Microstructure modeling analyzes order flow, bid-ask spreads, and price formation to understand market behavior at granular levels, essential for high-frequency trading strategies. Liquidity risk modeling quantifies the ease of executing large trades without significant price impact, focusing on market depth and resilience during periods of stress. Explore the distinctions and applications of these models to optimize trading performance and risk management.
Why it is important
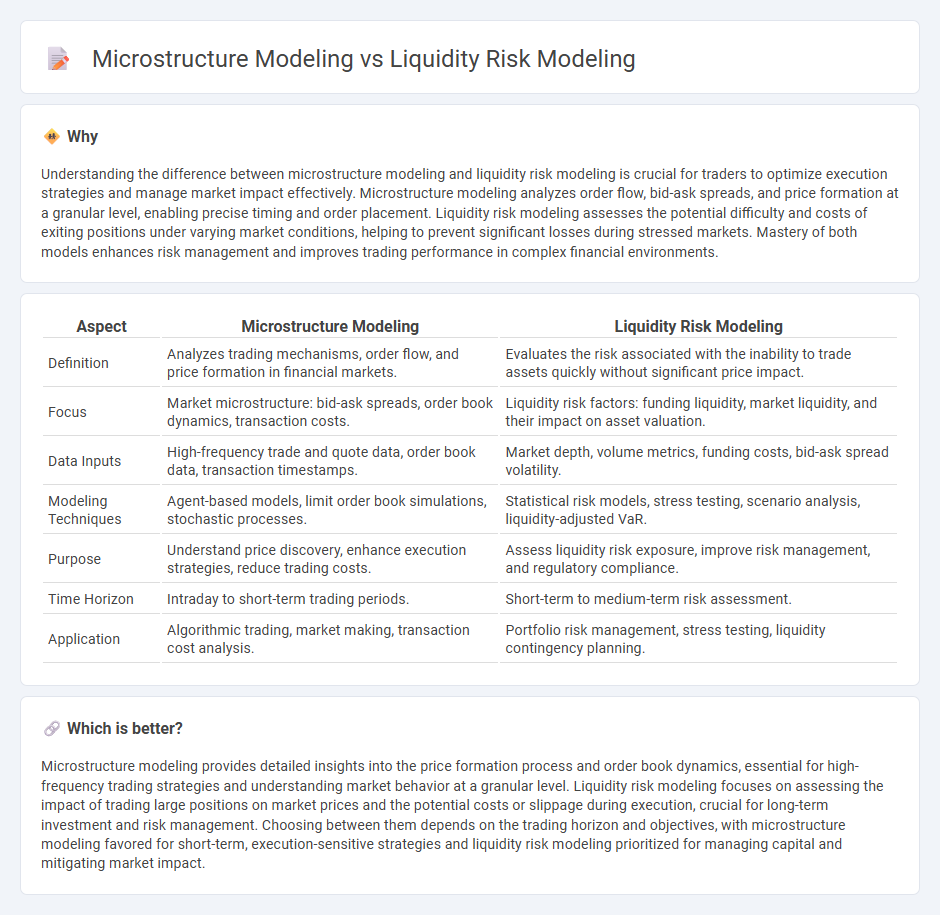
Understanding the difference between microstructure modeling and liquidity risk modeling is crucial for traders to optimize execution strategies and manage market impact effectively. Microstructure modeling analyzes order flow, bid-ask spreads, and price formation at a granular level, enabling precise timing and order placement. Liquidity risk modeling assesses the potential difficulty and costs of exiting positions under varying market conditions, helping to prevent significant losses during stressed markets. Mastery of both models enhances risk management and improves trading performance in complex financial environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Modeling | Liquidity Risk Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes trading mechanisms, order flow, and price formation in financial markets. | Evaluates the risk associated with the inability to trade assets quickly without significant price impact. |
| Focus | Market microstructure: bid-ask spreads, order book dynamics, transaction costs. | Liquidity risk factors: funding liquidity, market liquidity, and their impact on asset valuation. |
| Data Inputs | High-frequency trade and quote data, order book data, transaction timestamps. | Market depth, volume metrics, funding costs, bid-ask spread volatility. |
| Modeling Techniques | Agent-based models, limit order book simulations, stochastic processes. | Statistical risk models, stress testing, scenario analysis, liquidity-adjusted VaR. |
| Purpose | Understand price discovery, enhance execution strategies, reduce trading costs. | Assess liquidity risk exposure, improve risk management, and regulatory compliance. |
| Time Horizon | Intraday to short-term trading periods. | Short-term to medium-term risk assessment. |
| Application | Algorithmic trading, market making, transaction cost analysis. | Portfolio risk management, stress testing, liquidity contingency planning. |
Which is better?
