On-chain analytics offers real-time insights by analyzing blockchain transaction data, providing traders with transparency on asset flows and investor behaviors. Quantitative analysis relies on mathematical models and historical market data to predict price movements and optimize trading strategies. Explore the key differences and benefits of these approaches to enhance your trading decisions.
Why it is important
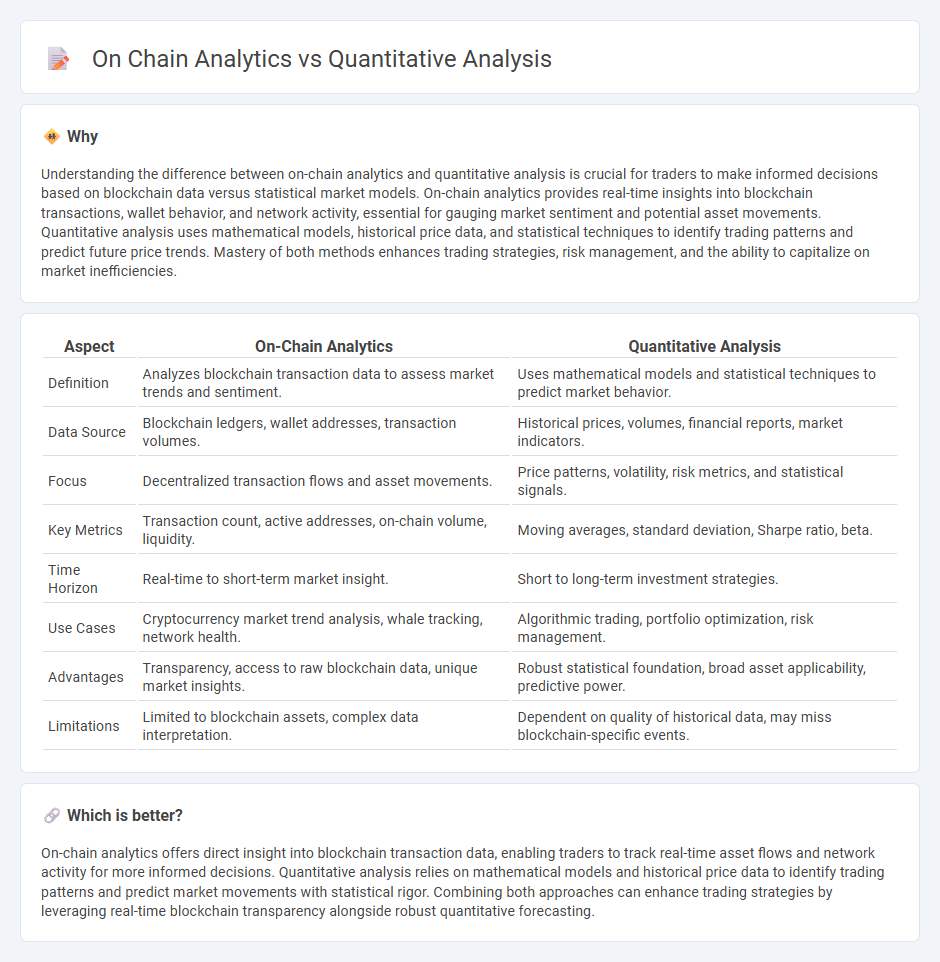
Understanding the difference between on-chain analytics and quantitative analysis is crucial for traders to make informed decisions based on blockchain data versus statistical market models. On-chain analytics provides real-time insights into blockchain transactions, wallet behavior, and network activity, essential for gauging market sentiment and potential asset movements. Quantitative analysis uses mathematical models, historical price data, and statistical techniques to identify trading patterns and predict future price trends. Mastery of both methods enhances trading strategies, risk management, and the ability to capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | On-Chain Analytics | Quantitative Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes blockchain transaction data to assess market trends and sentiment. | Uses mathematical models and statistical techniques to predict market behavior. |
| Data Source | Blockchain ledgers, wallet addresses, transaction volumes. | Historical prices, volumes, financial reports, market indicators. |
| Focus | Decentralized transaction flows and asset movements. | Price patterns, volatility, risk metrics, and statistical signals. |
| Key Metrics | Transaction count, active addresses, on-chain volume, liquidity. | Moving averages, standard deviation, Sharpe ratio, beta. |
| Time Horizon | Real-time to short-term market insight. | Short to long-term investment strategies. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency market trend analysis, whale tracking, network health. | Algorithmic trading, portfolio optimization, risk management. |
| Advantages | Transparency, access to raw blockchain data, unique market insights. | Robust statistical foundation, broad asset applicability, predictive power. |
| Limitations | Limited to blockchain assets, complex data interpretation. | Dependent on quality of historical data, may miss blockchain-specific events. |
Which is better?
On-chain analytics offers direct insight into blockchain transaction data, enabling traders to track real-time asset flows and network activity for more informed decisions. Quantitative analysis relies on mathematical models and historical price data to identify trading patterns and predict market movements with statistical rigor. Combining both approaches can enhance trading strategies by leveraging real-time blockchain transparency alongside robust quantitative forecasting.
Connection
On-chain analytics provide real-time blockchain data such as transaction volume, wallet activity, and token flows, which feed quantitative analysis models to identify trading patterns and market trends. Quantitative analysis leverages algorithms and statistical methods to process this blockchain data, enabling traders to develop predictive strategies and optimize portfolio performance. Combining both approaches enhances decision-making by offering transparent, data-driven insights directly sourced from decentralized ledgers.
Key Terms
Data Modeling
Quantitative analysis employs statistical and mathematical models to interpret data, whereas on-chain analytics focuses on blockchain transaction data, offering granular insights into decentralized networks. Data modeling in quantitative analysis includes time series forecasting and regression models, while on-chain analytics leverages entity resolution and transaction graph analysis to map relationships and behaviors. Explore our detailed guide to understand how data modeling differentiates these approaches and drives decision-making in finance and blockchain.
Algorithmic Signals
Algorithmic signals in quantitative analysis utilize mathematical models and statistical techniques to predict market trends and inform trading decisions. On-chain analytics focuses on blockchain data such as transaction volumes, wallet activity, and network health to provide real-time insights into market behavior. Explore how combining algorithmic signals with on-chain analytics can enhance investment strategies.
Blockchain Metrics
Quantitative analysis in blockchain focuses on numerical data to assess market trends and price movements, while on-chain analytics examines blockchain-specific metrics such as transaction volume, hash rates, and wallet activity to evaluate network health and behavior. Key blockchain metrics include transaction throughput, gas fees, active addresses, and token velocity, offering critical insights into blockchain performance and adoption. Explore more to understand how these analytics techniques empower data-driven decisions in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Source and External Links
What Is Quantitative Analysis? Definition and Methods | Indeed.com - Quantitative analysis is a data collection and assessment tool that uses numerical data and statistical modeling to predict outcomes and identify trends for decision-making across various fields including finance and research.
Quantitative Data Analysis. A Complete Guide [2025] - SixSigma.us - Quantitative data analysis involves systematically collecting, organizing, and applying statistical techniques such as descriptive statistics, predictive modeling, and machine learning to extract insights, forecast outcomes, and enable data-driven decisions.
Quantitative analysis (finance) - Wikipedia - In finance, quantitative analysis refers to using mathematical and statistical methods to model financial instruments and manage investments, often applied by "quants" specializing in areas like derivatives pricing, risk management, and algorithmic trading.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com