Delta-neutral strategies involve hedging positions to maintain a market-neutral exposure, minimizing risk from price fluctuations by balancing options and underlying assets. Swing trading strategies focus on capturing short- to medium-term price movements by holding positions for several days to weeks, leveraging technical analysis to identify entry and exit points. Explore detailed comparisons of delta-neutral and swing trading techniques to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral strategies and swing trading strategies is crucial for effective risk management and goal alignment in trading. Delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing directional risk by balancing options positions, ideal for hedging and volatility exploitation. Swing trading strategies aim to capture short- to medium-term price movements based on market trends and technical analysis. Mastering these distinctions enables traders to select approaches that optimize returns according to market conditions and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
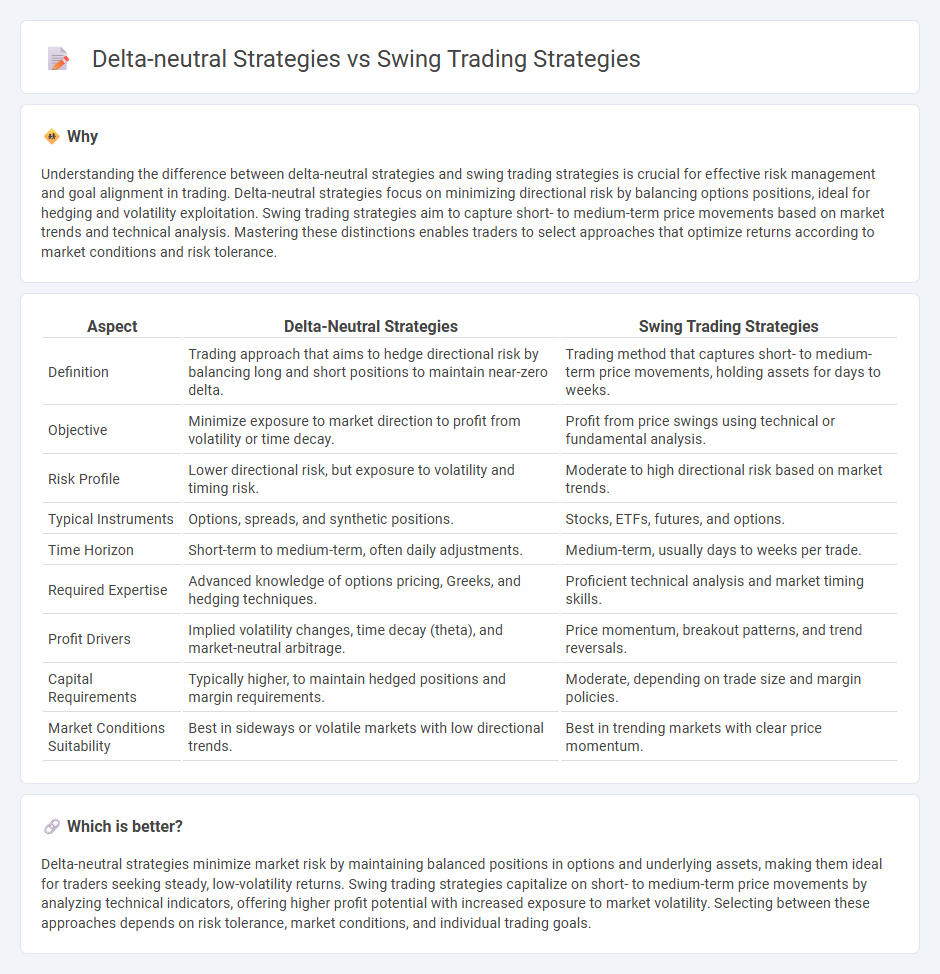
| Aspect | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Swing Trading Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach that aims to hedge directional risk by balancing long and short positions to maintain near-zero delta. | Trading method that captures short- to medium-term price movements, holding assets for days to weeks. |
| Objective | Minimize exposure to market direction to profit from volatility or time decay. | Profit from price swings using technical or fundamental analysis. |
| Risk Profile | Lower directional risk, but exposure to volatility and timing risk. | Moderate to high directional risk based on market trends. |
| Typical Instruments | Options, spreads, and synthetic positions. | Stocks, ETFs, futures, and options. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term to medium-term, often daily adjustments. | Medium-term, usually days to weeks per trade. |
| Required Expertise | Advanced knowledge of options pricing, Greeks, and hedging techniques. | Proficient technical analysis and market timing skills. |
| Profit Drivers | Implied volatility changes, time decay (theta), and market-neutral arbitrage. | Price momentum, breakout patterns, and trend reversals. |
| Capital Requirements | Typically higher, to maintain hedged positions and margin requirements. | Moderate, depending on trade size and margin policies. |
| Market Conditions Suitability | Best in sideways or volatile markets with low directional trends. | Best in trending markets with clear price momentum. |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies minimize market risk by maintaining balanced positions in options and underlying assets, making them ideal for traders seeking steady, low-volatility returns. Swing trading strategies capitalize on short- to medium-term price movements by analyzing technical indicators, offering higher profit potential with increased exposure to market volatility. Selecting between these approaches depends on risk tolerance, market conditions, and individual trading goals.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies and swing trading strategies are connected through their focus on managing risk and capitalizing on price fluctuations. Delta-neutral approaches aim to hedge directional risk by balancing options and underlying assets, while swing trading targets short- to medium-term price movements to capture gains. Combining these methods allows traders to maintain market neutrality while exploiting volatility during swing trading periods.
Key Terms
Holding Period
Swing trading strategies typically involve holding positions for several days to weeks to capitalize on medium-term market trends, while delta-neutral strategies maintain minimal directional risk through options and can have much shorter holding periods. Delta-neutral approaches, such as gamma scalping or iron condors, require frequent adjustments to hedge volatility and price movements, making them suitable for traders focused on short-term precision. Explore the nuances of how these differing holding periods impact risk management and returns in trading.
Directional Bias
Swing trading strategies rely on directional bias by capitalizing on short- to medium-term price movements in trending markets, aiming to buy low and sell high within days or weeks. Delta-neutral strategies, by contrast, minimize directional risk through balanced options positions, achieving profit mainly from volatility and time decay rather than market direction. Explore detailed analyses and comparative insights into these strategies to optimize your trading approach.
Hedging
Swing trading strategies capitalize on short to medium-term price movements by holding positions for several days or weeks, aiming for capital gains through trend identification. Delta-neutral strategies prioritize hedging by balancing positive and negative delta positions to minimize exposure to directional market risk, often using options or multi-asset portfolios. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches manage risk and optimize returns for diverse trading objectives.
Source and External Links
What is swing trading & how does it work? - Saxo Bank - Swing trading strategies include breakout trading, which focuses on price breaking support or resistance levels with momentum, and trend trading, which uses technical indicators like moving averages and RSI to capture parts of a price trend.
A Complete Guide to Swing Trading Strategy and Techniques - Swing trading aims to capture gains between swing highs and lows using trend direction; traders buy dips in uptrends and sell rallies in downtrends, employing stop losses for risk management and combining indicators like moving averages and RSI for entry timing.
4 classic swing trading strategies for your trading success - Range trading is a swing strategy that exploits price oscillations within support and resistance lines during sideways or channelled markets, requiring precise identification and hedging against unexpected breakouts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com