Microstructure modeling provides detailed insights into the price formation process and order book dynamics, essential for high-frequency trading strategies and understanding market behavior at a granular level. Liquidity risk modeling focuses on assessing the impact of trading large positions on market prices and the potential costs or slippage during execution, crucial for long-term investment and risk management. Choosing between them depends on the trading horizon and objectives, with microstructure modeling favored for short-term, execution-sensitive strategies and liquidity risk modeling prioritized for managing capital and mitigating market impact.
Connection
Microstructure modeling analyzes the detailed processes of order flow, bid-ask spreads, and trading dynamics, providing insights into market liquidity fluctuations. Liquidity risk modeling quantifies the potential cost and difficulty of executing large trades without significantly impacting prices, relying heavily on microstructure metrics such as order book depth and market resiliency. The integration of microstructure features enhances liquidity risk models by capturing real-time trading frictions and price impact, enabling more accurate assessment of market liquidity risk in trading strategies.
Key Terms
**Liquidity Risk Modeling:**
Liquidity risk modeling assesses the potential losses a firm may incur when assets cannot be sold quickly without significant price discounts, focusing on market liquidity, funding liquidity, and the interactions between them. This modeling employs quantitative techniques such as stress testing, scenario analysis, and liquidity-adjusted Value at Risk (VaR) to measure and mitigate liquidity shortfalls under various market conditions. Explore in-depth approaches to optimize liquidity risk frameworks and enhance financial resilience.
Bid-Ask Spread
Liquidity risk modeling evaluates potential losses from the inability to execute trades without significant price impact, often quantifying bid-ask spread variability as a key indicator. Microstructure modeling analyzes the intricate dynamics of order flow and market depth that directly influence the formation and fluctuations of the bid-ask spread. Explore how these approaches dissect bid-ask spread behavior to better manage trading costs and market impact.
Market Depth
Liquidity risk modeling quantifies the potential losses arising from insufficient market depth, analyzing how large trades impact price stability and the cost of execution. Microstructure modeling delves into the mechanisms driving market depth, such as order book dynamics, bid-ask spreads, and trade frequency, to capture fine-grained liquidity variations. Explore further to understand how integrating these approaches enhances market depth assessment and risk management.
Source and External Links
Chapter 9. Modeling Correlated Systemic Bank Liquidity Risks - This chapter proposes a detailed methodology combining solvency and systemic liquidity risk modeling for banks, using Monte Carlo simulations to capture correlated economic factors and assess banks' vulnerability to liquidity shortfalls during stressed market conditions.
Modeling Liquidity Risk, With Implications for Market Risk Measurement and Management - This paper outlines a liquidity risk modeling approach integrated into value-at-risk frameworks, highlighting the importance of explicitly modeling liquidity effects to avoid significant underestimation of market risk, particularly for emerging markets.
Part 1. Modeling the Liability Liquidity Risk - Amundi Research Center - This research presents a framework for liquidity stress testing focused on liability liquidity risk, proposing statistical models to estimate redemption shocks and behavioral models to better capture the dynamics of fund liabilities under stress scenarios.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com