Algorithmic arbitrage employs automated trading systems to exploit price discrepancies across markets with precise, rule-based strategies, often executing high-frequency trades. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models and historical data correlations to identify and capitalize on price inefficiencies, typically involving pairs or baskets of securities. Explore these methodologies to understand how advanced analytics shape modern trading strategies.
Why it is important
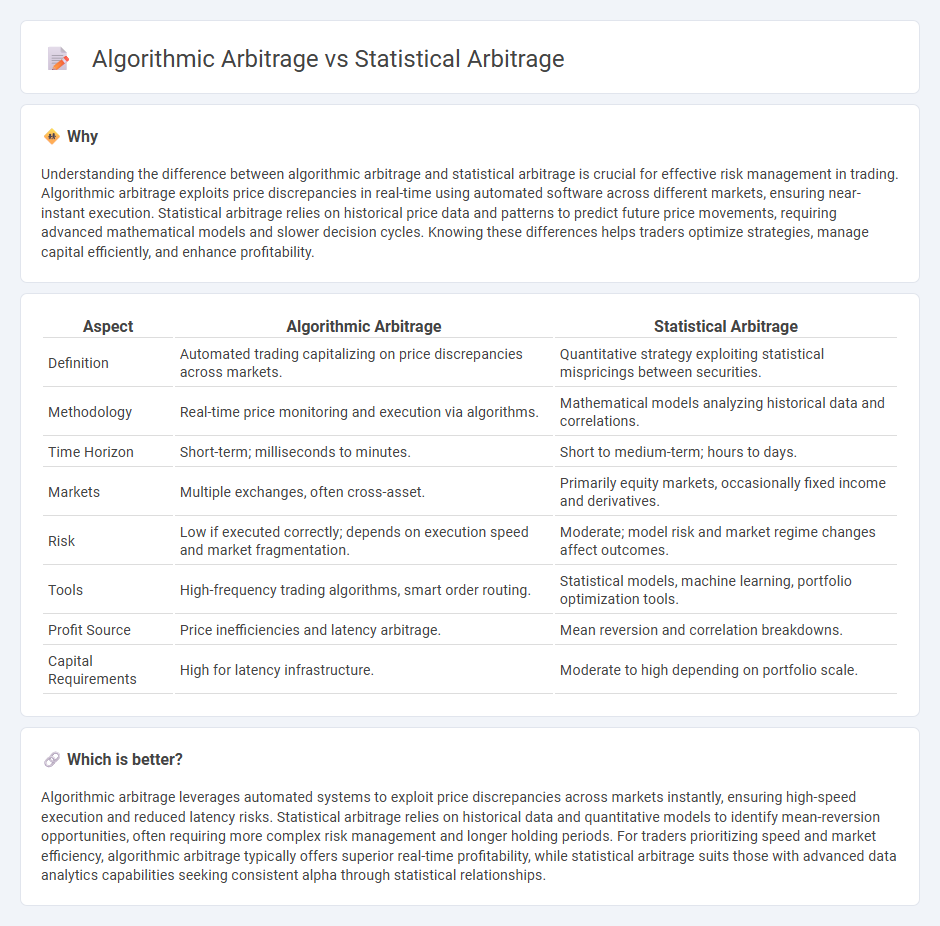
Understanding the difference between algorithmic arbitrage and statistical arbitrage is crucial for effective risk management in trading. Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies in real-time using automated software across different markets, ensuring near-instant execution. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical price data and patterns to predict future price movements, requiring advanced mathematical models and slower decision cycles. Knowing these differences helps traders optimize strategies, manage capital efficiently, and enhance profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Arbitrage | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated trading capitalizing on price discrepancies across markets. | Quantitative strategy exploiting statistical mispricings between securities. |
| Methodology | Real-time price monitoring and execution via algorithms. | Mathematical models analyzing historical data and correlations. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term; milliseconds to minutes. | Short to medium-term; hours to days. |
| Markets | Multiple exchanges, often cross-asset. | Primarily equity markets, occasionally fixed income and derivatives. |
| Risk | Low if executed correctly; depends on execution speed and market fragmentation. | Moderate; model risk and market regime changes affect outcomes. |
| Tools | High-frequency trading algorithms, smart order routing. | Statistical models, machine learning, portfolio optimization tools. |
| Profit Source | Price inefficiencies and latency arbitrage. | Mean reversion and correlation breakdowns. |
| Capital Requirements | High for latency infrastructure. | Moderate to high depending on portfolio scale. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic arbitrage leverages automated systems to exploit price discrepancies across markets instantly, ensuring high-speed execution and reduced latency risks. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical data and quantitative models to identify mean-reversion opportunities, often requiring more complex risk management and longer holding periods. For traders prioritizing speed and market efficiency, algorithmic arbitrage typically offers superior real-time profitability, while statistical arbitrage suits those with advanced data analytics capabilities seeking consistent alpha through statistical relationships.
Connection
Algorithmic arbitrage and statistical arbitrage both leverage advanced computational models to exploit price inefficiencies across financial markets, enhancing trade execution speed and accuracy. Algorithmic arbitrage automates the identification and execution of arbitrage opportunities by processing real-time market data, while statistical arbitrage employs quantitative methods and historical price patterns to predict price movements and guide automated trades. Together, they integrate data-driven strategies and automation to optimize profitability in high-frequency trading environments.
Key Terms
Statistical arbitrage:
Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies between related financial instruments based on historical price data and statistical correlations. It relies on mean reversion strategies and complex mathematical algorithms to execute high-frequency trades, balancing risk through diversified portfolios. Explore deeper insights into statistical arbitrage strategies and their applications to enhance your trading knowledge.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage relies on mean reversion by identifying pricing inefficiencies through historical price relationships and exploiting temporary deviations expected to revert to the mean. Algorithmic arbitrage employs automated trading algorithms to execute mean reversion strategies at high speed and scale, leveraging advanced quantitative models and real-time data analysis. Explore the differences in strategy implementation and technology to understand which approach suits your trading goals best.
Pair Trading
Statistical arbitrage, especially in pair trading, relies on identifying historically correlated asset pairs whose price divergences are expected to revert to the mean, exploiting temporary mispricings using statistical models like cointegration and mean reversion. Algorithmic arbitrage automates this process through predefined algorithms that execute trades at high speeds to capture small price discrepancies across markets or securities. Explore deeper insights into how statistical and algorithmic approaches enhance pair trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral quantitative trading strategy that exploits pricing discrepancies between related securities via complex algorithms and mean reversion, aiming for consistent returns while managing risk through simultaneous long and short positions.
Statistical arbitrage - Statistical arbitrage (StatArb) involves using mean reversion models over diversified portfolios held for short durations, relying on statistical and econometric techniques to generate contrarian trading signals with high portfolio turnover and automated execution.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative strategy in finance that capitalizes on pricing deviations using data-driven models and automated trading systems to exploit temporary market inefficiencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com