Penny Jump and Dark Pools represent two distinct trading mechanisms influencing market dynamics and liquidity. Penny Jump refers to the practice of making small price improvements by fractions of a cent to gain execution priority, while Dark Pools are private exchanges where large blocks of shares are traded anonymously to minimize market impact. Explore more to understand how these trading strategies affect price discovery and market transparency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between penny jumps and dark pools is crucial for traders to make informed decisions and manage risks effectively. Penny jumps indicate small price movements that can signal market sentiment or momentum shifts, impacting short-term trading strategies. Dark pools facilitate large, private trades without immediate market impact, allowing traders to execute sizable orders discreetly and maintain market stability. Distinguishing these concepts helps optimize trade execution and capitalize on market opportunities with greater precision.
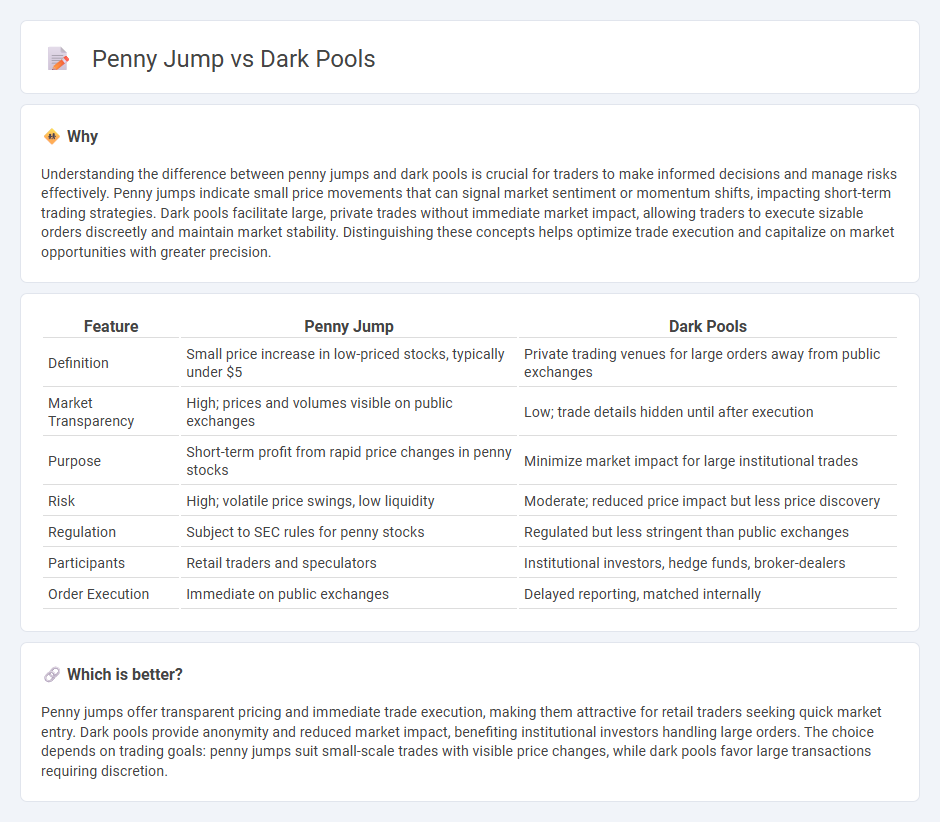
Comparison Table
| Feature | Penny Jump | Dark Pools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small price increase in low-priced stocks, typically under $5 | Private trading venues for large orders away from public exchanges |
| Market Transparency | High; prices and volumes visible on public exchanges | Low; trade details hidden until after execution |
| Purpose | Short-term profit from rapid price changes in penny stocks | Minimize market impact for large institutional trades |
| Risk | High; volatile price swings, low liquidity | Moderate; reduced price impact but less price discovery |
| Regulation | Subject to SEC rules for penny stocks | Regulated but less stringent than public exchanges |
| Participants | Retail traders and speculators | Institutional investors, hedge funds, broker-dealers |
| Order Execution | Immediate on public exchanges | Delayed reporting, matched internally |
Which is better?
Penny jumps offer transparent pricing and immediate trade execution, making them attractive for retail traders seeking quick market entry. Dark pools provide anonymity and reduced market impact, benefiting institutional investors handling large orders. The choice depends on trading goals: penny jumps suit small-scale trades with visible price changes, while dark pools favor large transactions requiring discretion.
Connection
Penny jumps occur when a stock's price increases by the minimum price increment, often triggered by trades executed in dark pools--private trading venues where large blocks of shares are bought or sold anonymously. Dark pools reduce market impact and information leakage, allowing institutional investors to execute sizable orders without causing significant price distortions, which can lead to penny jumps when these trades migrate to public exchanges. The interaction between dark pool executions and public market liquidity contributes to price discovery and subtle price movements like penny jumps in equity trading.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Dark pools provide institutional investors with private venues to execute large trades without impacting public market prices, enhancing liquidity by reducing market visibility and price slippage. Penny jumps, small price increments typically seen in penny stocks, reflect low liquidity and can lead to higher volatility and wider bid-ask spreads. Discover how understanding these liquidity dynamics can improve trading strategies and market efficiency.
Transparency
Dark pools operate as private trading venues that offer limited transparency, allowing institutional investors to execute large orders without revealing their strategies to the broader market. Penny jump refers to the practice of placing orders at a price increment of one cent above the best bid, promoting price discovery and higher transparency in public exchanges. Explore the dynamics between dark pools and penny jump mechanisms to understand their distinct impacts on market transparency.
Order Execution
Dark pools offer institutional investors a private trading environment to execute large orders with minimal market impact, reducing price slippage and protecting trade intentions. Penny jump strategies aim to improve order execution by placing bids or offers just one cent better than the current price, enhancing the likelihood of order fulfillment at favorable prices. Explore how these mechanisms influence trade efficiency and price discovery in modern markets.
Source and External Links
Can You Swim in a Dark Pool? | FINRA.org - Dark pools are private trading venues designed to enable large institutional investors to trade sizable blocks of shares anonymously without moving the market until after the trade is executed, helping to reduce price volatility and market impact.
A Beginner's Guide to Dark Pool Trading - Nasdaq - Dark pools are alternative trading systems that provide opacity and allow institutional traders to execute large orders discreetly, with nearly half of market trading volume now occurring in these types of venues and others off-exchange.
Dark pool - Wikipedia - Dark pools are private forums for trading financial instruments that conceal order size and identity to avoid market impact, which benefits institutional traders but may reduce market transparency and efficiency for retail investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com