Stop hunting manipulates market orders by triggering stop-losses, causing rapid price movements to profit from forced liquidations. Spoofing involves placing large fake orders to create misleading market signals, influencing traders' decisions before canceling those orders. Explore the differences and strategies behind stop hunting and spoofing to enhance your trading knowledge.
Why it is important
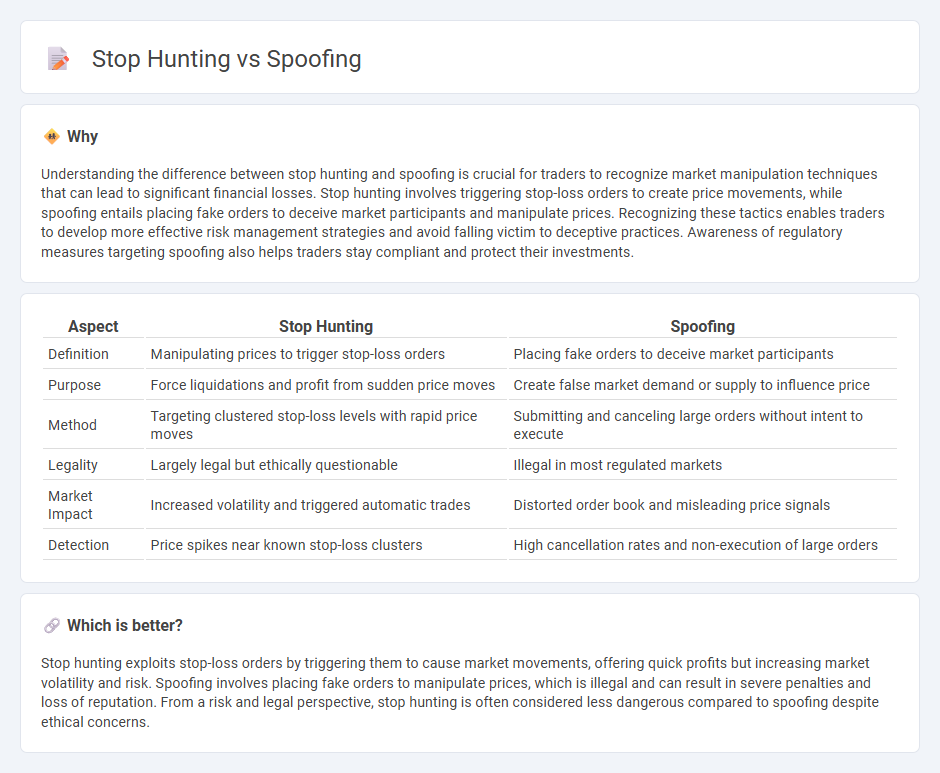
Understanding the difference between stop hunting and spoofing is crucial for traders to recognize market manipulation techniques that can lead to significant financial losses. Stop hunting involves triggering stop-loss orders to create price movements, while spoofing entails placing fake orders to deceive market participants and manipulate prices. Recognizing these tactics enables traders to develop more effective risk management strategies and avoid falling victim to deceptive practices. Awareness of regulatory measures targeting spoofing also helps traders stay compliant and protect their investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Stop Hunting | Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulating prices to trigger stop-loss orders | Placing fake orders to deceive market participants |
| Purpose | Force liquidations and profit from sudden price moves | Create false market demand or supply to influence price |
| Method | Targeting clustered stop-loss levels with rapid price moves | Submitting and canceling large orders without intent to execute |
| Legality | Largely legal but ethically questionable | Illegal in most regulated markets |
| Market Impact | Increased volatility and triggered automatic trades | Distorted order book and misleading price signals |
| Detection | Price spikes near known stop-loss clusters | High cancellation rates and non-execution of large orders |
Which is better?
Stop hunting exploits stop-loss orders by triggering them to cause market movements, offering quick profits but increasing market volatility and risk. Spoofing involves placing fake orders to manipulate prices, which is illegal and can result in severe penalties and loss of reputation. From a risk and legal perspective, stop hunting is often considered less dangerous compared to spoofing despite ethical concerns.
Connection
Stop hunting and spoofing are interconnected market manipulation tactics often employed by traders to influence price movements. Spoofing involves placing large, deceptive orders to create false market signals, while stop hunting targets the triggering of stop-loss orders by pushing prices to specific levels. Both strategies exploit market psychology and liquidity gaps to generate profits at the expense of unsuspecting investors.
Key Terms
Fake Orders (Spoofing)
Spoofing involves placing fake orders to create a false impression of supply or demand, misleading traders and manipulating market prices temporarily. In contrast, stop hunting targets clustered stop-loss orders to trigger rapid price movements for profit, often exploiting market psychology rather than fabricating orders. Discover more about how fake orders impact trading strategies and market integrity.
Liquidity Pools (Stop Hunting)
Stop hunting targets liquidity pools by triggering large stop-loss orders clustered around specific price levels, causing rapid market movements and liquidity extraction. Spoofing involves placing fake orders to create false market signals, manipulating traders' perception without immediate execution. Discover more about how liquidity pools play a critical role in stop hunting strategies.
Order Book Manipulation
Spoofing involves placing large orders with no intention of execution to create false market signals, misleading other traders by exploiting order book visibility. Stop hunting targets clustered stop-loss orders, triggering forced liquidations by pushing prices to these levels through aggressive order book interactions. Explore in-depth techniques used in order book manipulation and their impact on trading strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Spoofing & How to Prevent it - Spoofing is when a cybercriminal masquerades as a trusted entity, often using fake emails or websites alongside social engineering to trick victims into actions like transferring money or revealing personal data, leading to severe consequences such as data breaches or malware infection.
Spoofing | Spoof Calls | What is a Spoofing Attack - Spoofing in cybersecurity refers to impersonation attacks across various forms such as email, caller ID, GPS, and websites, aiming to steal data, money, or spread malware by exploiting victims' trust in familiar organizations.
What Is Spoofing? Definition, Types & More - Spoofing is a tactic used by threat actors to disguise the source of communication as trusted, commonly via emails or phone calls, potentially causing data breaches or financial losses; protection involves email protocols like SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and security training.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com