Dark pool prints offer traders the ability to execute large orders anonymously, minimizing market impact and revealing limited price information until after trades are completed. High frequency trading relies on advanced algorithms and low latency connections to capitalize on minute price discrepancies within milliseconds, often increasing market liquidity but also contributing to volatility. Explore these trading strategies in depth to understand their influence on modern financial markets.
Why it is important
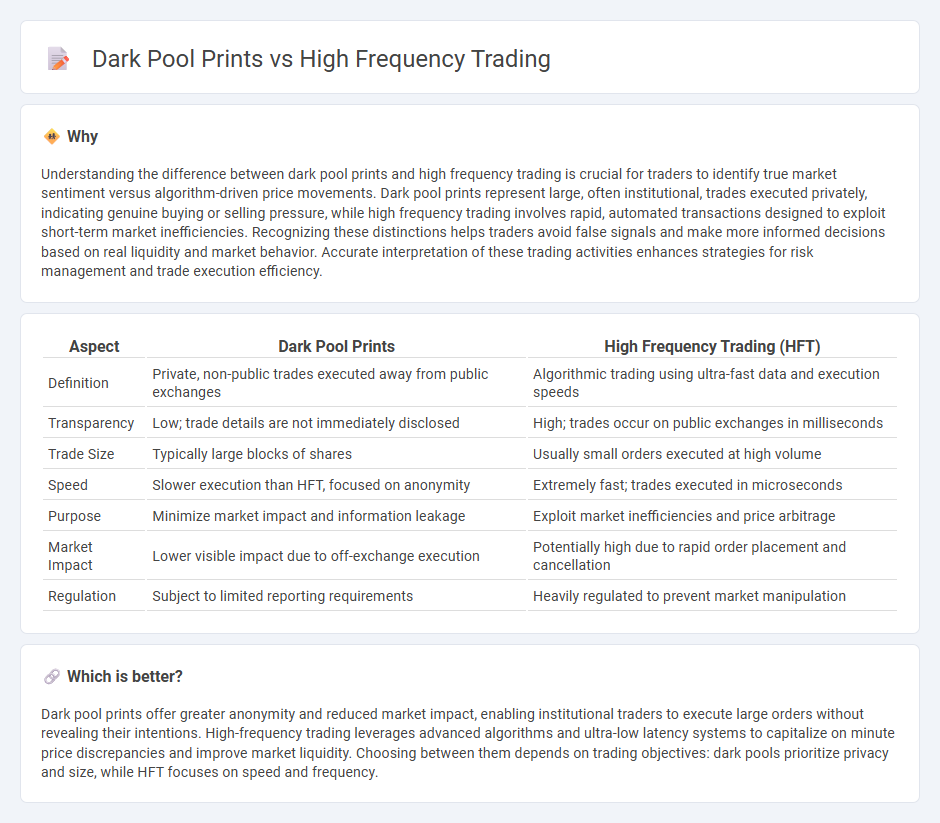
Understanding the difference between dark pool prints and high frequency trading is crucial for traders to identify true market sentiment versus algorithm-driven price movements. Dark pool prints represent large, often institutional, trades executed privately, indicating genuine buying or selling pressure, while high frequency trading involves rapid, automated transactions designed to exploit short-term market inefficiencies. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders avoid false signals and make more informed decisions based on real liquidity and market behavior. Accurate interpretation of these trading activities enhances strategies for risk management and trade execution efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pool Prints | High Frequency Trading (HFT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private, non-public trades executed away from public exchanges | Algorithmic trading using ultra-fast data and execution speeds |
| Transparency | Low; trade details are not immediately disclosed | High; trades occur on public exchanges in milliseconds |
| Trade Size | Typically large blocks of shares | Usually small orders executed at high volume |
| Speed | Slower execution than HFT, focused on anonymity | Extremely fast; trades executed in microseconds |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact and information leakage | Exploit market inefficiencies and price arbitrage |
| Market Impact | Lower visible impact due to off-exchange execution | Potentially high due to rapid order placement and cancellation |
| Regulation | Subject to limited reporting requirements | Heavily regulated to prevent market manipulation |
Which is better?
Dark pool prints offer greater anonymity and reduced market impact, enabling institutional traders to execute large orders without revealing their intentions. High-frequency trading leverages advanced algorithms and ultra-low latency systems to capitalize on minute price discrepancies and improve market liquidity. Choosing between them depends on trading objectives: dark pools prioritize privacy and size, while HFT focuses on speed and frequency.
Connection
Dark pool prints provide large-volume trade data executed privately, which high frequency trading (HFT) algorithms analyze to identify market liquidity and price trends. HFT uses this hidden information to execute rapid trades ahead of public market reactions, capitalizing on the delayed price impact of dark pool transactions. This synergy enhances market efficiency but also raises concerns about fairness and transparency in trading.
Key Terms
**High Frequency Trading:**
High Frequency Trading (HFT) leverages advanced algorithms and high-speed data networks to execute trades within microseconds, capitalizing on minimal price discrepancies across markets. This strategy enhances market liquidity but can contribute to increased volatility and challenges in price transparency compared to dark pool prints, where large trades occur privately to minimize market impact. Explore further to understand how HFT influences market dynamics and trading strategies.
Algorithmic Trading
High frequency trading (HFT) leverages sophisticated algorithms to execute large volumes of orders at extremely fast speeds, capitalizing on minute market inefficiencies. Dark pool prints represent trade executions in private exchanges, providing anonymity and reducing market impact but limiting transparency compared to public order books. Explore the nuances of algorithmic trading strategies to understand how HFT and dark pools shape modern financial markets.
Latency
High frequency trading (HFT) relies on ultra-low latency to execute trades within microseconds, gaining competitive advantage through rapid order placement and market data processing. Dark pool prints, on the other hand, involve trade executions in private exchanges where latency is less critical but anonymity and reduced market impact are prioritized. Explore further to understand how latency differentials shape trading strategies and market behavior.
Source and External Links
High-Frequency Trading Explained: What Is It and How Do You Get ... - High-frequency trading uses powerful computers and advanced algorithms to execute a large number of trades at extremely high speeds, often in microseconds, to capitalize on tiny price differences across markets and generate profits from small margins repeated many times.
High Frequency Trading (HFT) - Definition, Pros and Cons - HFT is a form of algorithmic trading marked by very rapid trade execution, numerous transactions, and brief investment horizons, mainly employed by large institutional investors to profit from small price fluctuations and arbitrage opportunities.
High-frequency trading - Wikipedia - High-frequency trading is a type of automated quantitative trading characterized by short holding periods, high turnover rates, and strategies such as market-making and arbitrage that rely on fast processing of large data volumes to exploit small market inefficiencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com