Quantitative sentiment analysis leverages natural language processing to interpret market sentiment from news, social media, and financial reports, providing real-time insights into investor behavior. Statistical arbitrage employs mathematical models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies across correlated securities, relying on historical data and mean-reversion principles. Discover how integrating these strategies can enhance trading performance and risk management.
Why it is important
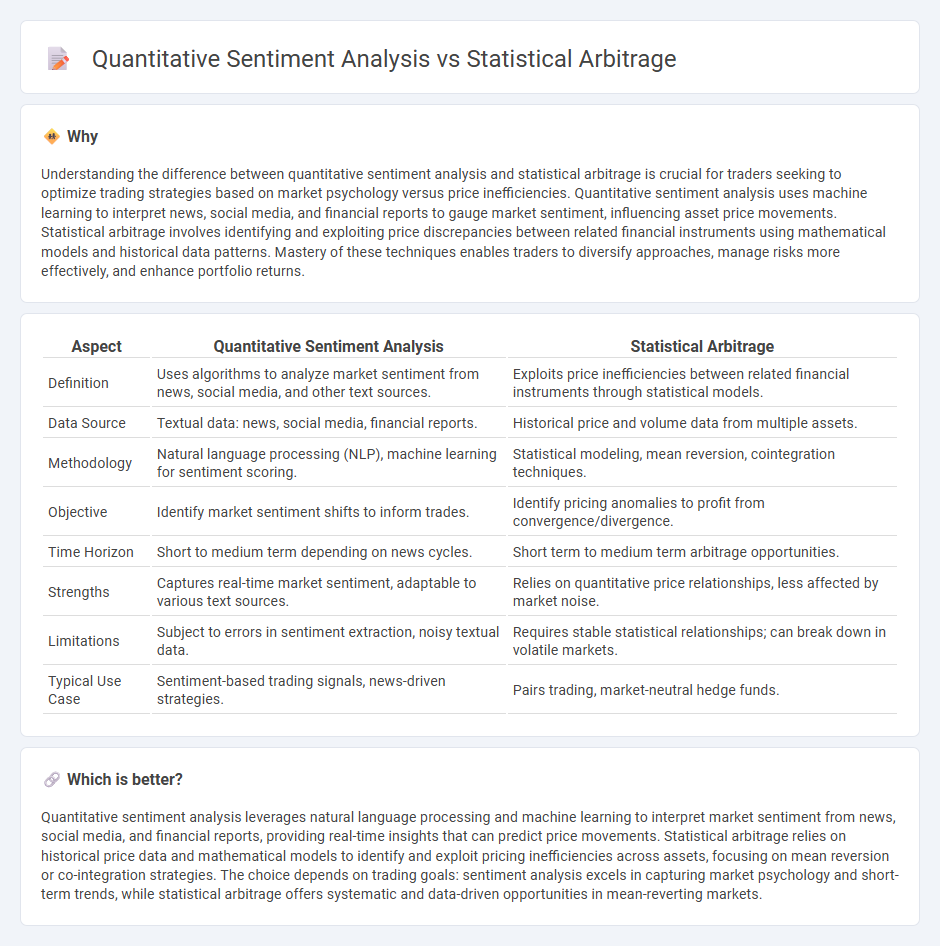
Understanding the difference between quantitative sentiment analysis and statistical arbitrage is crucial for traders seeking to optimize trading strategies based on market psychology versus price inefficiencies. Quantitative sentiment analysis uses machine learning to interpret news, social media, and financial reports to gauge market sentiment, influencing asset price movements. Statistical arbitrage involves identifying and exploiting price discrepancies between related financial instruments using mathematical models and historical data patterns. Mastery of these techniques enables traders to diversify approaches, manage risks more effectively, and enhance portfolio returns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Sentiment Analysis | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses algorithms to analyze market sentiment from news, social media, and other text sources. | Exploits price inefficiencies between related financial instruments through statistical models. |
| Data Source | Textual data: news, social media, financial reports. | Historical price and volume data from multiple assets. |
| Methodology | Natural language processing (NLP), machine learning for sentiment scoring. | Statistical modeling, mean reversion, cointegration techniques. |
| Objective | Identify market sentiment shifts to inform trades. | Identify pricing anomalies to profit from convergence/divergence. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term depending on news cycles. | Short term to medium term arbitrage opportunities. |
| Strengths | Captures real-time market sentiment, adaptable to various text sources. | Relies on quantitative price relationships, less affected by market noise. |
| Limitations | Subject to errors in sentiment extraction, noisy textual data. | Requires stable statistical relationships; can break down in volatile markets. |
| Typical Use Case | Sentiment-based trading signals, news-driven strategies. | Pairs trading, market-neutral hedge funds. |
Which is better?
Quantitative sentiment analysis leverages natural language processing and machine learning to interpret market sentiment from news, social media, and financial reports, providing real-time insights that can predict price movements. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical price data and mathematical models to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies across assets, focusing on mean reversion or co-integration strategies. The choice depends on trading goals: sentiment analysis excels in capturing market psychology and short-term trends, while statistical arbitrage offers systematic and data-driven opportunities in mean-reverting markets.
Connection
Quantitative sentiment analysis transforms unstructured market data into measurable signals that feed statistical arbitrage models, enhancing predictive accuracy in trading strategies. Statistical arbitrage leverages these sentiment-driven insights to identify mispricings and execute high-frequency trades with optimized risk-reward profiles. Integrating real-time sentiment scores into algorithmic frameworks accelerates decision-making and improves portfolio returns in volatile financial markets.
Key Terms
Statistical Arbitrage:
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and mathematical models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies across securities, often using mean reversion and correlation strategies. It relies on high-frequency trading algorithms and large datasets to execute numerous trades with minimal risk and high precision. Explore deeper into statistical arbitrage methodologies and their impact on market efficiency.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage relies on exploiting mean reversion by identifying price deviations from historical averages, using quantitative models to trade asset pairs or portfolios for profit. Quantitative sentiment analysis enhances mean reversion strategies by integrating natural language processing on financial news and social media to gauge market sentiment shifts before prices revert. Discover how combining mean reversion with sentiment data can optimize trading strategies and risk management.
Pair Trading
Pair trading in statistical arbitrage exploits mean-reverting price relationships between correlated asset pairs, using historical price data and statistical models like cointegration or correlation metrics to identify trading opportunities. Quantitative sentiment analysis enhances pair trading by incorporating real-time market sentiment derived from news, social media, and financial reports through natural language processing, enabling adaptive strategies based on investor behavior insights. Discover how integrating statistical arbitrage with sentiment-driven signals can optimize pair trading performance and risk management.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - WunderTrading - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral quantitative trading strategy that exploits pricing discrepancies between correlated securities using complex algorithms, aiming for consistent returns through mean reversion and hedging market risk.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage (Stat Arb) involves short-term trading of diversified portfolios using mean reversion and statistical/econometric models, often automated, to profit from small pricing inefficiencies in beta-neutral, quantitative approaches.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? | CQF - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative trading strategy exploiting pricing deviations from expected statistical relationships between related securities, widely used in quantitative finance for systematic trading.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com