Algorithmic arbitrage leverages sophisticated algorithms to exploit price discrepancies across different markets, ensuring rapid and risk-averse profits. Quantitative momentum strategies focus on statistical models to identify assets with strong price trends, aiming to maximize returns by capitalizing on market momentum. Explore in-depth strategies and performance metrics to understand which approach aligns with your trading goals.
Why it is important
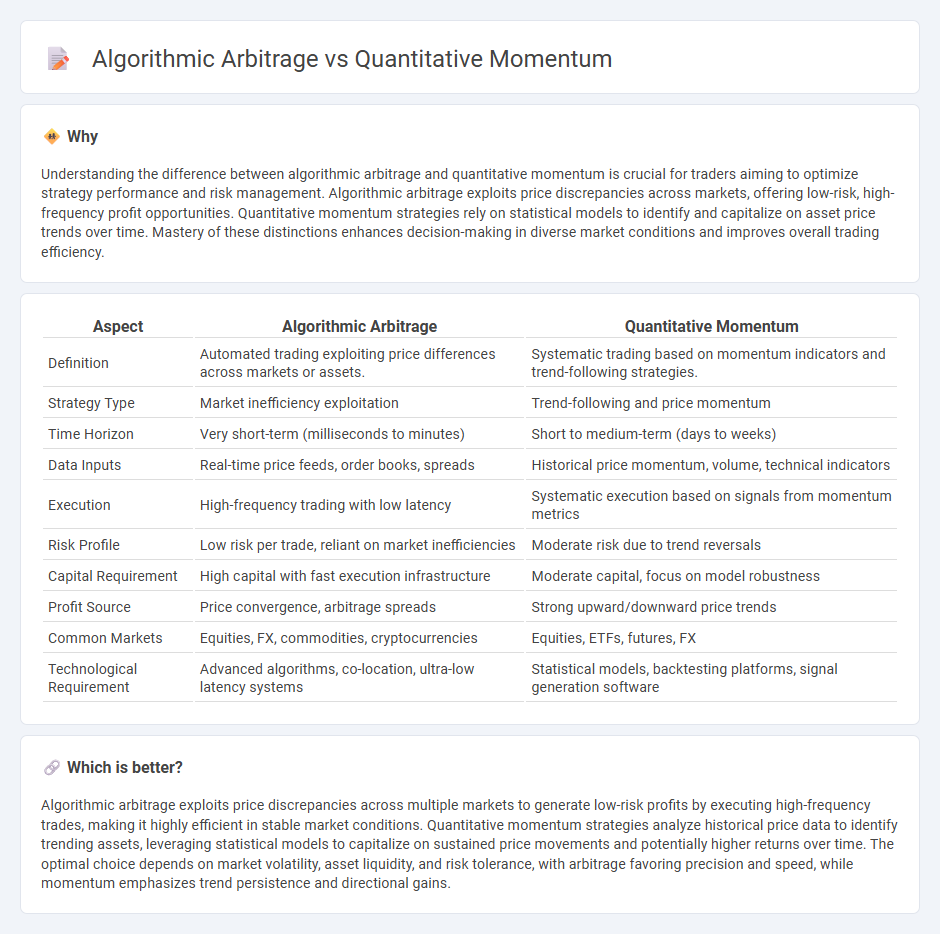
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and quantitative momentum is crucial for traders aiming to optimize strategy performance and risk management. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets, offering low-risk, high-frequency profit opportunities. Quantitative momentum strategies rely on statistical models to identify and capitalize on asset price trends over time. Mastery of these distinctions enhances decision-making in diverse market conditions and improves overall trading efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Quantitative Momentum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading exploiting price differences across markets or assets. | Systematic trading based on momentum indicators and trend-following strategies. |
| Strategy Type | Market inefficiency exploitation | Trend-following and price momentum |
| Time Horizon | Very short-term (milliseconds to minutes) | Short to medium-term (days to weeks) |
| Data Inputs | Real-time price feeds, order books, spreads | Historical price momentum, volume, technical indicators |
| Execution | High-frequency trading with low latency | Systematic execution based on signals from momentum metrics |
| Risk Profile | Low risk per trade, reliant on market inefficiencies | Moderate risk due to trend reversals |
| Capital Requirement | High capital with fast execution infrastructure | Moderate capital, focus on model robustness |
| Profit Source | Price convergence, arbitrage spreads | Strong upward/downward price trends |
| Common Markets | Equities, FX, commodities, cryptocurrencies | Equities, ETFs, futures, FX |
| Technological Requirement | Advanced algorithms, co-location, ultra-low latency systems | Statistical models, backtesting platforms, signal generation software |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across multiple markets to generate low-risk profits by executing high-frequency trades, making it highly efficient in stable market conditions. Quantitative momentum strategies analyze historical price data to identify trending assets, leveraging statistical models to capitalize on sustained price movements and potentially higher returns over time. The optimal choice depends on market volatility, asset liquidity, and risk tolerance, with arbitrage favoring precision and speed, while momentum emphasizes trend persistence and directional gains.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage and quantitative momentum strategies both rely on data-driven models to identify market inefficiencies and generate profits. These approaches use statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms to detect price differentials and momentum trends across multiple assets. Integrating momentum signals within arbitrage algorithms enhances trade execution by capturing short-term price movements alongside relative value discrepancies.
Key Terms
Signal Generation
Quantitative momentum strategies capitalize on stock price trends by generating signals based on relative strength and momentum indicators, optimizing entries and exits using statistical models. Algorithmic arbitrage focuses on exploiting price discrepancies across markets, utilizing high-frequency signals derived from order book imbalances and latency arbitrage to execute trades rapidly. Explore the detailed mechanisms and performance metrics behind these signal generation techniques to enhance your trading strategy.
Execution Speed
Quantitative momentum strategies leverage statistical analysis to identify and exploit asset price trends, requiring rapid execution speeds to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. Algorithmic arbitrage focuses on detecting and executing trades across markets to profit from price discrepancies, demanding ultra-low latency systems for timely order placement. Explore how advancements in execution speed technology shape the performance of these sophisticated trading strategies.
Market Inefficiencies
Quantitative momentum exploits market inefficiencies by identifying securities with consistent price trends, leveraging data-driven models to capture sustained asset returns before price corrections occur. Algorithmic arbitrage capitalizes on temporary price discrepancies across markets or instruments, executing rapid trades to profit from transient inefficiencies without directional bias. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies uniquely harness market anomalies to optimize portfolio performance.
Source and External Links
Quantitative Momentum: A Practitioner's Guide to Building ... - This book by Wes Gray is a comprehensive guide explaining momentum investing and how it is a systematic stock selection strategy with behavioral psychology roots that outperforms the market, offering tools to build and implement momentum strategies for individual investors.
Quantitative Momentum: A Practitioner's Guide to Building ... - The book details how momentum is distinct from growth investing and how it has been rigorously tested to deliver long-term market-beating results, providing expert insights and practical advice for individual investors to adopt momentum investing strategies beyond asset allocation into stock selection.
The Quantitative Momentum Investing Philosophy - This resource explains the concept of momentum quality in stocks by comparing different momentum paths, emphasizing the importance of stable, consistent returns over time versus sudden spikes driven by limited investor attention, thereby illustrating the nuanced approach in quantitative momentum investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com