Liquidity sweeps involve rapidly executing large trades to capitalize on available liquidity pockets, while arbitrage exploits price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets for risk-free profit. Both strategies require advanced algorithms and real-time data processing to maximize returns in volatile markets. Explore these trading techniques further to enhance your market strategies.
Why it is important
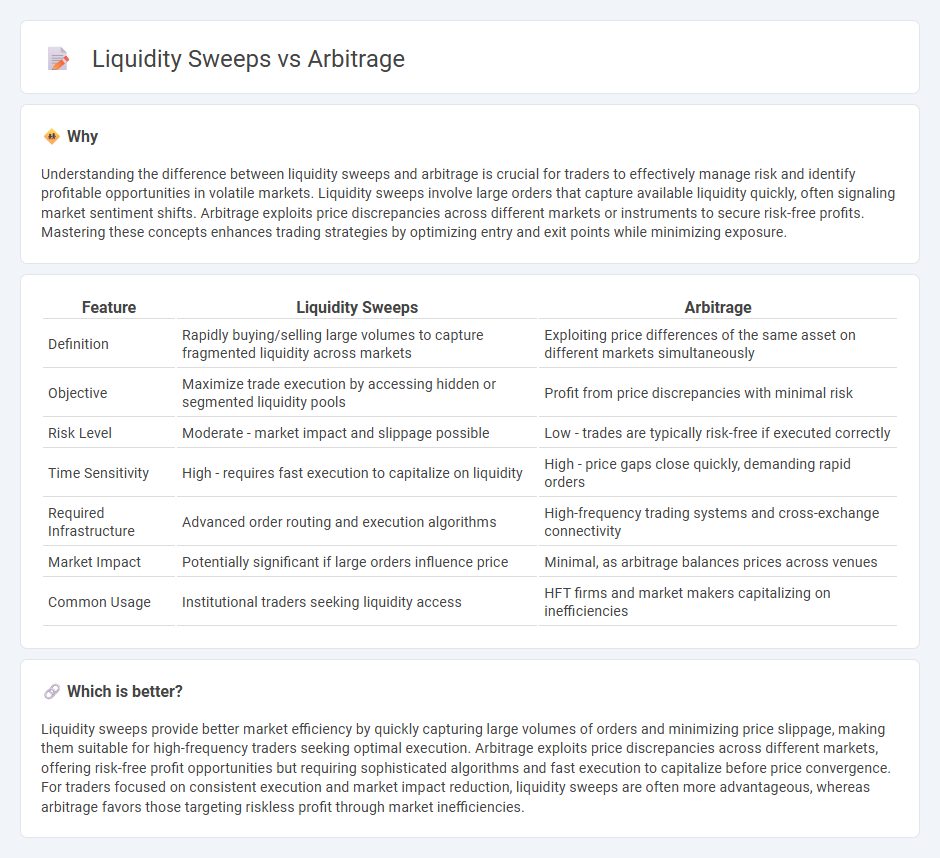
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and arbitrage is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and identify profitable opportunities in volatile markets. Liquidity sweeps involve large orders that capture available liquidity quickly, often signaling market sentiment shifts. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments to secure risk-free profits. Mastering these concepts enhances trading strategies by optimizing entry and exit points while minimizing exposure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Sweeps | Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapidly buying/selling large volumes to capture fragmented liquidity across markets | Exploiting price differences of the same asset on different markets simultaneously |
| Objective | Maximize trade execution by accessing hidden or segmented liquidity pools | Profit from price discrepancies with minimal risk |
| Risk Level | Moderate - market impact and slippage possible | Low - trades are typically risk-free if executed correctly |
| Time Sensitivity | High - requires fast execution to capitalize on liquidity | High - price gaps close quickly, demanding rapid orders |
| Required Infrastructure | Advanced order routing and execution algorithms | High-frequency trading systems and cross-exchange connectivity |
| Market Impact | Potentially significant if large orders influence price | Minimal, as arbitrage balances prices across venues |
| Common Usage | Institutional traders seeking liquidity access | HFT firms and market makers capitalizing on inefficiencies |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps provide better market efficiency by quickly capturing large volumes of orders and minimizing price slippage, making them suitable for high-frequency traders seeking optimal execution. Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets, offering risk-free profit opportunities but requiring sophisticated algorithms and fast execution to capitalize before price convergence. For traders focused on consistent execution and market impact reduction, liquidity sweeps are often more advantageous, whereas arbitrage favors those targeting riskless profit through market inefficiencies.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps exploit price discrepancies by rapidly buying or selling assets, creating opportunities for arbitrage traders to profit from these temporary imbalances across different markets. Arbitrage strategies depend on such liquidity sweeps to identify and execute trades that capitalize on inefficiencies in asset pricing. The interplay between liquidity sweeps and arbitrage ensures continuous market efficiency by aligning prices across exchanges through swift, high-frequency transactions.
Key Terms
Arbitrage:
Arbitrage exploits price differences across markets or assets, enabling traders to profit from temporary inefficiencies without market risk. Liquidity sweeps involve rapidly buying or selling assets to balance order books or capture value from large orders, often impacting market liquidity. Explore deeper insights into arbitrage strategies and their market implications.
Price Differential
Arbitrage exploits price differentials across markets by simultaneously buying low in one market and selling high in another, ensuring profit from the spread. Liquidity sweeps aggregate fragmented liquidity across order books to minimize slippage and achieve better execution prices, rather than directly profiting from price discrepancies. Explore how understanding these mechanisms can enhance trading strategies and risk management.
Market Efficiency
Arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across markets to enhance market efficiency by aligning asset prices closer to their true values, while liquidity sweeps target fragmented liquidity pools to consolidate trades and reduce spreads, thereby boosting overall market fluidity. Both mechanisms contribute significantly to minimizing inefficiencies, but arbitrage primarily drives price discovery whereas liquidity sweeps improve order execution quality. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies optimize trading ecosystems and market performance.
Source and External Links
Arbitrage - Wikipedia - Arbitrage is the practice of profiting from price differences of the same or very similar assets in different markets, typically viewed as a risk-free transaction that yields positive cash flow without negative cash flow in any state.
What Is Arbitrage? 3 Strategies to Know - Arbitrage is an investment strategy involving simultaneous buying and selling of an asset in different markets to exploit price differences, with key types including pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, and convertible arbitrage.
What is arbitrage and how does it work in financial markets | StoneX - Arbitrageurs profit by exploiting price differences for the same asset across markets, including methods such as pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage (trading stocks around mergers), and triangular arbitrage in forex markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com