Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing fees. Liquidity pools facilitate decentralized trading by aggregating assets, allowing users to trade against pooled funds and earn rewards from transaction fees. Explore the differences and benefits of these key trading mechanisms to optimize your crypto strategy.
Why it is important
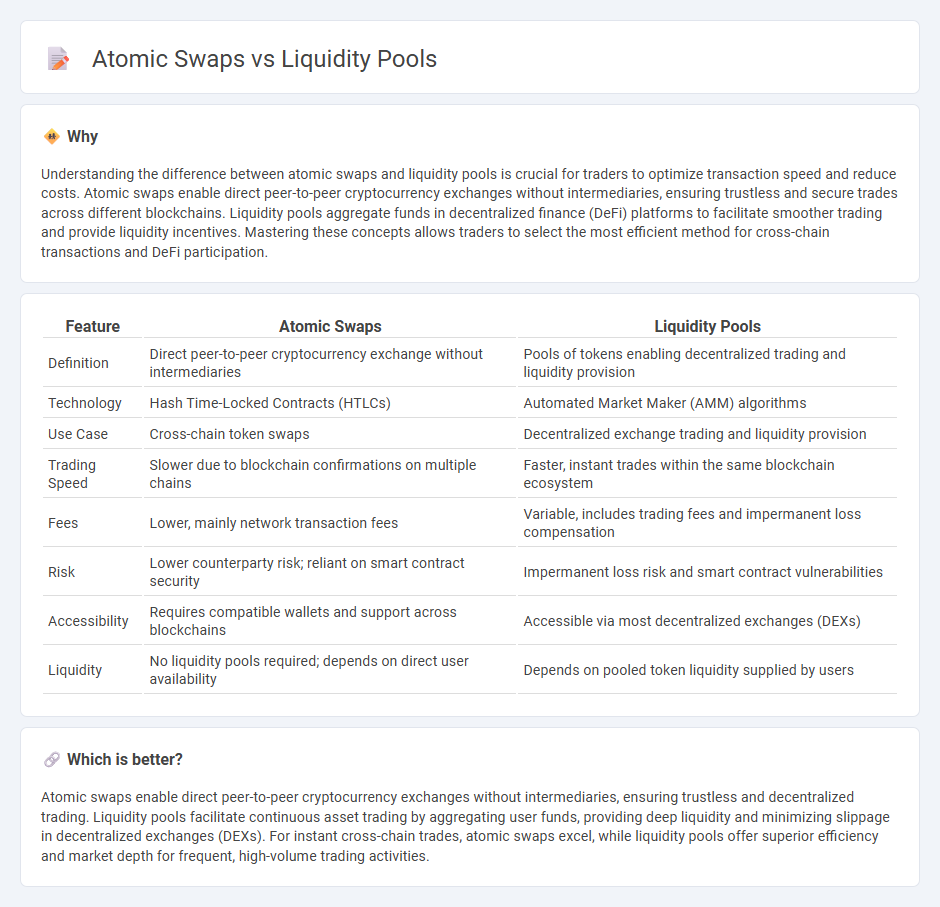
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and liquidity pools is crucial for traders to optimize transaction speed and reduce costs. Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, ensuring trustless and secure trades across different blockchains. Liquidity pools aggregate funds in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to facilitate smoother trading and provide liquidity incentives. Mastering these concepts allows traders to select the most efficient method for cross-chain transactions and DeFi participation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Liquidity Pools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchange without intermediaries | Pools of tokens enabling decentralized trading and liquidity provision |
| Technology | Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) | Automated Market Maker (AMM) algorithms |
| Use Case | Cross-chain token swaps | Decentralized exchange trading and liquidity provision |
| Trading Speed | Slower due to blockchain confirmations on multiple chains | Faster, instant trades within the same blockchain ecosystem |
| Fees | Lower, mainly network transaction fees | Variable, includes trading fees and impermanent loss compensation |
| Risk | Lower counterparty risk; reliant on smart contract security | Impermanent loss risk and smart contract vulnerabilities |
| Accessibility | Requires compatible wallets and support across blockchains | Accessible via most decentralized exchanges (DEXs) |
| Liquidity | No liquidity pools required; depends on direct user availability | Depends on pooled token liquidity supplied by users |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, ensuring trustless and decentralized trading. Liquidity pools facilitate continuous asset trading by aggregating user funds, providing deep liquidity and minimizing slippage in decentralized exchanges (DEXs). For instant cross-chain trades, atomic swaps excel, while liquidity pools offer superior efficiency and market depth for frequent, high-volume trading activities.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, relying on smart contracts to ensure trustless transactions. Liquidity pools provide the necessary token reserves to facilitate these swaps instantly by maintaining a balanced supply of assets. Together, they enhance decentralized trading efficiency by combining secure, cross-chain swaps with seamless asset availability.
Key Terms
Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
Liquidity pools in decentralized exchanges (DEXs) utilize collective token reserves to enable seamless, automated trading without traditional order books, enhancing market depth and reducing slippage for users. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer token exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, promoting cross-chain interoperability but often facing limitations in speed and complexity. Explore how these mechanisms shape the future of decentralized trading by revolutionizing liquidity and asset exchange.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Liquidity pools in Automated Market Makers (AMMs) enable seamless, decentralized token exchanges by aggregating user funds to provide continuous liquidity without relying on traditional order books. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trades across different blockchains, eliminating intermediaries but often facing limitations in scalability and liquidity depth compared to AMMs. Explore the detailed mechanics and efficiency comparisons between liquidity pools and atomic swaps to understand their impact on decentralized finance.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Liquidity pools enable decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) trading by aggregating assets to facilitate instant token swaps without relying on order books, increasing market liquidity and reducing slippage. Atomic swaps provide direct P2P exchanges of cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring trustless and secure transactions via smart contracts. Explore the fundamental differences between liquidity pools and atomic swaps to understand their roles in enhancing decentralized P2P trading.
Source and External Links
Liquidity Pools Explained: How They Work, Key Risks & Security - Liquidity pools are collections of cryptocurrency tokens locked in smart contracts that enable decentralized trading, price discovery, and yield farming, with various types like two-token, stablecoin, multi-asset, and concentrated pools, each offering unique benefits and risks.
Liquidity Pools for Beginners: DeFi 101 - Liquidity pools allow anyone to become a liquidity provider by depositing assets into a pool for a trading pair, earning fees from trades and enabling efficient, decentralized trading without the need for large trading volumes or intermediaries.
The role of liquidity pools in cryptocurrency markets - Liquidity pools are essential for decentralized exchanges (DEXs), allowing users to trade directly against pooled assets via smart contracts while earning passive income, but they come with risks such as impermanent loss and potential smart contract vulnerabilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com