Gamma scalping involves managing option positions to profit from price volatility by continuously adjusting the delta, while strangle strategies focus on buying or selling call and put options at different strike prices to capitalize on significant price movements. Traders use gamma scalping to reduce risk and lock in gains during fluctuating markets, whereas strangles provide a way to benefit from large price swings with limited initial investment. Explore the mechanics, benefits, and risks of both strategies to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
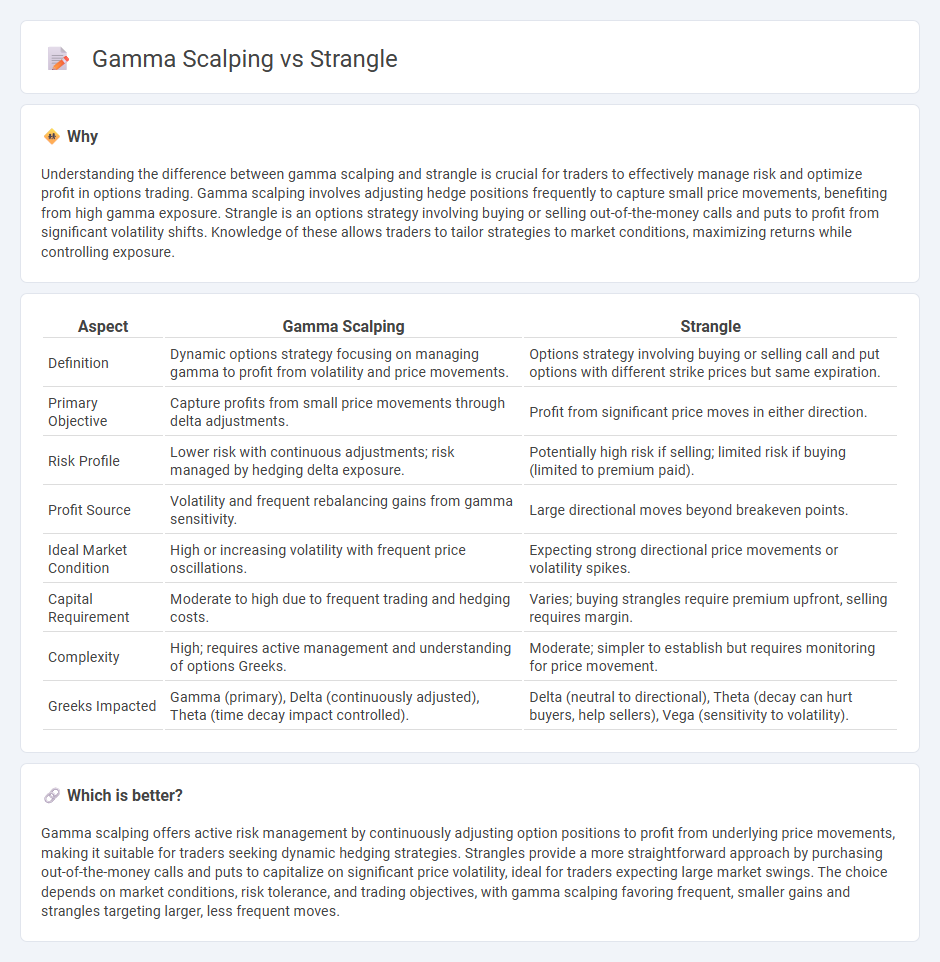
Understanding the difference between gamma scalping and strangle is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize profit in options trading. Gamma scalping involves adjusting hedge positions frequently to capture small price movements, benefiting from high gamma exposure. Strangle is an options strategy involving buying or selling out-of-the-money calls and puts to profit from significant volatility shifts. Knowledge of these allows traders to tailor strategies to market conditions, maximizing returns while controlling exposure.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Strangle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dynamic options strategy focusing on managing gamma to profit from volatility and price movements. | Options strategy involving buying or selling call and put options with different strike prices but same expiration. |
| Primary Objective | Capture profits from small price movements through delta adjustments. | Profit from significant price moves in either direction. |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk with continuous adjustments; risk managed by hedging delta exposure. | Potentially high risk if selling; limited risk if buying (limited to premium paid). |
| Profit Source | Volatility and frequent rebalancing gains from gamma sensitivity. | Large directional moves beyond breakeven points. |
| Ideal Market Condition | High or increasing volatility with frequent price oscillations. | Expecting strong directional price movements or volatility spikes. |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high due to frequent trading and hedging costs. | Varies; buying strangles require premium upfront, selling requires margin. |
| Complexity | High; requires active management and understanding of options Greeks. | Moderate; simpler to establish but requires monitoring for price movement. |
| Greeks Impacted | Gamma (primary), Delta (continuously adjusted), Theta (time decay impact controlled). | Delta (neutral to directional), Theta (decay can hurt buyers, help sellers), Vega (sensitivity to volatility). |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers active risk management by continuously adjusting option positions to profit from underlying price movements, making it suitable for traders seeking dynamic hedging strategies. Strangles provide a more straightforward approach by purchasing out-of-the-money calls and puts to capitalize on significant price volatility, ideal for traders expecting large market swings. The choice depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and trading objectives, with gamma scalping favoring frequent, smaller gains and strangles targeting larger, less frequent moves.
Connection
Gamma scalping involves dynamically adjusting option positions to manage gamma risk, which is closely related to the delta sensitivity of option portfolios. A strangle strategy, consisting of buying or selling out-of-the-money call and put options, creates a position with significant gamma exposure that traders often gamma scalp to profit from underlying asset price volatility. By continuously rebalancing the delta through gamma scalping, traders can enhance returns and mitigate risks associated with strangle positions in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Options Premium
Strangle strategies involve buying out-of-the-money call and put options to profit from significant price movements, typically requiring higher options premiums due to dual contracts. Gamma scalping capitalizes on hedging long options positions by dynamically adjusting delta, minimizing premium costs through active trading rather than upfront premium expenditure. Explore deeper intricacies of options premium management and strategic execution to optimize trading outcomes.
Volatility
Strangle options strategies profit from significant volatility by simultaneously buying out-of-the-money call and put options, capturing large price swings without directional bias. Gamma scalping, on the other hand, involves dynamic delta hedging to benefit from small price fluctuations and volatility decay, requiring active management of the underlying position. Explore the distinct approaches and risk profiles of strangle versus gamma scalping to optimize your volatility trading strategy.
Delta Neutral
Strangle and gamma scalping are advanced options strategies that emphasize maintaining a delta-neutral position to manage directional risk effectively. A strangle involves holding out-of-the-money call and put options, creating a view on volatility without directional bias, while gamma scalping adjusts option positions continuously to hedge delta exposure as prices fluctuate, capitalizing on gamma decay. Explore the mechanics and benefits of both strategies to enhance your options trading toolkit.
Source and External Links
Strangle (options) - Wikipedia - In finance, a strangle is an options trading strategy involving buying or selling one call and one put option with the same expiration date but different strike prices, allowing profit from large price movement regardless of direction.
Strangling - Wikipedia - Strangling or strangulation is the act of compressing the neck to restrict oxygen flow, which can lead to unconsciousness or death; it includes hanging, ligature strangulation, and manual strangulation.
Strangle - Definition, Meaning & Synonyms - Vocabulary.com - To strangle means to cut off someone's breathing by squeezing the throat, and can also mean to stop or hinder something from growing or developing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com