Front running involves executing orders ahead of pending large trades to capitalize on expected market movements, often raising ethical and regulatory concerns. Scalp trading focuses on making numerous quick trades to profit from small price fluctuations, relying heavily on speed and market timing. Explore the detailed strategies and risks associated with front running and scalp trading to enhance your trading knowledge.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between front running and scalp trading is crucial to ensure ethical trading practices and avoid legal repercussions. Front running involves exploiting non-public information to trade ahead of client orders, which is illegal and undermines market integrity. Scalp trading, a legitimate strategy, focuses on making quick, small profits by capitalizing on minor price movements. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders maintain compliance and optimize trading strategies effectively.
Comparison Table
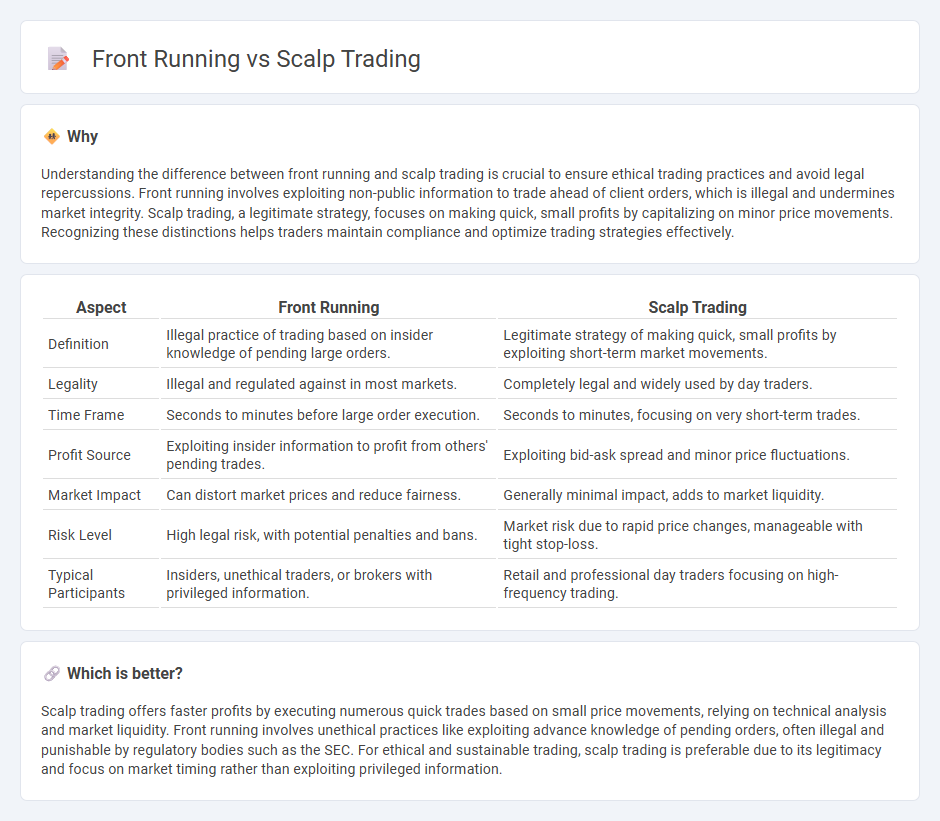
| Aspect | Front Running | Scalp Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal practice of trading based on insider knowledge of pending large orders. | Legitimate strategy of making quick, small profits by exploiting short-term market movements. |
| Legality | Illegal and regulated against in most markets. | Completely legal and widely used by day traders. |
| Time Frame | Seconds to minutes before large order execution. | Seconds to minutes, focusing on very short-term trades. |
| Profit Source | Exploiting insider information to profit from others' pending trades. | Exploiting bid-ask spread and minor price fluctuations. |
| Market Impact | Can distort market prices and reduce fairness. | Generally minimal impact, adds to market liquidity. |
| Risk Level | High legal risk, with potential penalties and bans. | Market risk due to rapid price changes, manageable with tight stop-loss. |
| Typical Participants | Insiders, unethical traders, or brokers with privileged information. | Retail and professional day traders focusing on high-frequency trading. |
Which is better?
Scalp trading offers faster profits by executing numerous quick trades based on small price movements, relying on technical analysis and market liquidity. Front running involves unethical practices like exploiting advance knowledge of pending orders, often illegal and punishable by regulatory bodies such as the SEC. For ethical and sustainable trading, scalp trading is preferable due to its legitimacy and focus on market timing rather than exploiting privileged information.
Connection
Front running and scalp trading are connected through their focus on exploiting short-term market movements for quick profits. Front running involves traders using advance knowledge of pending large orders to execute trades ahead and capitalize on price changes, while scalp trading relies on rapid buying and selling of assets to capture small price gaps. Both strategies demand high-speed execution and detailed market analysis, often leveraging algorithmic trading systems to optimize timing and gain competitive advantages.
Key Terms
**Scalp Trading:**
Scalp trading involves executing numerous quick trades to capture small price movements, often within seconds or minutes, relying on high liquidity and tight spreads to maximize profits. Traders use technical analysis and real-time data to identify entry and exit points, aiming for rapid gains rather than long-term positions. Discover more about scalp trading strategies and how they differ from front running in our detailed analysis.
Bid-Ask Spread
Scalp trading exploits small price fluctuations within the bid-ask spread to profit from rapid buying and selling, often holding positions for seconds to minutes. Front running involves a trader using advance knowledge of large upcoming orders to trade ahead, capitalizing on anticipated price moves and widening the bid-ask spread temporarily. Explore more about how these strategies impact market liquidity and trader behavior.
Liquidity
Scalp trading exploits short-term price fluctuations by rapidly buying and selling assets to capitalize on liquidity in highly active markets, ensuring swift execution and minimal exposure to market risk. Front running involves anticipating large incoming orders, using privileged information or market signals to trade ahead and profit from subsequent price movements, directly impacting liquidity availability. Explore the nuances of these trading strategies to deepen your understanding of liquidity dynamics in financial markets.
Source and External Links
Scalping (Day Trading Technique) - Corporate Finance Institute - Scalping is a day trading strategy where an investor buys and sells an individual stock multiple times within the same day to make small profits repeatedly, focusing on volatile stocks and quick trades, often holding positions only for minutes.
What is a scalping strategy in the stock market and how does it work? - TD - Scalping is a hyper-short-term trading strategy relying on technical analysis with popular indicators such as Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD to quickly buy and sell securities for small profits multiple times a day.
Forex Scalping | What is scalp trading? - Forex.com - Scalping in forex is a very short-term strategy that aims to take many small profits by opening and closing positions rapidly, requiring good nerves, technical analysis skills, and strict risk management to avoid significant losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com