Tape reading focuses on analyzing real-time order flow and price movements to gauge market sentiment and anticipate short-term price changes. Quantitative analysis leverages mathematical models and large datasets to identify trading signals and optimize strategies through statistical methods. Explore deeper insights into tape reading and quantitative analysis to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
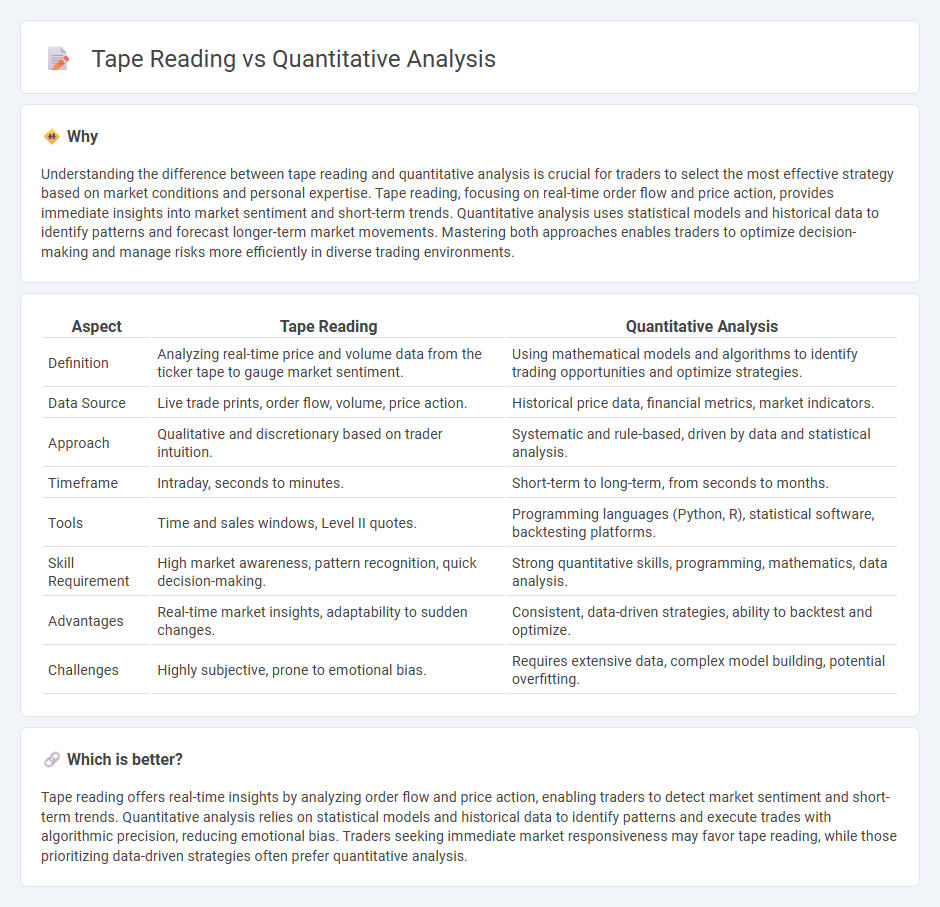
Understanding the difference between tape reading and quantitative analysis is crucial for traders to select the most effective strategy based on market conditions and personal expertise. Tape reading, focusing on real-time order flow and price action, provides immediate insights into market sentiment and short-term trends. Quantitative analysis uses statistical models and historical data to identify patterns and forecast longer-term market movements. Mastering both approaches enables traders to optimize decision-making and manage risks more efficiently in diverse trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tape Reading | Quantitative Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzing real-time price and volume data from the ticker tape to gauge market sentiment. | Using mathematical models and algorithms to identify trading opportunities and optimize strategies. |
| Data Source | Live trade prints, order flow, volume, price action. | Historical price data, financial metrics, market indicators. |
| Approach | Qualitative and discretionary based on trader intuition. | Systematic and rule-based, driven by data and statistical analysis. |
| Timeframe | Intraday, seconds to minutes. | Short-term to long-term, from seconds to months. |
| Tools | Time and sales windows, Level II quotes. | Programming languages (Python, R), statistical software, backtesting platforms. |
| Skill Requirement | High market awareness, pattern recognition, quick decision-making. | Strong quantitative skills, programming, mathematics, data analysis. |
| Advantages | Real-time market insights, adaptability to sudden changes. | Consistent, data-driven strategies, ability to backtest and optimize. |
| Challenges | Highly subjective, prone to emotional bias. | Requires extensive data, complex model building, potential overfitting. |
Which is better?
Tape reading offers real-time insights by analyzing order flow and price action, enabling traders to detect market sentiment and short-term trends. Quantitative analysis relies on statistical models and historical data to identify patterns and execute trades with algorithmic precision, reducing emotional bias. Traders seeking immediate market responsiveness may favor tape reading, while those prioritizing data-driven strategies often prefer quantitative analysis.
Connection
Tape reading provides real-time insight into market liquidity and order flow by analyzing the time and sales data, which enhances the effectiveness of quantitative analysis models that rely on historical and statistical data. Quantitative analysis leverages algorithms to identify patterns and predict price movements, utilizing tape reading data to fine-tune entry and exit points. Integrating tape reading with quantitative strategies allows traders to combine microstructure analysis with statistical rigor, improving decision accuracy and market timing.
Key Terms
**Quantitative Analysis:**
Quantitative analysis utilizes statistical models and large datasets to identify trading opportunities, relying on algorithmic strategies and historical price patterns to generate predictive insights. It emphasizes objective data processing and computational efficiency, often leveraging machine learning techniques and high-frequency trading systems for optimized decision-making. Explore how quantitative analysis can transform your investment strategies with advanced data-driven tools.
Algorithms
Quantitative analysis leverages complex algorithms and statistical models to evaluate vast datasets, identifying patterns and predicting market trends with high precision. Tape reading, traditionally centered on real-time order flow and volume analysis, relies more on intuitive interpretation of market liquidity and momentum without extensive algorithmic computation. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how algorithmic strategies enhance quantitative analysis beyond traditional tape reading techniques.
Backtesting
Quantitative analysis relies on mathematical models and historical data to develop and test trading strategies through backtesting, ensuring statistical validity and performance consistency. Tape reading involves real-time interpretation of market data and order flow, making backtesting challenging due to the dynamic and interpretive nature of the technique. Explore detailed methodologies to enhance your understanding of backtesting in both quantitative and tape reading approaches.
Source and External Links
What Is Quantitative Analysis? Definition and Methods | Indeed.com - Quantitative analysis is a method of collecting and evaluating numerical data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and inform decision-making across various fields including finance and business operations.
Quantitative Analysis - Definition, Techniques and Applications | Corporate Finance Institute - It is the process of collecting measurable and verifiable data, utilizing techniques like regression analysis, linear programming, and data mining to assess business performance and make predictions.
Quantitative analysis (chemistry) | EBSCO Research Starters - In chemistry, quantitative analysis determines exact amounts of substances in samples using methods such as gravimetric analysis, titrimetry, chromatography, and spectroscopy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com