High frequency trading bots execute rapid, algorithm-driven trades exploiting tiny price discrepancies within milliseconds, leveraging advanced technology and minimal latency. Statistical arbitrage relies on mathematical models to identify and capitalize on price inefficiencies across related securities, focusing on mean-reversion and correlation patterns over longer time frames. Explore the distinct strategies and performance metrics behind these trading approaches to optimize your investment tactics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between high-frequency trading bots and statistical arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies, as high-frequency bots execute thousands of orders per second to exploit minute price discrepancies, while statistical arbitrage uses complex mathematical models to identify and capitalize on pricing inefficiencies over a longer time. This knowledge helps traders tailor risk management and technological investments to their specific trading goals. Choosing the appropriate approach can significantly impact profitability and market impact. Expertise in these methods improves decision-making in fast-paced financial markets.
Comparison Table
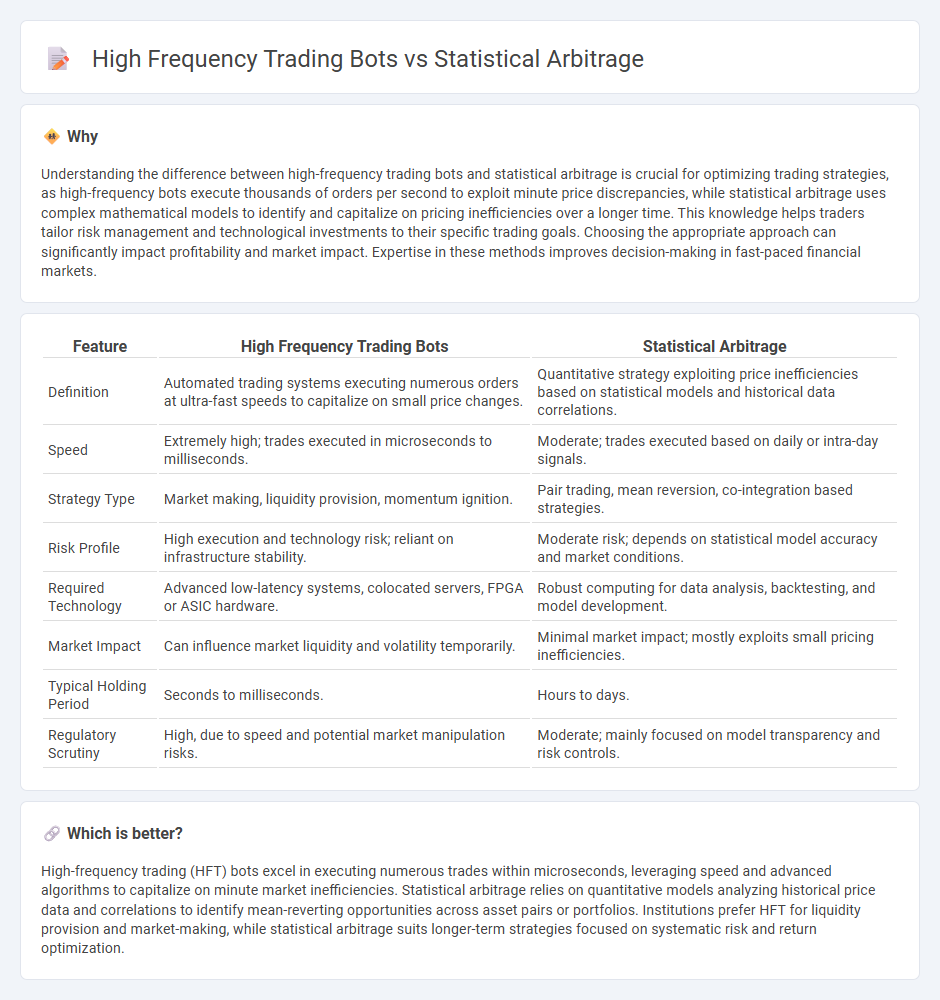
| Feature | High Frequency Trading Bots | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading systems executing numerous orders at ultra-fast speeds to capitalize on small price changes. | Quantitative strategy exploiting price inefficiencies based on statistical models and historical data correlations. |
| Speed | Extremely high; trades executed in microseconds to milliseconds. | Moderate; trades executed based on daily or intra-day signals. |
| Strategy Type | Market making, liquidity provision, momentum ignition. | Pair trading, mean reversion, co-integration based strategies. |
| Risk Profile | High execution and technology risk; reliant on infrastructure stability. | Moderate risk; depends on statistical model accuracy and market conditions. |
| Required Technology | Advanced low-latency systems, colocated servers, FPGA or ASIC hardware. | Robust computing for data analysis, backtesting, and model development. |
| Market Impact | Can influence market liquidity and volatility temporarily. | Minimal market impact; mostly exploits small pricing inefficiencies. |
| Typical Holding Period | Seconds to milliseconds. | Hours to days. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | High, due to speed and potential market manipulation risks. | Moderate; mainly focused on model transparency and risk controls. |
Which is better?
High-frequency trading (HFT) bots excel in executing numerous trades within microseconds, leveraging speed and advanced algorithms to capitalize on minute market inefficiencies. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models analyzing historical price data and correlations to identify mean-reverting opportunities across asset pairs or portfolios. Institutions prefer HFT for liquidity provision and market-making, while statistical arbitrage suits longer-term strategies focused on systematic risk and return optimization.
Connection
High frequency trading bots utilize statistical arbitrage strategies by rapidly executing trades based on quantitative models that identify pricing inefficiencies across markets. These bots analyze vast datasets in milliseconds to exploit small price discrepancies, ensuring profitable trades before market corrections occur. The synergy between high speed execution and statistical arbitrage algorithms enhances market liquidity while reducing arbitrage opportunities for slower traders.
Key Terms
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage strategies leverage mean reversion principles by identifying price discrepancies and predicting asset prices will revert to their historical averages, whereas high frequency trading bots execute rapid trades based on minimal price movements and market inefficiencies. Mean reversion models in statistical arbitrage analyze historical price data and correlation structures to exploit short-term deviations, aiming for consistent, risk-adjusted returns. Discover how mean reversion underpins these trading techniques and their role in modern quantitative finance.
Latency
Statistical arbitrage strategies rely on historical price patterns and correlations, making latency less critical compared to high frequency trading (HFT) bots that execute trades in milliseconds based on real-time market data. HFT bots demand ultra-low latency infrastructure, including colocated servers and optimized network connections, to capitalize on fleeting price discrepancies before competitors react. Explore advanced latency reduction techniques and their impact on trading performance to gain deeper insights.
Market Microstructure
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and co-integration to identify mean-reverting asset pairs, exploiting pricing inefficiencies in the equity and futures markets. High-frequency trading bots operate on market microstructure by executing rapid order flows, capturing bid-ask spread differentials and reacting to order book dynamics within milliseconds. Explore the intricacies of market microstructure to understand how these trading strategies differ in execution and profitability.
Source and External Links
The Power of Statistical Arbitrage in Finance - PyQuant News - Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models to identify temporary price discrepancies between related financial instruments, exploiting mean reversion principles to generate profits by buying undervalued and selling overvalued assets.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage is a short-term, quantitative trading strategy involving diversified portfolios and mean reversion models, often implemented with automated trading systems to exploit small pricing inefficiencies in many securities simultaneously.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? | CQF - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative strategy that exploits deviations from expected statistical relationships between related securities to capture pricing inefficiencies in financial markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com