Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals to capitalize on market fluctuations, ensuring profits in both rising and falling markets. Momentum trading focuses on identifying and following strong price trends, aiming to enter positions during sustained movements for maximum gains. Explore the key differences and strategies behind grid trading and momentum trading to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between grid trading and momentum trading is crucial for optimizing risk management and maximizing profit potential in various market conditions. Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at set intervals to profit from market volatility, while momentum trading focuses on capitalizing on trending price movements using technical indicators. Understanding these strategies helps traders select the most effective approach based on market trends, volatility, and individual risk tolerance. This knowledge enables more precise trade execution and better alignment with overall investment goals.
Comparison Table
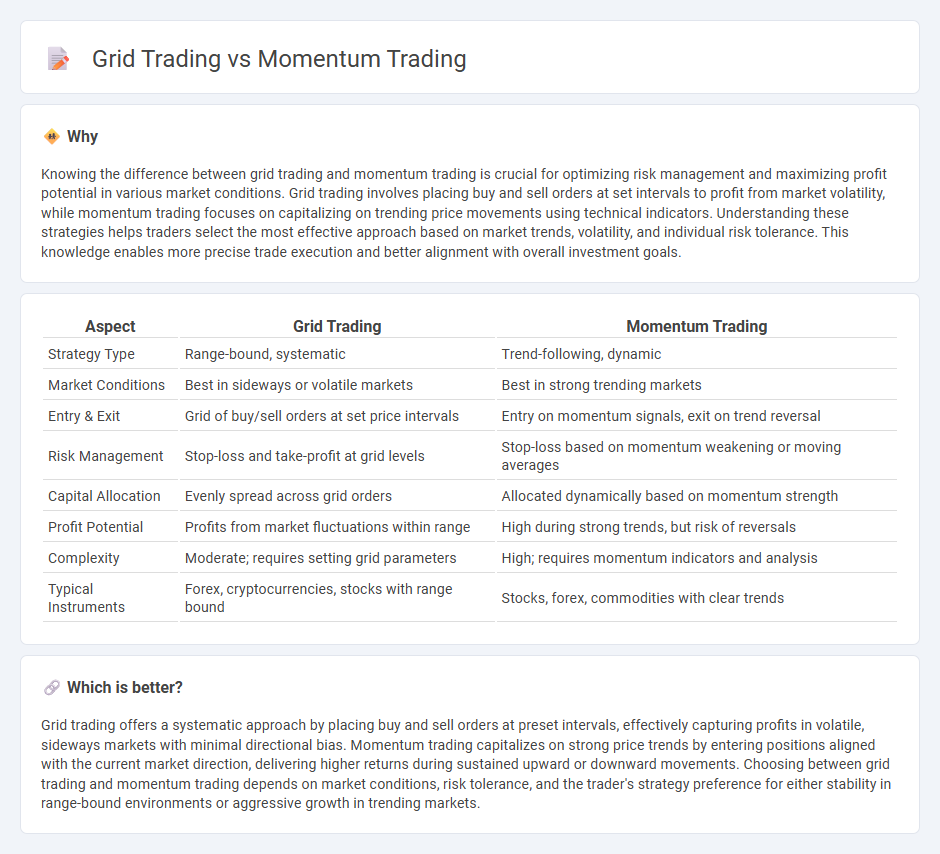
| Aspect | Grid Trading | Momentum Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Range-bound, systematic | Trend-following, dynamic |
| Market Conditions | Best in sideways or volatile markets | Best in strong trending markets |
| Entry & Exit | Grid of buy/sell orders at set price intervals | Entry on momentum signals, exit on trend reversal |
| Risk Management | Stop-loss and take-profit at grid levels | Stop-loss based on momentum weakening or moving averages |
| Capital Allocation | Evenly spread across grid orders | Allocated dynamically based on momentum strength |
| Profit Potential | Profits from market fluctuations within range | High during strong trends, but risk of reversals |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires setting grid parameters | High; requires momentum indicators and analysis |
| Typical Instruments | Forex, cryptocurrencies, stocks with range bound | Stocks, forex, commodities with clear trends |
Which is better?
Grid trading offers a systematic approach by placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals, effectively capturing profits in volatile, sideways markets with minimal directional bias. Momentum trading capitalizes on strong price trends by entering positions aligned with the current market direction, delivering higher returns during sustained upward or downward movements. Choosing between grid trading and momentum trading depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and the trader's strategy preference for either stability in range-bound environments or aggressive growth in trending markets.
Connection
Grid trading and momentum trading both capitalize on market price fluctuations, with grid trading placing systematic buy and sell orders at predefined intervals to capture profits in ranging markets, while momentum trading focuses on entering trades in the direction of strong price trends. The connection lies in their reliance on price movement patterns: grid trading benefits from oscillations within a trend's momentum, and momentum traders exploit the acceleration of price moves that can trigger grid entry points. Integrating grid strategies with momentum signals can enhance trade timing, optimize position sizing, and improve risk management in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Momentum Trading:
Momentum trading capitalizes on the continuation of existing price trends by identifying assets with strong upward or downward momentum, using technical indicators like moving averages and RSI to time entry and exit points effectively. This strategy thrives in volatile markets by quickly riding price swings, aiming for rapid profits from sustained moves rather than long-term holds. Explore deeper insights into momentum trading techniques and risk management strategies for optimized portfolio growth.
Trend
Momentum trading capitalizes on identifying and riding strong market trends by buying assets showing upward price momentum and selling those with downward momentum. Grid trading, in contrast, profits from market volatility by setting buy and sell orders at predetermined price intervals, often without relying on trend direction. Explore the key strategies and performance metrics of momentum and grid trading to determine which approach aligns better with your investment goals.
Volume
Momentum trading leverages high trading volume to identify strong price trends and capitalize on rapid market movements, often using volume spikes as key entry signals. Grid trading operates independently of volume by placing systematic buy and sell orders at predetermined intervals, aiming to profit from market fluctuations within a range. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which strategy aligns best with your volume-related trading goals.
Source and External Links
Momentum Trading: Types, Strategies and More - Part I - Momentum trading involves buying or selling assets based on recent price trends, with two main types: time-series momentum, which focuses on an asset's own historical performance, and cross-sectional momentum, which compares assets relative to each other to pick top performers for buying.
Momentum Trading: Types, Strategies, and More - Momentum trading strategies capitalize on continuing trends by buying assets with strong recent upward or downward momentum, distinguishing between time-series (individual asset performance over time) and cross-sectional momentum (relative performance ranking within a group of assets).
Momentum Trading for Beginners (What They Don't ...) - Momentum trading is a strategy of buying and selling assets by following the strength of price moves, using technical indicators and price action to identify strong momentum and manage risk effectively for fast-moving markets like stocks, crypto, and forex.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com