Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in perpetual futures funding rates across exchanges to generate riskless profits, while triangular arbitrage capitalizes on price inefficiencies among three currency pairs within the same market. Both strategies aim to leverage market inefficiencies but differ in execution, risk exposure, and required infrastructure. Explore deeper into funding rate and triangular arbitrage to understand which strategy aligns best with your trading goals.
Why it is important
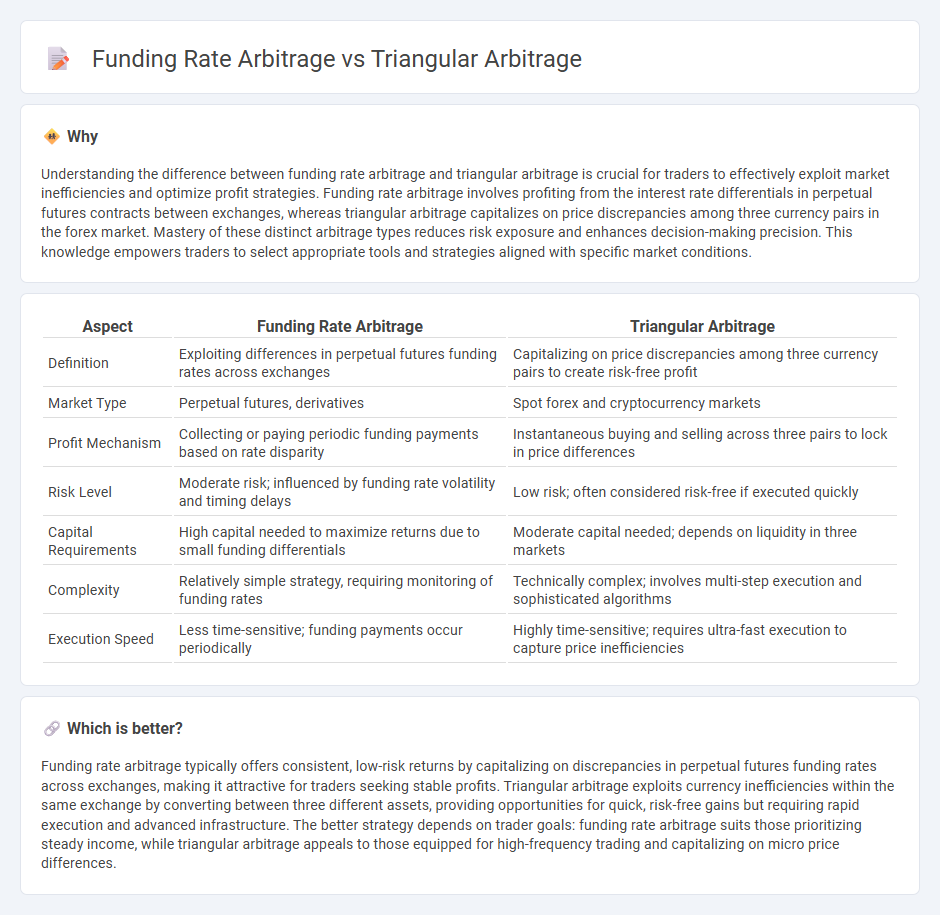
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and triangular arbitrage is crucial for traders to effectively exploit market inefficiencies and optimize profit strategies. Funding rate arbitrage involves profiting from the interest rate differentials in perpetual futures contracts between exchanges, whereas triangular arbitrage capitalizes on price discrepancies among three currency pairs in the forex market. Mastery of these distinct arbitrage types reduces risk exposure and enhances decision-making precision. This knowledge empowers traders to select appropriate tools and strategies aligned with specific market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Triangular Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in perpetual futures funding rates across exchanges | Capitalizing on price discrepancies among three currency pairs to create risk-free profit |
| Market Type | Perpetual futures, derivatives | Spot forex and cryptocurrency markets |
| Profit Mechanism | Collecting or paying periodic funding payments based on rate disparity | Instantaneous buying and selling across three pairs to lock in price differences |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk; influenced by funding rate volatility and timing delays | Low risk; often considered risk-free if executed quickly |
| Capital Requirements | High capital needed to maximize returns due to small funding differentials | Moderate capital needed; depends on liquidity in three markets |
| Complexity | Relatively simple strategy, requiring monitoring of funding rates | Technically complex; involves multi-step execution and sophisticated algorithms |
| Execution Speed | Less time-sensitive; funding payments occur periodically | Highly time-sensitive; requires ultra-fast execution to capture price inefficiencies |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage typically offers consistent, low-risk returns by capitalizing on discrepancies in perpetual futures funding rates across exchanges, making it attractive for traders seeking stable profits. Triangular arbitrage exploits currency inefficiencies within the same exchange by converting between three different assets, providing opportunities for quick, risk-free gains but requiring rapid execution and advanced infrastructure. The better strategy depends on trader goals: funding rate arbitrage suits those prioritizing steady income, while triangular arbitrage appeals to those equipped for high-frequency trading and capitalizing on micro price differences.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage and triangular arbitrage are connected through their shared goal of exploiting price inefficiencies in financial markets. Funding rate arbitrage capitalizes on differences in perpetual swap funding rates across exchanges, while triangular arbitrage leverages discrepancies between three currency pairs within the forex or crypto markets. Both strategies require real-time data analysis and rapid execution to profit from temporary imbalances, highlighting their reliance on market liquidity and price synchronization.
Key Terms
**Triangular Arbitrage:**
Triangular arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between three different currency pairs in the forex market, enabling traders to lock in a risk-free profit by simultaneously buying and selling currencies. This strategy relies on the constant price differences caused by market inefficiencies and provides opportunities for quick, low-risk gains without exposure to market volatility. Explore how triangular arbitrage compares to funding rate arbitrage and learn detailed strategies to maximize profitability.
Currency pairs
Triangular arbitrage exploits price discrepancies among three currency pairs within the forex market to secure risk-free profits by simultaneously buying and selling different currencies. Funding rate arbitrage focuses on the difference between the perpetual swap funding rate and the spot market price, allowing traders to profit from borrowing costs in pairs such as BTC/USD or ETH/USD. Explore deeper insights on how these currency pair strategies can optimize your trading portfolio.
Exchange rates
Triangular arbitrage exploits discrepancies between three different currency exchange rates to generate risk-free profits within the forex market, capitalizing on mispricings across EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and EUR/JPY pairs. Funding rate arbitrage, primarily observed in cryptocurrency markets, involves borrowing funds at lower interest rates in one currency and lending in another with higher funding rates, profiting from differential interest rather than pure exchange rate mismatches. Explore detailed strategies and market conditions influencing these arbitrage opportunities to enhance your trading acumen.
Source and External Links
Triangular arbitrage - Wikipedia - Triangular arbitrage is a strategy involving three trades among three currencies, exploiting discrepancies between quoted exchange rates and implicit cross exchange rates to earn riskless profits by sequentially exchanging currencies in a cycle.
Triangular Arbitrage Opportunity - Definition and Example - This arbitrage opportunity arises when the exchange rate between currencies deviates from the cross-exchange rate, allowing traders to make profit by consecutively exchanging one currency to another and back, usually requiring large volumes and consideration of transaction costs.
Triangular Arbitrage Explained | Example With Bid & Ask - YouTube - A detailed explanation of triangular arbitrage in forex markets demonstrating how bid and ask prices are used to identify arbitrage opportunities through currency price-to-base relationships and step-by-step trading sequences.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com