Dark pool prints provide large-volume trades executed privately to minimize market impact, offering institutional investors anonymity and price stability. Automated market making uses algorithmic systems to set prices and provide liquidity continuously on decentralized exchanges, optimizing trade execution with real-time data. Discover how these trading mechanisms influence market dynamics and investment strategies.
Why it is important
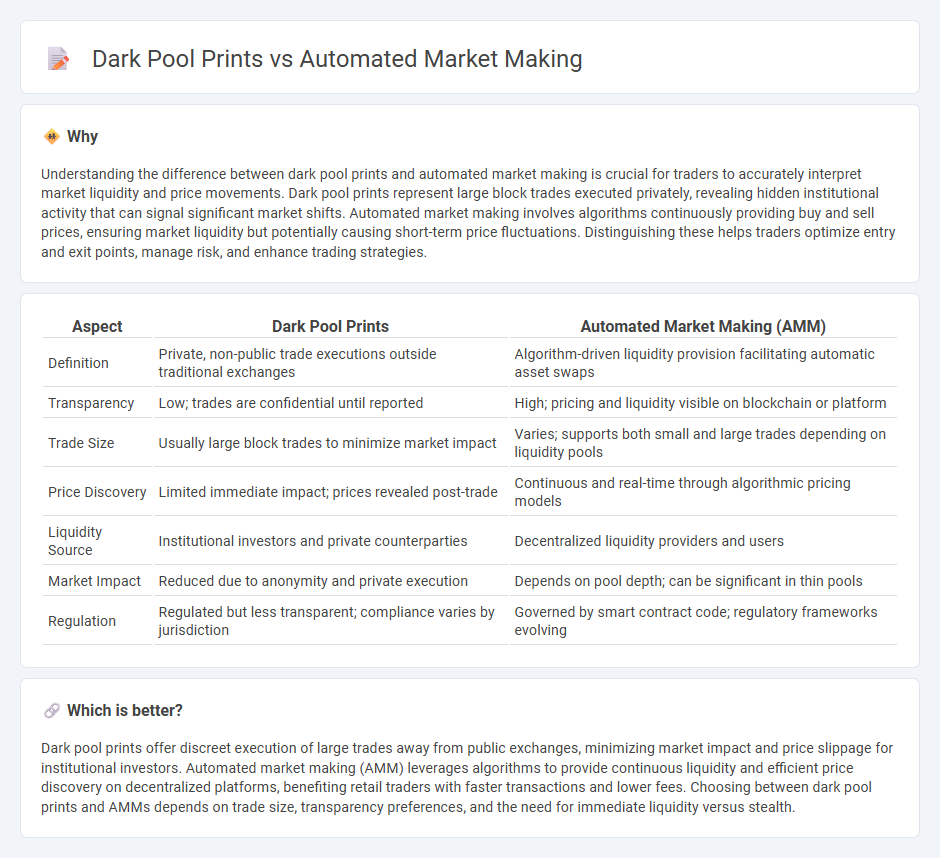
Understanding the difference between dark pool prints and automated market making is crucial for traders to accurately interpret market liquidity and price movements. Dark pool prints represent large block trades executed privately, revealing hidden institutional activity that can signal significant market shifts. Automated market making involves algorithms continuously providing buy and sell prices, ensuring market liquidity but potentially causing short-term price fluctuations. Distinguishing these helps traders optimize entry and exit points, manage risk, and enhance trading strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Prints | Automated Market Making (AMM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-public trade executions outside traditional exchanges | Algorithm-driven liquidity provision facilitating automatic asset swaps |
| Transparency | Low; trades are confidential until reported | High; pricing and liquidity visible on blockchain or platform |
| Trade Size | Usually large block trades to minimize market impact | Varies; supports both small and large trades depending on liquidity pools |
| Price Discovery | Limited immediate impact; prices revealed post-trade | Continuous and real-time through algorithmic pricing models |
| Liquidity Source | Institutional investors and private counterparties | Decentralized liquidity providers and users |
| Market Impact | Reduced due to anonymity and private execution | Depends on pool depth; can be significant in thin pools |
| Regulation | Regulated but less transparent; compliance varies by jurisdiction | Governed by smart contract code; regulatory frameworks evolving |
Which is better?
Dark pool prints offer discreet execution of large trades away from public exchanges, minimizing market impact and price slippage for institutional investors. Automated market making (AMM) leverages algorithms to provide continuous liquidity and efficient price discovery on decentralized platforms, benefiting retail traders with faster transactions and lower fees. Choosing between dark pool prints and AMMs depends on trade size, transparency preferences, and the need for immediate liquidity versus stealth.
Connection
Dark pool prints provide large block trades executed privately, which automated market making algorithms utilize by adjusting liquidity and pricing models in real time. These trades help automated market makers assess hidden market demand and supply, enhancing price efficiency and reducing slippage. The integration of dark pool data enables AMMs to optimize order execution strategies in decentralized finance and traditional exchanges.
Key Terms
Liquidity Provision
Automated market making uses algorithms to provide continuous liquidity by placing buy and sell orders within predefined spreads, enhancing market efficiency and price discovery. Dark pool prints represent large block trades executed off-exchange, offering liquidity without immediate market impact but less transparency. Explore the nuances of liquidity provision in these trading mechanisms to better understand their roles in modern markets.
Order Transparency
Automated market making relies on transparent order books that display real-time bid and ask prices, facilitating immediate liquidity and price discovery. Dark pool prints, by contrast, conceal order information to protect institutional traders from market impact, resulting in limited order transparency and delayed trade visibility. Explore the detailed implications of transparency differences between these trading venues for smarter investment decisions.
Price Discovery
Automated Market Making (AMM) enhances price discovery by providing continuous liquidity through algorithmic pricing models, enabling smoother trade execution and tighter spreads. Dark pool prints, conversely, conceal trade information until after execution, potentially delaying price transparency but allowing large orders to minimize market impact. Explore the nuances between AMM and dark pool prints to better understand their roles in modern financial markets.
Source and External Links
What is an Automated Market Maker? - Uniswap Blog - An automated market maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange running on smart contracts that prices trades automatically using algorithms instead of order books, allowing continuous, permissionless trading and enabling liquidity providers to earn fees by supplying token pairs to liquidity pools.
What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? - Gemini - AMMs are DeFi protocols that use liquidity pools and mathematical formulas to set prices and facilitate crypto trades without traditional buyers and sellers, providing 24/7 permissionless market access and price determination through constant product formulas.
What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? AMMs explained - AMMs allow traders to trade digital assets directly via smart contracts using liquidity pools instead of waiting for counterparties, enabling instant trades at algorithmically determined prices, contrasting with centralized exchanges that use order books.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com