Quantitative signals utilize mathematical models and historical data to generate systematic trading decisions, focusing on patterns and statistical relationships within market variables. Event-driven strategies capitalize on specific occurrences such as earnings announcements, mergers, or geopolitical events to exploit market inefficiencies arising from new information. Explore the differences and applications of these trading approaches to enhance your investment insights.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantitative signals and event-driven strategies is crucial for traders to optimize decision-making and risk management. Quantitative signals rely on statistical models and historical data patterns, providing systematic entry and exit points based on numerical trends. Event-driven strategies focus on exploiting market-moving news or events such as earnings reports or geopolitical developments, requiring real-time analysis and swift execution. Mastery of both approaches enables balanced portfolio strategies and enhances adaptability in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
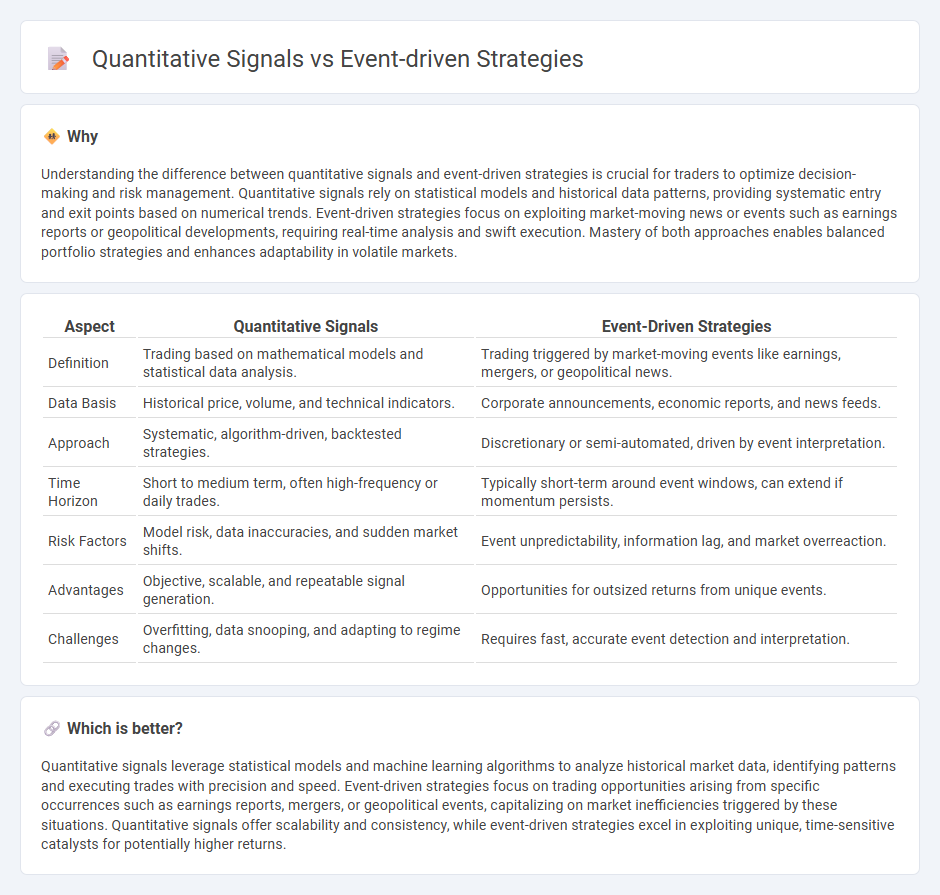
| Aspect | Quantitative Signals | Event-Driven Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on mathematical models and statistical data analysis. | Trading triggered by market-moving events like earnings, mergers, or geopolitical news. |
| Data Basis | Historical price, volume, and technical indicators. | Corporate announcements, economic reports, and news feeds. |
| Approach | Systematic, algorithm-driven, backtested strategies. | Discretionary or semi-automated, driven by event interpretation. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, often high-frequency or daily trades. | Typically short-term around event windows, can extend if momentum persists. |
| Risk Factors | Model risk, data inaccuracies, and sudden market shifts. | Event unpredictability, information lag, and market overreaction. |
| Advantages | Objective, scalable, and repeatable signal generation. | Opportunities for outsized returns from unique events. |
| Challenges | Overfitting, data snooping, and adapting to regime changes. | Requires fast, accurate event detection and interpretation. |
Which is better?
Quantitative signals leverage statistical models and machine learning algorithms to analyze historical market data, identifying patterns and executing trades with precision and speed. Event-driven strategies focus on trading opportunities arising from specific occurrences such as earnings reports, mergers, or geopolitical events, capitalizing on market inefficiencies triggered by these situations. Quantitative signals offer scalability and consistency, while event-driven strategies excel in exploiting unique, time-sensitive catalysts for potentially higher returns.
Connection
Quantitative signals and event-driven strategies intersect by using data-driven algorithms to identify market opportunities triggered by specific corporate or economic events. Quantitative signals analyze historical price patterns, volume, and volatility metrics, while event-driven strategies focus on occurrences like earnings reports, mergers, or regulatory changes to predict price movements. This integration enhances trade timing and risk management by combining statistical insights with real-time event analysis.
Key Terms
Event-driven strategies:
Event-driven strategies capitalize on specific occurrences such as mergers, acquisitions, earnings announcements, or regulatory changes that create market inefficiencies and opportunities for profit. These approaches rely on detailed analysis of event impacts on asset prices rather than broad market trends, providing distinct risk profiles compared to quantitative signals, which derive from statistical models and historical data patterns. Explore the nuances and advantages of event-driven strategies to enhance your investment decision-making.
Merger Arbitrage
Merger arbitrage relies on event-driven strategies that capitalize on price discrepancies arising from announced corporate mergers and acquisitions. Quantitative signals enhance this approach by analyzing historical deal success rates, spread patterns, and timing to optimize entry and exit points. Explore further to understand how integrating quantitative models can improve merger arbitrage outcomes.
Earnings Announcements
Event-driven strategies leverage earnings announcements to capitalize on stock price volatility triggered by unexpected financial results, often relying on timely market reactions and news flow analysis. Quantitative signals utilize historical earnings data and statistical models to predict price movements, integrating metrics such as earnings surprises, revision trends, and sentiment scores. Discover how these approaches can enhance portfolio performance through detailed insights and comparative analysis.
Source and External Links
Event Driven Trading Strategies: How They Work and Why ... - Event-driven strategies exploit price movements caused by significant corporate or market events by analyzing the impact and establishing positions such as merger arbitrage or distressed securities, while managing associated risks.
Event-Driven Investing | Fund Strategy + Examples - Event-driven investing focuses on capitalizing on pricing inefficiencies from corporate events like M&A, spin-offs, and bankruptcies, with common sub-strategies including merger arbitrage, distressed investing, special situations, and activist investing.
Event-Driven Strategies - These equity-oriented strategies target securities undergoing significant corporate change, aiming to exploit special situations in corporate life while managing risks related to concentration and economic cycles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com