Microstructure trading focuses on analyzing the detailed mechanisms of market operations, such as order flow, bid-ask spreads, and trade execution to capitalize on short-term price movements. Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models and historical price data to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies between related securities over various time frames. Discover the key strategies and differences between microstructure trading and statistical arbitrage to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
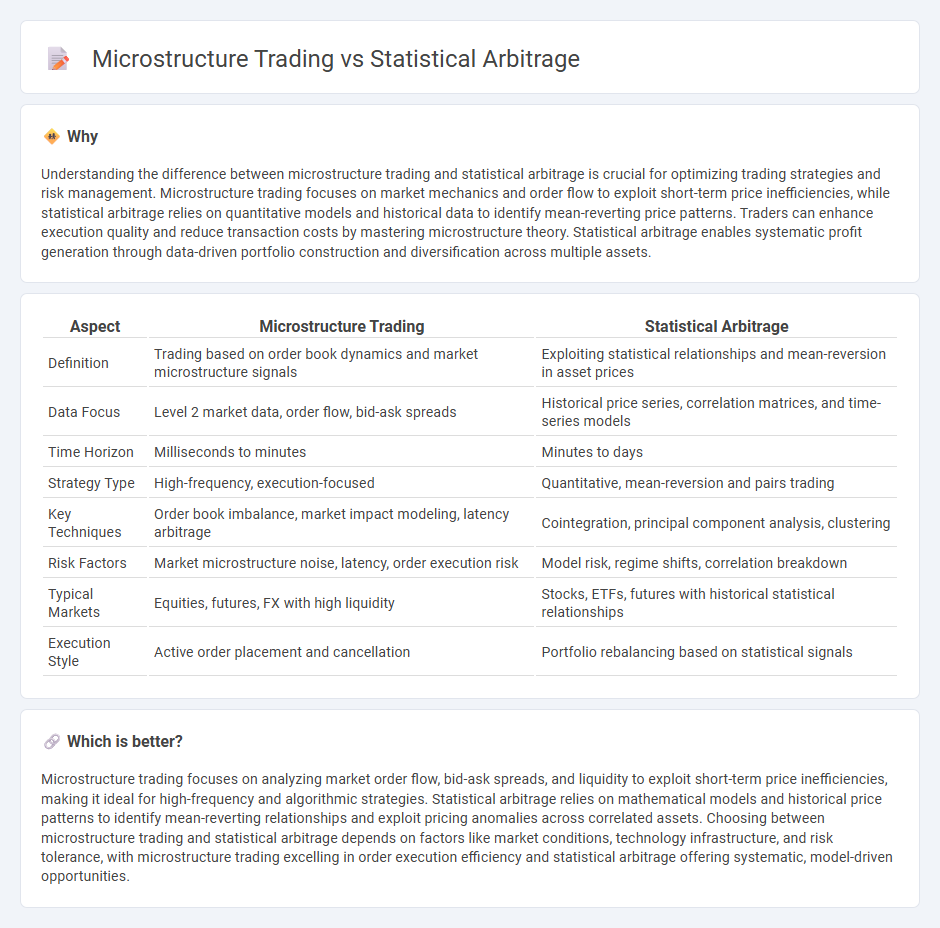
Understanding the difference between microstructure trading and statistical arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and risk management. Microstructure trading focuses on market mechanics and order flow to exploit short-term price inefficiencies, while statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models and historical data to identify mean-reverting price patterns. Traders can enhance execution quality and reduce transaction costs by mastering microstructure theory. Statistical arbitrage enables systematic profit generation through data-driven portfolio construction and diversification across multiple assets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Trading | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading based on order book dynamics and market microstructure signals | Exploiting statistical relationships and mean-reversion in asset prices |
| Data Focus | Level 2 market data, order flow, bid-ask spreads | Historical price series, correlation matrices, and time-series models |
| Time Horizon | Milliseconds to minutes | Minutes to days |
| Strategy Type | High-frequency, execution-focused | Quantitative, mean-reversion and pairs trading |
| Key Techniques | Order book imbalance, market impact modeling, latency arbitrage | Cointegration, principal component analysis, clustering |
| Risk Factors | Market microstructure noise, latency, order execution risk | Model risk, regime shifts, correlation breakdown |
| Typical Markets | Equities, futures, FX with high liquidity | Stocks, ETFs, futures with historical statistical relationships |
| Execution Style | Active order placement and cancellation | Portfolio rebalancing based on statistical signals |
Which is better?
Microstructure trading focuses on analyzing market order flow, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity to exploit short-term price inefficiencies, making it ideal for high-frequency and algorithmic strategies. Statistical arbitrage relies on mathematical models and historical price patterns to identify mean-reverting relationships and exploit pricing anomalies across correlated assets. Choosing between microstructure trading and statistical arbitrage depends on factors like market conditions, technology infrastructure, and risk tolerance, with microstructure trading excelling in order execution efficiency and statistical arbitrage offering systematic, model-driven opportunities.
Connection
Microstructure trading focuses on the analysis of market mechanisms and order flow to exploit short-term price inefficiencies. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models to identify mean-reverting price patterns and mispricings, often using high-frequency data derived from microstructure dynamics. The integration of microstructure trading insights enhances statistical arbitrage strategies by improving the precision of signal detection and execution in fragmented markets.
Key Terms
Mean Reversion (Statistical Arbitrage)
Mean Reversion in Statistical Arbitrage exploits price deviations from an asset's historical average, capitalizing on the tendency of prices to revert to their mean over time. In contrast, microstructure trading emphasizes order book dynamics and market micro-movements to identify short-term trading opportunities. Explore deeper differences and strategies within these trading methodologies for optimized market performance.
Order Flow (Microstructure Trading)
Order flow trading, a key aspect of microstructure trading, exploits the detailed dynamics of buy and sell orders within the order book to predict short-term price movements, making it distinct from statistical arbitrage that relies on broader historical price correlations. This approach uses high-frequency data on order placement, cancellation, and execution, emphasizing the granular structure of the market to gain an informational edge. Explore our in-depth analysis to uncover how order flow strategies can outperform traditional statistical models in intraday trading.
Execution Algorithms (Microstructure Trading)
Execution algorithms in microstructure trading optimize trade execution by analyzing real-time market data, order book dynamics, and price fluctuations to minimize market impact and trading costs. Unlike statistical arbitrage, which relies on identifying price inefficiencies across securities, execution algorithms focus on the precise timing and slicing of orders within microseconds to improve transaction quality. Explore how advanced execution algorithms enhance trade efficiency and market liquidity.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral, quantitative trading strategy that exploits price discrepancies between related securities using mathematical models, algorithms, and data analysis to achieve consistent returns by means such as pair trading, basket trading, and mean reversion, while requiring rigorous risk management to mitigate losses from reliance on historical patterns.
Statistical arbitrage - Statistical arbitrage is a short-term trading strategy using mean reversion models on broadly diversified portfolios, often automated to reduce costs, employing statistical and econometric approaches to generate contrarian trading signals by exploiting pricing inefficiencies in a beta-neutral, quantitative manner.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative finance strategy that seeks to profit from pricing deviations between securities through sophisticated quantitative methods and automated trading systems, focusing on extracting alpha from short-term mispricings in financial markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com