High-frequency trading (HFT) leverages advanced algorithms and ultra-fast data processing to execute thousands of trades within seconds, aiming to capitalize on minute price discrepancies. Proprietary trading involves financial firms trading stocks, bonds, currencies, or derivatives using their own capital, seeking to generate direct profits rather than commissions. Explore the unique strategies and risks associated with high-frequency versus proprietary trading to deepen your understanding.
Why it is important
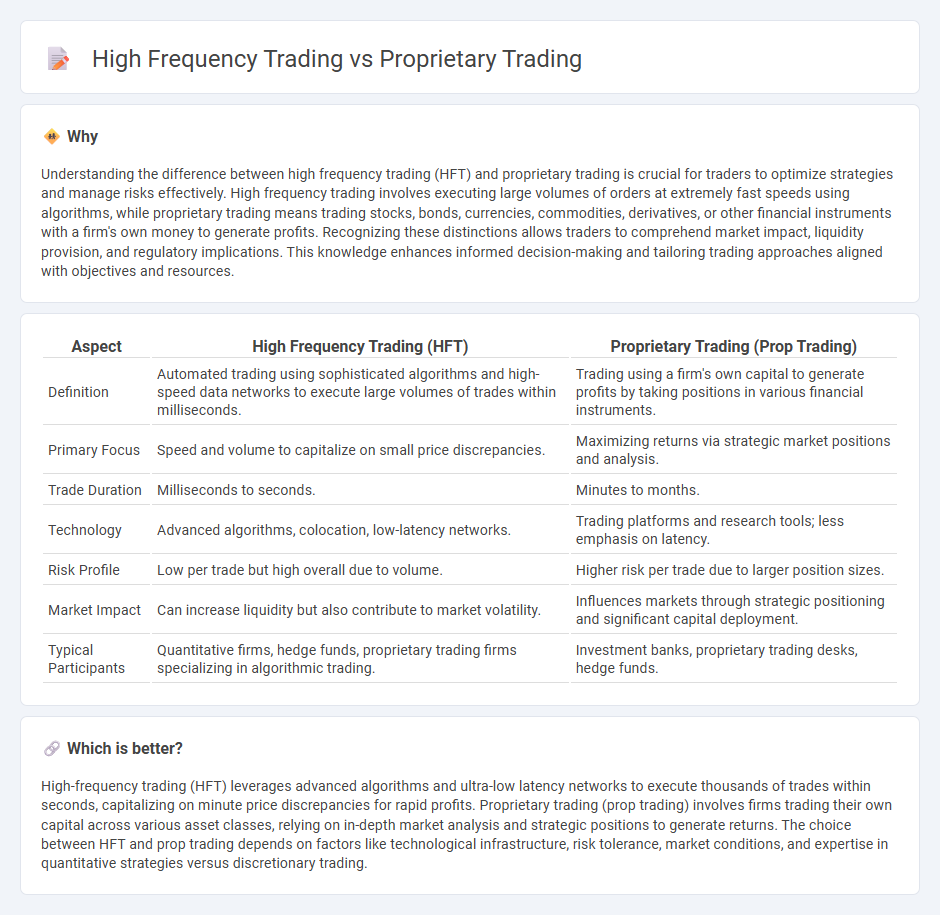
Understanding the difference between high frequency trading (HFT) and proprietary trading is crucial for traders to optimize strategies and manage risks effectively. High frequency trading involves executing large volumes of orders at extremely fast speeds using algorithms, while proprietary trading means trading stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives, or other financial instruments with a firm's own money to generate profits. Recognizing these distinctions allows traders to comprehend market impact, liquidity provision, and regulatory implications. This knowledge enhances informed decision-making and tailoring trading approaches aligned with objectives and resources.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | High Frequency Trading (HFT) | Proprietary Trading (Prop Trading) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading using sophisticated algorithms and high-speed data networks to execute large volumes of trades within milliseconds. | Trading using a firm's own capital to generate profits by taking positions in various financial instruments. |
| Primary Focus | Speed and volume to capitalize on small price discrepancies. | Maximizing returns via strategic market positions and analysis. |
| Trade Duration | Milliseconds to seconds. | Minutes to months. |
| Technology | Advanced algorithms, colocation, low-latency networks. | Trading platforms and research tools; less emphasis on latency. |
| Risk Profile | Low per trade but high overall due to volume. | Higher risk per trade due to larger position sizes. |
| Market Impact | Can increase liquidity but also contribute to market volatility. | Influences markets through strategic positioning and significant capital deployment. |
| Typical Participants | Quantitative firms, hedge funds, proprietary trading firms specializing in algorithmic trading. | Investment banks, proprietary trading desks, hedge funds. |
Which is better?
High-frequency trading (HFT) leverages advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency networks to execute thousands of trades within seconds, capitalizing on minute price discrepancies for rapid profits. Proprietary trading (prop trading) involves firms trading their own capital across various asset classes, relying on in-depth market analysis and strategic positions to generate returns. The choice between HFT and prop trading depends on factors like technological infrastructure, risk tolerance, market conditions, and expertise in quantitative strategies versus discretionary trading.
Connection
High frequency trading (HFT) and proprietary trading are connected through their shared goal of leveraging advanced algorithms and high-speed data feeds to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Proprietary trading firms often utilize high-frequency trading strategies to execute large volumes of rapid transactions, maximizing profit opportunities from minimal price movements. Both trading types rely on cutting-edge technology, quantitative analysis, and low-latency connections to achieve competitive advantages in financial markets.
Key Terms
Capital Allocation
Proprietary trading involves firms using their own capital to trade financial instruments for direct profit, emphasizing strategic capital allocation to maximize returns while managing risk exposure. High frequency trading (HFT) allocates capital to execute large volumes of orders at extremely high speeds, leveraging sophisticated algorithms and low latency systems to capitalize on minute price discrepancies. Discover more about the nuances of capital deployment strategies in proprietary versus high frequency trading.
Algorithmic Strategies
Proprietary trading employs advanced algorithmic strategies to execute large-volume trades aiming for significant returns by capitalizing on market inefficiencies. High frequency trading utilizes ultra-fast algorithms and low-latency systems to conduct thousands of trades per second, profiting from minimal price fluctuations. Explore how these algorithmic strategies differentiate proprietary trading and high frequency trading in detail.
Trade Execution Speed
Proprietary trading involves firms using their own capital to trade financial instruments aiming for direct market profits, with execution speed varying based on strategy and technology. High-frequency trading (HFT) relies on ultra-fast algorithms and low-latency infrastructure to execute thousands of orders per second, capitalizing on minimal price discrepancies. Explore the detailed differences in execution speed and technological requirements between proprietary and high-frequency trading to enhance your trading insights.
Source and External Links
Proprietary trading - Wikipedia - Proprietary trading, or prop trading, is when a firm trades financial instruments like stocks, bonds, or derivatives using its own money to make a profit rather than trading on behalf of clients, often employing various strategies such as arbitrage or global macro trading.
Proprietary Trading - What is Prop Trading & How Does It Work? - Prop trading occurs when banks or firms use their own capital to trade in stocks, derivatives, and commodities to earn profits directly, using sophisticated software and market information, and is one of the more profitable yet riskier operations regulated by rules like the Volcker Rule.
Prop Trading Firms: Here's How They Work - Nasdaq - Proprietary trading firms are specialized entities that deploy their own capital across various markets aiming for direct profit, supporting market liquidity through trading a range of assets like equities, forex, and crypto, and distributing capital to skilled traders in a performance-driven environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com