Perpetual contracts are derivative instruments allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely without expiry, using a funding rate mechanism to anchor prices to the underlying asset. Swap contracts involve exchanging cash flows or financial instruments between parties for a specified period, often used to hedge risk or speculate on price movements. Explore the advantages and risks of perpetual versus swap contracts to enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between perpetual contracts and swap contracts is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and leverage in cryptocurrency and derivatives markets. Perpetual contracts have no expiration date, allowing continuous trading with funding rates balancing long and short positions, unlike swap contracts that typically settle at a fixed date. This knowledge ensures traders optimize strategies for liquidity, margin requirements, and price exposure. Mistaking one for the other can lead to unexpected losses due to differing settlement and fee structures.
Comparison Table
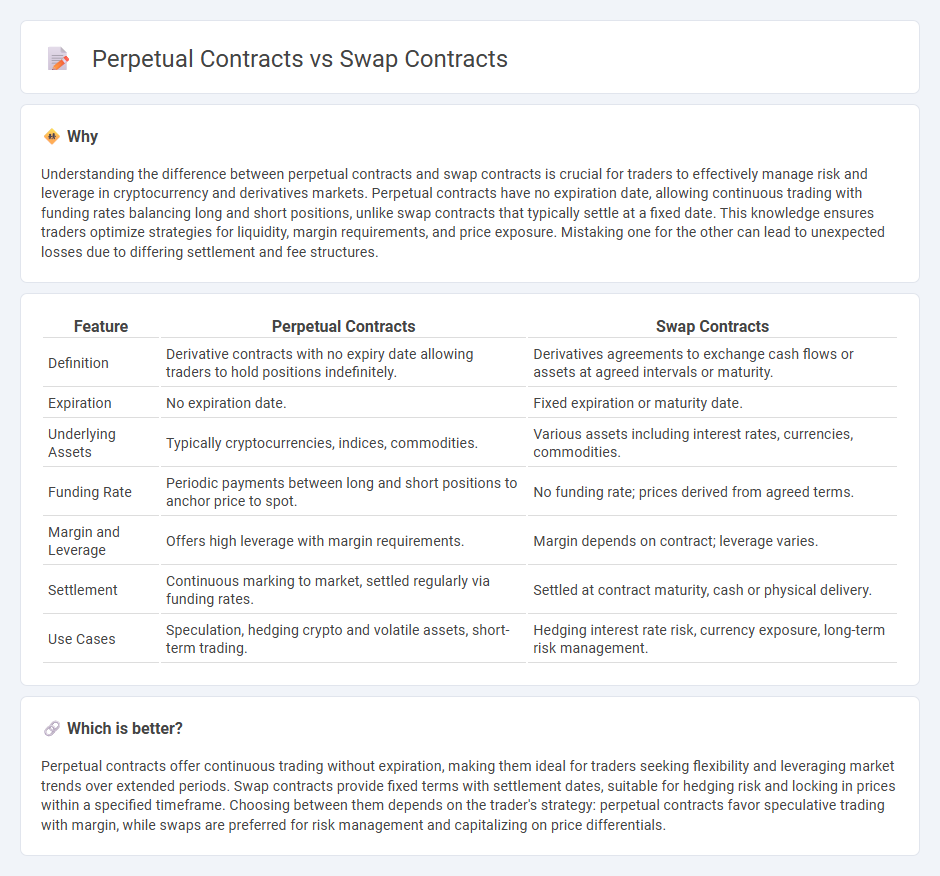
| Feature | Perpetual Contracts | Swap Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivative contracts with no expiry date allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely. | Derivatives agreements to exchange cash flows or assets at agreed intervals or maturity. |
| Expiration | No expiration date. | Fixed expiration or maturity date. |
| Underlying Assets | Typically cryptocurrencies, indices, commodities. | Various assets including interest rates, currencies, commodities. |
| Funding Rate | Periodic payments between long and short positions to anchor price to spot. | No funding rate; prices derived from agreed terms. |
| Margin and Leverage | Offers high leverage with margin requirements. | Margin depends on contract; leverage varies. |
| Settlement | Continuous marking to market, settled regularly via funding rates. | Settled at contract maturity, cash or physical delivery. |
| Use Cases | Speculation, hedging crypto and volatile assets, short-term trading. | Hedging interest rate risk, currency exposure, long-term risk management. |
Which is better?
Perpetual contracts offer continuous trading without expiration, making them ideal for traders seeking flexibility and leveraging market trends over extended periods. Swap contracts provide fixed terms with settlement dates, suitable for hedging risk and locking in prices within a specified timeframe. Choosing between them depends on the trader's strategy: perpetual contracts favor speculative trading with margin, while swaps are preferred for risk management and capitalizing on price differentials.
Connection
Perpetual contracts and swap contracts are connected through their function as derivative instruments enabling traders to speculate on the price movements of underlying assets without owning them. Both contract types feature no expiration date, allowing continuous position holding, and they use funding rates or periodic interest payments to anchor contract prices to spot market values. These mechanisms facilitate liquidity and risk management in trading cryptocurrency, forex, and commodities markets.
Key Terms
Expiry Date
Swap contracts have a fixed expiry date, requiring settlement or rollover at contract maturity, typically ranging from days to months. Perpetual contracts lack an expiry date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely while using periodic funding rates to anchor prices to the underlying asset. Explore the detailed mechanics and trading strategies for both contract types to optimize your market approach.
Funding Rate
Swap contracts and perpetual contracts differ primarily in their funding rate mechanisms; perpetual contracts use periodic funding payments between long and short positions to anchor the contract price to the underlying asset, while swap contracts typically have fixed expiration dates without such funding rates. The funding rate in perpetual contracts fluctuates based on the price difference between the contract and spot market, incentivizing traders to balance demand and maintain price stability. Explore detailed comparisons and how funding rates impact trading strategies for deeper insights.
Settlement
Swap contracts settle on a predetermined date, typically involving the exchange of underlying assets or cash flows based on price differences. Perpetual contracts, lacking a fixed expiration, use a funding rate mechanism to maintain price alignment with the underlying asset, settling profits and losses continuously. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which contract suits your trading strategy best.
Source and External Links
Swap - Definition, Types, Applications, Example - A swap is a derivative contract between two parties involving the exchange of pre-agreed cash flows from two financial instruments, typically used to hedge risks such as interest rate or currency exposure, and usually traded over-the-counter rather than on exchanges.
Swap (finance) - Wikipedia - In finance, a swap is an agreement where two counterparties exchange financial instruments or cash flows (such as fixed-for-floating interest payments) for a set time to better manage risk or alter payment structures, effectively acting as a series of forward contracts.
Swap Risks - Definition, Types & Example - Financial Edge Training - Swap contracts carry two main risks: price risk from fluctuations in underlying rates or indices and counterparty risk from potential default, and they are widely used for risk management such as hedging interest rate or currency exposure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com