A gamma squeeze occurs when options market makers hedge their positions by buying the underlying stock as its price rises, amplifying upward momentum, while a short squeeze happens when short sellers rush to cover positions, driving the stock price sharply higher. Gamma squeezes are closely linked to the options market dynamics, whereas short squeezes primarily involve stock borrowing and short selling pressure. Explore the distinct mechanisms and implications of both phenomena to deepen your trading strategies.
Why it is important
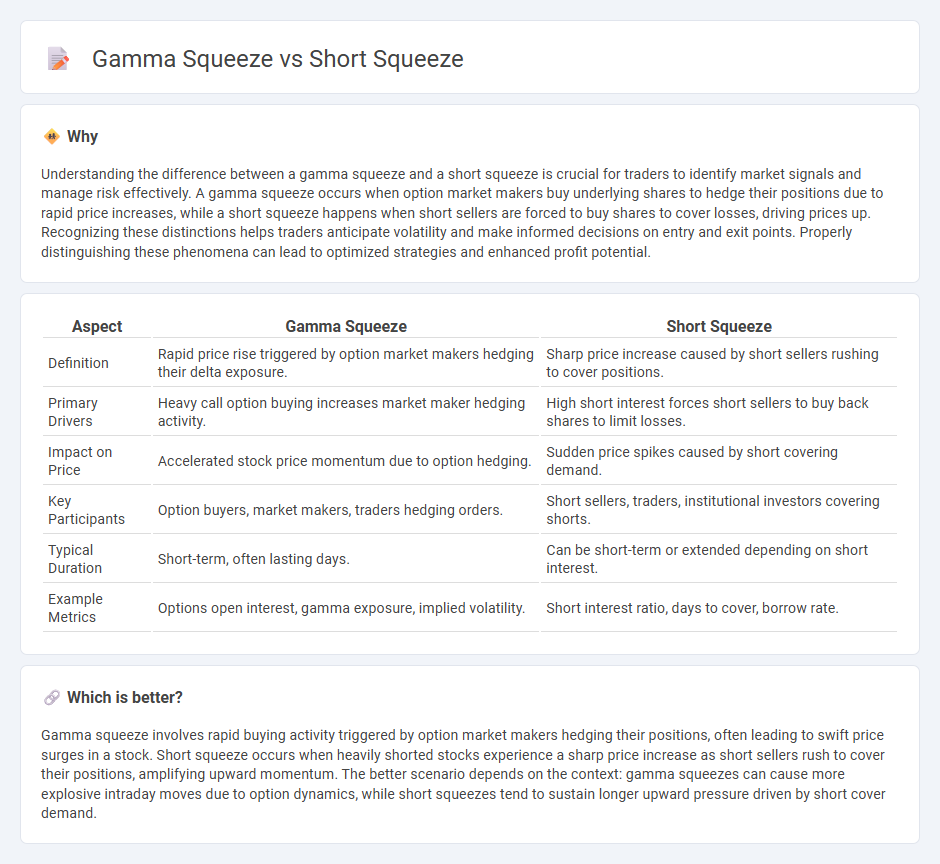
Understanding the difference between a gamma squeeze and a short squeeze is crucial for traders to identify market signals and manage risk effectively. A gamma squeeze occurs when option market makers buy underlying shares to hedge their positions due to rapid price increases, while a short squeeze happens when short sellers are forced to buy shares to cover losses, driving prices up. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders anticipate volatility and make informed decisions on entry and exit points. Properly distinguishing these phenomena can lead to optimized strategies and enhanced profit potential.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Squeeze | Short Squeeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid price rise triggered by option market makers hedging their delta exposure. | Sharp price increase caused by short sellers rushing to cover positions. |
| Primary Drivers | Heavy call option buying increases market maker hedging activity. | High short interest forces short sellers to buy back shares to limit losses. |
| Impact on Price | Accelerated stock price momentum due to option hedging. | Sudden price spikes caused by short covering demand. |
| Key Participants | Option buyers, market makers, traders hedging orders. | Short sellers, traders, institutional investors covering shorts. |
| Typical Duration | Short-term, often lasting days. | Can be short-term or extended depending on short interest. |
| Example Metrics | Options open interest, gamma exposure, implied volatility. | Short interest ratio, days to cover, borrow rate. |
Which is better?
Gamma squeeze involves rapid buying activity triggered by option market makers hedging their positions, often leading to swift price surges in a stock. Short squeeze occurs when heavily shorted stocks experience a sharp price increase as short sellers rush to cover their positions, amplifying upward momentum. The better scenario depends on the context: gamma squeezes can cause more explosive intraday moves due to option dynamics, while short squeezes tend to sustain longer upward pressure driven by short cover demand.
Connection
A gamma squeeze occurs when options market makers buy the underlying stock to hedge their positions, driving up the stock price and amplifying upward momentum. A short squeeze happens when short sellers rush to cover their positions as the stock price rises, intensifying price spikes. Both squeezes are interconnected as a gamma squeeze can trigger a short squeeze, creating a feedback loop that leads to rapid and significant stock price increases.
Key Terms
Short Interest
Short squeeze occurs when high short interest forces short sellers to buy shares to cover positions, driving prices up rapidly. Gamma squeeze involves options market makers hedging their positions by buying the underlying stock, amplifying upward momentum, often linked to high open interest in call options. Explore the key differences and impact of short interest on these market phenomena to deepen your understanding.
Options Gamma
Options gamma represents the rate of change in an option's delta relative to the underlying asset's price, playing a crucial role in gamma squeeze dynamics. A gamma squeeze occurs when market makers rapidly buy the underlying asset to hedge increasing delta from short options, driving prices sharply higher. Explore how options gamma intricately influences these market phenomena and shapes volatility.
Forced Buying
Short squeeze involves forced buying when short sellers rush to cover their positions as the stock price rises, creating upward price pressure. Gamma squeeze occurs when option market makers hedge by purchasing the underlying asset due to increased option delta exposure, fueling further price spikes. Explore the mechanics and impacts of forced buying in both events to understand market dynamics better.
Source and External Links
Short Squeeze - Overview, How It Works, and How to Spot It - A short squeeze is a market event where a sharp rise in an asset's price forces traders who previously sold short to buy shares to close their positions, creating further buying pressure and pushing prices even higher.
Short squeeze - Wikipedia - A short squeeze occurs when demand for a stock rapidly increases as short sellers rush to cover their positions, causing a sharp rise in stock price that is not necessarily related to the company's fundamentals.
What's a Short Squeeze and Why Does It Happen? - Charles Schwab - A short squeeze typically happens when a stock with high short interest unexpectedly rises in price, forcing short sellers to buy back shares to limit losses, often magnifying the stock's upward move due to the high volume of covering trades.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com