Quantitative momentum strategies in trading focus on identifying securities exhibiting strong price trends using mathematical models and historical price data to forecast future performance. Statistical arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between correlated assets by applying complex statistical methods and high-frequency trading algorithms to capitalize on short-term market anomalies. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these sophisticated techniques can enhance your trading portfolio.
Why it is important
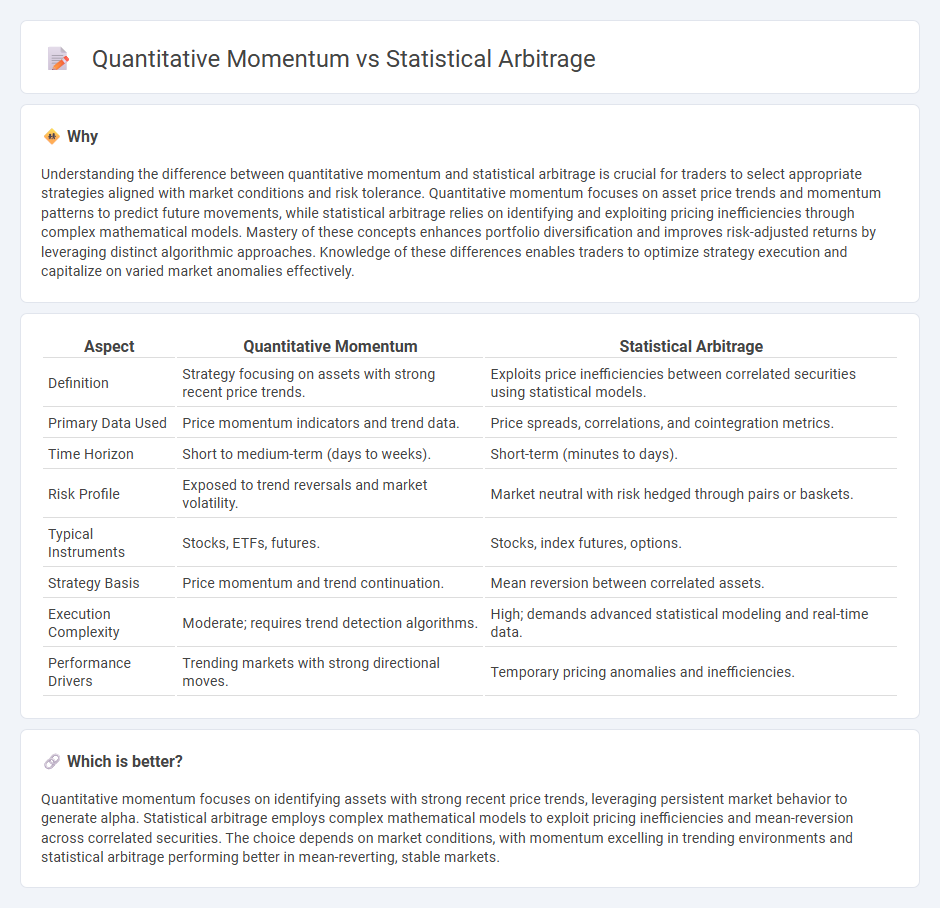
Understanding the difference between quantitative momentum and statistical arbitrage is crucial for traders to select appropriate strategies aligned with market conditions and risk tolerance. Quantitative momentum focuses on asset price trends and momentum patterns to predict future movements, while statistical arbitrage relies on identifying and exploiting pricing inefficiencies through complex mathematical models. Mastery of these concepts enhances portfolio diversification and improves risk-adjusted returns by leveraging distinct algorithmic approaches. Knowledge of these differences enables traders to optimize strategy execution and capitalize on varied market anomalies effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Momentum | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy focusing on assets with strong recent price trends. | Exploits price inefficiencies between correlated securities using statistical models. |
| Primary Data Used | Price momentum indicators and trend data. | Price spreads, correlations, and cointegration metrics. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term (days to weeks). | Short-term (minutes to days). |
| Risk Profile | Exposed to trend reversals and market volatility. | Market neutral with risk hedged through pairs or baskets. |
| Typical Instruments | Stocks, ETFs, futures. | Stocks, index futures, options. |
| Strategy Basis | Price momentum and trend continuation. | Mean reversion between correlated assets. |
| Execution Complexity | Moderate; requires trend detection algorithms. | High; demands advanced statistical modeling and real-time data. |
| Performance Drivers | Trending markets with strong directional moves. | Temporary pricing anomalies and inefficiencies. |
Which is better?
Quantitative momentum focuses on identifying assets with strong recent price trends, leveraging persistent market behavior to generate alpha. Statistical arbitrage employs complex mathematical models to exploit pricing inefficiencies and mean-reversion across correlated securities. The choice depends on market conditions, with momentum excelling in trending environments and statistical arbitrage performing better in mean-reverting, stable markets.
Connection
Quantitative momentum strategies identify assets with strong price trends using mathematical models, while statistical arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies by analyzing historical price relationships and mean reversion patterns. Both approaches rely on rigorous statistical analysis and algorithmic trading to detect and capitalize on market anomalies. Combining quantitative momentum with statistical arbitrage enhances portfolio diversification and improves risk-adjusted returns through complementary trading signals.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies through mean-reversion strategies, analyzing historical price data and correlations to generate alpha in equity markets. This approach uses sophisticated quantitative models and high-frequency trading algorithms to identify mispricings across large portfolios while minimizing risk exposure. Explore in-depth insights and performance metrics to understand the mechanics of statistical arbitrage.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage strategies capitalize on mean reversion by identifying price discrepancies and expecting asset prices to revert to their historical averages, while quantitative momentum strategies typically focus on persistent trends rather than reversals. Mean reversion techniques analyze price series deviations using metrics such as z-scores and Bollinger Bands to exploit short-term mispricings in equities or ETFs. Explore detailed methodologies and performance comparisons to understand which strategy aligns with your investment objectives.
Pair Trading
Statistical arbitrage leverages mean-reversion techniques to exploit price inefficiencies between paired assets, while quantitative momentum focuses on capitalizing on trending price movements identified through algorithmic models. Pair trading, a common statistical arbitrage strategy, identifies correlated securities and executes simultaneous long and short positions to hedge market risk. Explore detailed comparisons, performance metrics, and strategy implementations to deepen your understanding of these approaches.
Source and External Links
The Power of Statistical Arbitrage in Finance - Statistical arbitrage ("stat arb") is a quantitative trading strategy that exploits temporary price discrepancies between related financial instruments based on mean reversion, using statistical models for data analysis, model development, and trade execution.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage involves short-term, beta-neutral trading strategies over broadly diversified portfolios using mean reversion and other statistical techniques, often automated for high portfolio turnover and used widely by hedge funds and investment banks.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative trading approach in finance that exploits pricing deviations and inefficiencies between securities, relying on statistical and mathematical methods to generate trading signals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com