Delta-neutral strategies involve creating a portfolio where the overall delta value is zero, minimizing exposure to price movements in the underlying asset and reducing risk. Buy-and-hold strategies focus on long-term investment, holding assets regardless of short-term market fluctuations to benefit from potential appreciation and dividends. Explore the advantages and applications of each approach to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
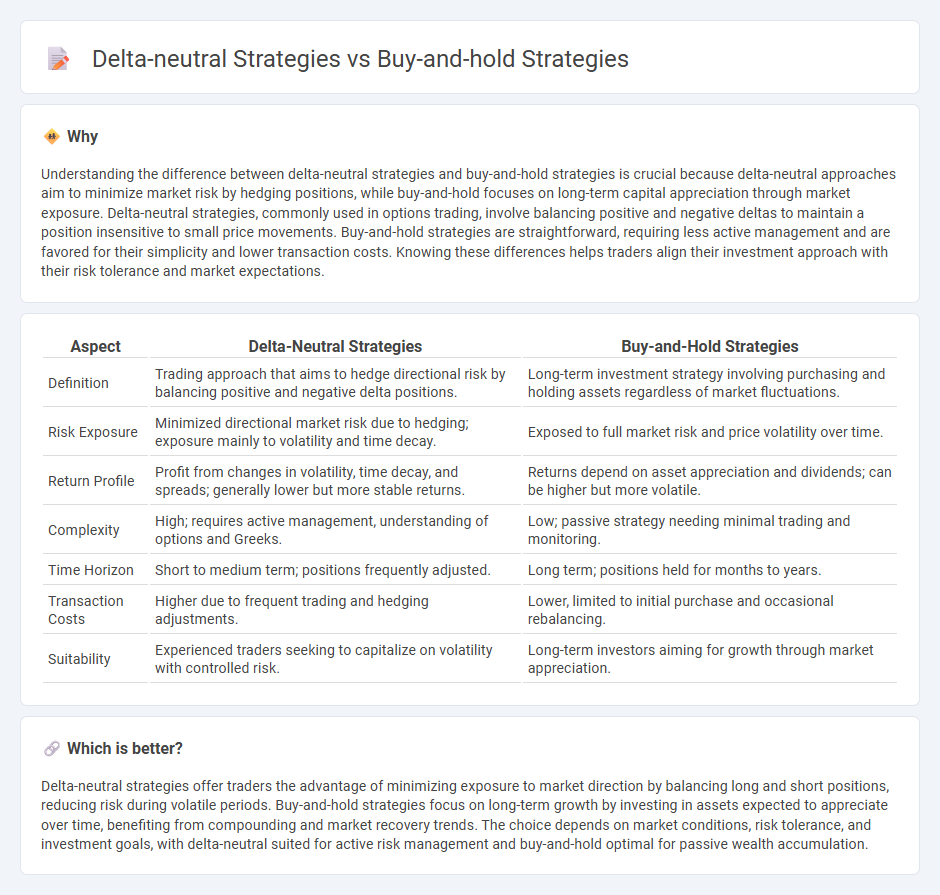
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral strategies and buy-and-hold strategies is crucial because delta-neutral approaches aim to minimize market risk by hedging positions, while buy-and-hold focuses on long-term capital appreciation through market exposure. Delta-neutral strategies, commonly used in options trading, involve balancing positive and negative deltas to maintain a position insensitive to small price movements. Buy-and-hold strategies are straightforward, requiring less active management and are favored for their simplicity and lower transaction costs. Knowing these differences helps traders align their investment approach with their risk tolerance and market expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Buy-and-Hold Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach that aims to hedge directional risk by balancing positive and negative delta positions. | Long-term investment strategy involving purchasing and holding assets regardless of market fluctuations. |
| Risk Exposure | Minimized directional market risk due to hedging; exposure mainly to volatility and time decay. | Exposed to full market risk and price volatility over time. |
| Return Profile | Profit from changes in volatility, time decay, and spreads; generally lower but more stable returns. | Returns depend on asset appreciation and dividends; can be higher but more volatile. |
| Complexity | High; requires active management, understanding of options and Greeks. | Low; passive strategy needing minimal trading and monitoring. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term; positions frequently adjusted. | Long term; positions held for months to years. |
| Transaction Costs | Higher due to frequent trading and hedging adjustments. | Lower, limited to initial purchase and occasional rebalancing. |
| Suitability | Experienced traders seeking to capitalize on volatility with controlled risk. | Long-term investors aiming for growth through market appreciation. |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies offer traders the advantage of minimizing exposure to market direction by balancing long and short positions, reducing risk during volatile periods. Buy-and-hold strategies focus on long-term growth by investing in assets expected to appreciate over time, benefiting from compounding and market recovery trends. The choice depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and investment goals, with delta-neutral suited for active risk management and buy-and-hold optimal for passive wealth accumulation.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies and buy-and-hold strategies both aim to manage risk and achieve consistent returns, but they do so through different mechanisms. Delta-neutral strategies involve balancing positions to offset price movements in underlying assets, minimizing directional risk, whereas buy-and-hold strategies focus on long-term appreciation by maintaining ownership of securities regardless of short-term volatility. Combining these approaches can enhance portfolio stability by integrating active risk management with passive investment growth.
Key Terms
Time Horizon
Buy-and-hold strategies prioritize long-term investment horizons, relying on stock appreciation and dividend income over extended periods to build wealth. Delta-neutral strategies focus on short to medium-term time frames, aiming to profit from minimal market movement and volatility while hedging against directional risk. Explore deeper insights on how time horizon impacts these contrasting investment approaches.
Risk Exposure
Buy-and-hold strategies maintain long-term market exposure by holding assets through fluctuations, risking market volatility and systemic downturns. Delta-neutral strategies aim to minimize directional risk by balancing options and underlying assets to achieve near-zero net delta, reducing exposure to price movements but requiring active management. Explore more about optimizing risk exposure between these approaches to enhance portfolio resilience.
Rebalancing
Buy-and-hold strategies require minimal rebalancing as positions are maintained for the long term, emphasizing steady growth and passive income through dividends or capital appreciation. Delta-neutral strategies involve frequent rebalancing to maintain a market-neutral position, minimizing directional risk by adjusting options and underlying assets dynamically. Explore more about the distinct rebalancing techniques to optimize portfolio performance in both strategies.
Source and External Links
Buy and Hold Strategy - What Is It, Examples, Advantages - The buy-and-hold strategy involves holding assets for a long term, typically starting from five years, to benefit from price rises and dividends, offering advantages like reduced transaction costs and stress, but it carries risks such as premature asset sales and misselection of investments.
Buy and Hold: Definition, Advantages, Risks, How to Build One - This strategy entails purchasing securities to keep for years or decades, emphasizing strong fundamentals and growth potential with the goal of capital appreciation, allowing investors to withstand market volatility without frequent trading.
Buy and Hold Strategy: A Simple Way to Invest | SoFi - Buy and hold helps protect investors from emotional decision-making and market timing, promoting steady investing through approaches like dollar-cost averaging, which reduces temptation to react to short-term market fluctuations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com