Perpetual swaps and CFDs (Contracts for Difference) are popular derivatives used in trading to speculate on asset price movements without owning the underlying asset. Perpetual swaps offer continuous contract durations with no expiration dates, often featuring leverage and funding fees, while CFDs provide flexible contract terms and allow traders to profit from price fluctuations across various markets. Explore the differences in structure, risk, and strategy between perpetual swaps and CFDs to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
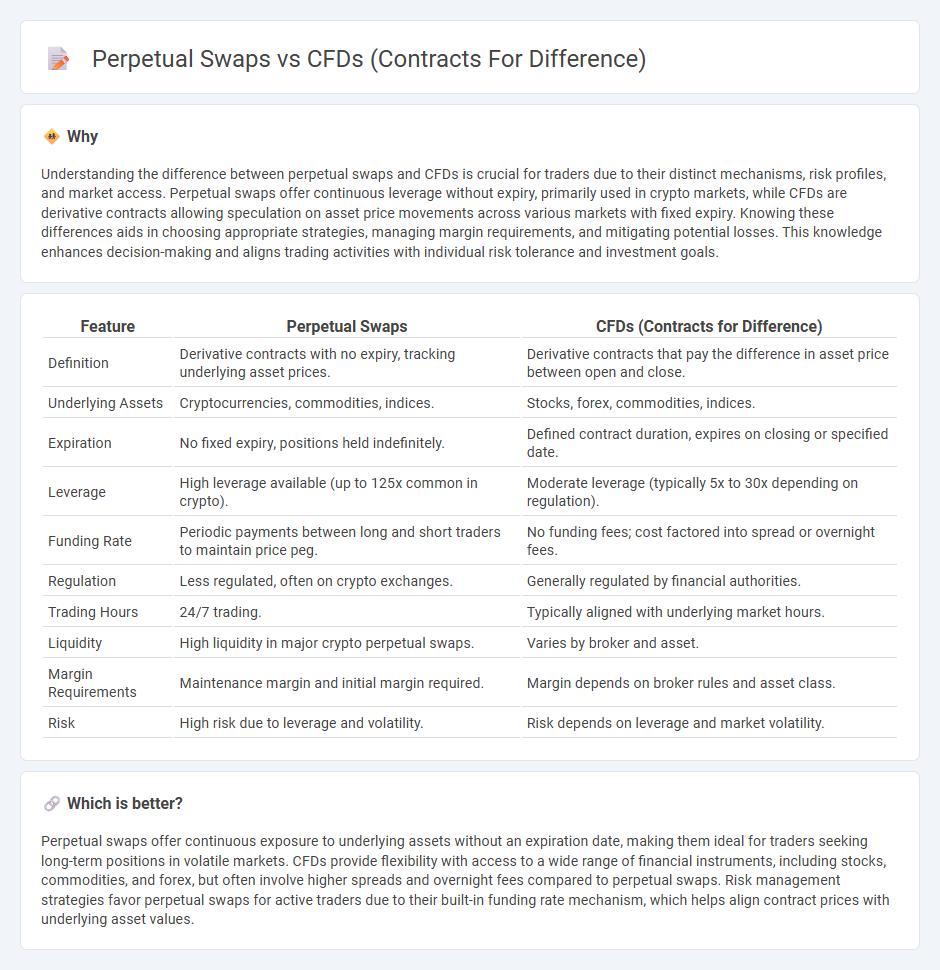
Understanding the difference between perpetual swaps and CFDs is crucial for traders due to their distinct mechanisms, risk profiles, and market access. Perpetual swaps offer continuous leverage without expiry, primarily used in crypto markets, while CFDs are derivative contracts allowing speculation on asset price movements across various markets with fixed expiry. Knowing these differences aids in choosing appropriate strategies, managing margin requirements, and mitigating potential losses. This knowledge enhances decision-making and aligns trading activities with individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Perpetual Swaps | CFDs (Contracts for Difference) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivative contracts with no expiry, tracking underlying asset prices. | Derivative contracts that pay the difference in asset price between open and close. |
| Underlying Assets | Cryptocurrencies, commodities, indices. | Stocks, forex, commodities, indices. |
| Expiration | No fixed expiry, positions held indefinitely. | Defined contract duration, expires on closing or specified date. |
| Leverage | High leverage available (up to 125x common in crypto). | Moderate leverage (typically 5x to 30x depending on regulation). |
| Funding Rate | Periodic payments between long and short traders to maintain price peg. | No funding fees; cost factored into spread or overnight fees. |
| Regulation | Less regulated, often on crypto exchanges. | Generally regulated by financial authorities. |
| Trading Hours | 24/7 trading. | Typically aligned with underlying market hours. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity in major crypto perpetual swaps. | Varies by broker and asset. |
| Margin Requirements | Maintenance margin and initial margin required. | Margin depends on broker rules and asset class. |
| Risk | High risk due to leverage and volatility. | Risk depends on leverage and market volatility. |
Which is better?
Perpetual swaps offer continuous exposure to underlying assets without an expiration date, making them ideal for traders seeking long-term positions in volatile markets. CFDs provide flexibility with access to a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, commodities, and forex, but often involve higher spreads and overnight fees compared to perpetual swaps. Risk management strategies favor perpetual swaps for active traders due to their built-in funding rate mechanism, which helps align contract prices with underlying asset values.
Connection
Perpetual swaps and CFDs (Contracts for Difference) are connected through their function as derivative trading instruments that allow traders to speculate on asset price movements without owning the underlying assets. Both products offer leverage and the ability to go long or short, enabling exposure to markets like cryptocurrencies, stocks, and commodities with minimal capital. The key difference lies in perpetual swaps' lack of expiration dates and funding rate mechanisms, while CFDs typically have defined contract periods and may incorporate dividends or rollover fees.
Key Terms
Leverage
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) and perpetual swaps both offer leveraged trading, allowing investors to control larger positions with smaller capital outlays. CFDs typically provide flexible leverage ratios depending on the asset class and broker policies, while perpetual swaps commonly offer higher, more standardized leverage, especially in cryptocurrency markets. Explore more to understand how leverage impacts risk management and trading strategies in these derivative instruments.
Expiry/Settlement
CFDs (Contracts for Difference) do not have a fixed expiry date, allowing traders to hold positions indefinitely while paying or receiving financing fees based on the position size. Perpetual swaps also lack expiry dates but feature an automatic settlement mechanism through funding rates exchanged between long and short positions, ensuring the contract price closely tracks the underlying asset. Discover more about the nuances of expiry and settlement to optimize your trading strategy.
Funding Fees
CFDs (Contracts for Difference) do not typically involve funding fees, allowing traders to hold positions without ongoing costs related to interest payments. Perpetual swaps include funding fees, which are periodic payments exchanged between long and short positions to anchor the contract price to the underlying asset's spot price. Explore further to understand how funding fees impact the overall cost and strategy in trading these derivatives.
Source and External Links
Contract for Difference (CFD) - Corporate Finance Institute - A CFD is a contract enabling two parties to trade on financial instruments based on the price difference between entry and closing prices, allowing leverage, flexibility, and trading without owning the underlying asset.
Contracts for Difference (CFD) - MFSA - CFDs are leveraged agreements between a buyer and seller to exchange the price difference of an asset and allow taking long or short positions without owning the underlying asset.
Contract for difference - Wikipedia - CFDs are financial agreements where two parties exchange the difference between the current asset value and its value at contract initiation, popularized in retail trading since the late 1990s.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com