed to minimize market impact by evenly distributing trades over a specified time period, achieving an average price reflective of the entire interval. TWAP algorithms are ideal for executing large orders in fragmented markets or low-liquidity conditions, prioritizing time-based slices rather than volume or price trends. Explore how TWAP compares with other execution algorithms to optimize trade timing and reduce implementation shortfall.
Market Impact
Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) algorithms minimize market impact by spreading orders evenly over a specified period to avoid significant price fluctuations. Execution algorithms tailor trade slicing based on real-time liquidity and volatility data, thereby adapting dynamically to reduce adverse price movements. Explore detailed strategies to optimize execution and minimize market impact effectively.
Order Slicing
Order slicing is a critical technique in execution algorithms aimed at minimizing market impact by breaking large orders into smaller, strategically timed trades. TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) uses order slicing to distribute trades evenly across a specified time interval, optimizing execution prices relative to the average market price. Explore how advanced order slicing methods enhance TWAP and other execution algorithms for improved trading efficiency.
Source and External Links
TWAP vs. VWAP Price Algorithms - Chainlink - TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) is a pricing algorithm that calculates the average price of an asset over a set period by summing prices at multiple points and dividing by the number of points, often used in DeFi and trading strategies to minimize slippage by breaking large orders into equal parts over time.
Time-Weighted Average Price Trading Strategies - TrendSpider - TWAP is a trading indicator measuring the average price of an asset over a specific time frame by averaging prices without weighting by volume, used in algorithmic trading to execute trades evenly over time and reduce market impact compared to VWAP.
Time Weighted Average Price - TradingView - TWAP is an indicator for managing trades by calculating the average price of a security over time and is commonly used to split large orders into smaller trades executed over intervals to avoid market disruption.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com