Tokenized assets enable fractional ownership and seamless trading on digital platforms, offering enhanced liquidity compared to traditional private equity, which involves direct investment in non-public companies with longer lock-up periods. Blockchain technology underpins tokenized assets, ensuring transparency and real-time settlement, while private equity relies on complex valuation and illiquid market conditions. Discover how tokenized assets are transforming investment strategies and market access.
Why it is important
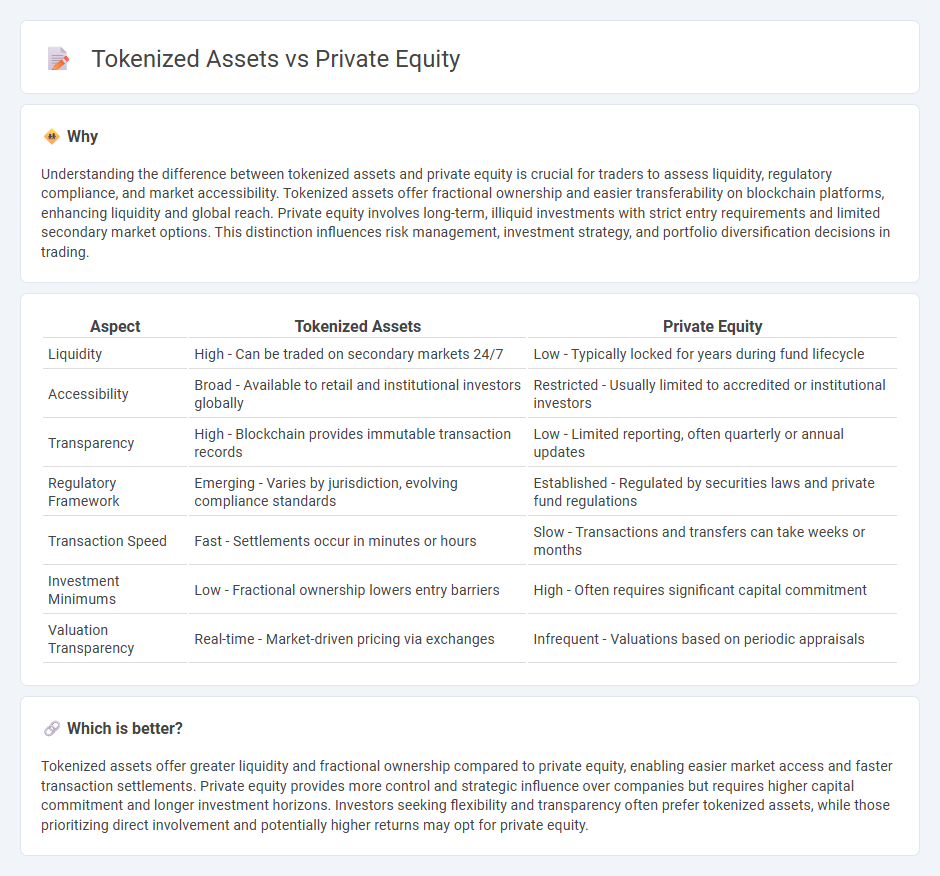
Understanding the difference between tokenized assets and private equity is crucial for traders to assess liquidity, regulatory compliance, and market accessibility. Tokenized assets offer fractional ownership and easier transferability on blockchain platforms, enhancing liquidity and global reach. Private equity involves long-term, illiquid investments with strict entry requirements and limited secondary market options. This distinction influences risk management, investment strategy, and portfolio diversification decisions in trading.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenized Assets | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | High - Can be traded on secondary markets 24/7 | Low - Typically locked for years during fund lifecycle |
| Accessibility | Broad - Available to retail and institutional investors globally | Restricted - Usually limited to accredited or institutional investors |
| Transparency | High - Blockchain provides immutable transaction records | Low - Limited reporting, often quarterly or annual updates |
| Regulatory Framework | Emerging - Varies by jurisdiction, evolving compliance standards | Established - Regulated by securities laws and private fund regulations |
| Transaction Speed | Fast - Settlements occur in minutes or hours | Slow - Transactions and transfers can take weeks or months |
| Investment Minimums | Low - Fractional ownership lowers entry barriers | High - Often requires significant capital commitment |
| Valuation Transparency | Real-time - Market-driven pricing via exchanges | Infrequent - Valuations based on periodic appraisals |
Which is better?
Tokenized assets offer greater liquidity and fractional ownership compared to private equity, enabling easier market access and faster transaction settlements. Private equity provides more control and strategic influence over companies but requires higher capital commitment and longer investment horizons. Investors seeking flexibility and transparency often prefer tokenized assets, while those prioritizing direct involvement and potentially higher returns may opt for private equity.
Connection
Tokenized assets revolutionize private equity by enabling fractional ownership, increased liquidity, and streamlined transactions via blockchain technology. This integration allows private equity investors to trade shares of traditionally illiquid assets more efficiently and transparently on digital platforms. Enhanced accessibility and reduced barriers foster a broader investor base and improved market dynamics within private equity.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Private equity investments typically have limited liquidity, with capital locked in for several years until exit events such as IPOs or acquisitions occur, posing challenges for investors seeking quick access to funds. Tokenized assets leverage blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership and peer-to-peer trading, significantly enhancing liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell shares of private equity on secondary markets almost instantaneously. Discover how tokenization is transforming traditional private equity liquidity and offering new opportunities for capital efficiency.
Ownership structure
Private equity involves direct ownership in companies through equity shares, giving investors significant control rights and influence over management decisions. Tokenized assets represent ownership via blockchain-based digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity while maintaining transparency and secure transferability. Explore the detailed differences in ownership structure and investor benefits to understand which option aligns with your portfolio goals.
Regulatory compliance
Private equity investments are subject to stringent regulatory frameworks including SEC oversight, accredited investor requirements, and extensive disclosure obligations to ensure investor protection and fraud prevention. Tokenized assets operate under evolving regulations that blend securities laws with blockchain-specific guidelines, often involving smart contract audits and compliance with AML/KYC protocols to maintain transparency and legal adherence. Explore the detailed regulatory considerations shaping the future of private equity and tokenized asset markets.
Source and External Links
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance provided in return for an equity stake in unquoted companies, focusing on supporting management buyouts and creating sustainable growth through active ownership and close collaboration with company management teams with typical holding periods of 4-7 years.
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment managers raising funds from institutional investors to acquire equity stakes in private companies, using equity and debt financing to generate returns through strategies such as revenue growth, margin expansion, and governance restructuring over a typical investment horizon of 4-7 years.
Why Invest in Private Equity: Pros and Cons | Moonfare - Private equity offers the potential for higher returns and portfolio diversification due to its lower correlation with public markets, achieved by taking a long-term, active investment approach to driving value creation in private companies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com