Perpetual swaps offer traders leveraged exposure to cryptocurrency price movements without an expiration date, enabling continuous market participation and the ability to profit from both rising and falling prices. Unlike spot trading, which involves the immediate exchange of assets and ownership transfer, perpetual swaps rely on margin and funding rates to maintain contract prices close to the underlying asset. Explore the key differences between perpetual swaps and spot trading to optimize your trading strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between perpetual swaps and spot trading is crucial for effective risk management and maximizing profit potential in cryptocurrency markets. Perpetual swaps offer leveraged exposure without an expiry date, enabling traders to amplify gains or losses, while spot trading involves immediate asset purchase or sale at current market prices. Knowledge of funding rates in perpetual swaps helps avoid unexpected costs and informs better position timing. Spot trading provides straightforward ownership of assets, suitable for long-term investment strategies.
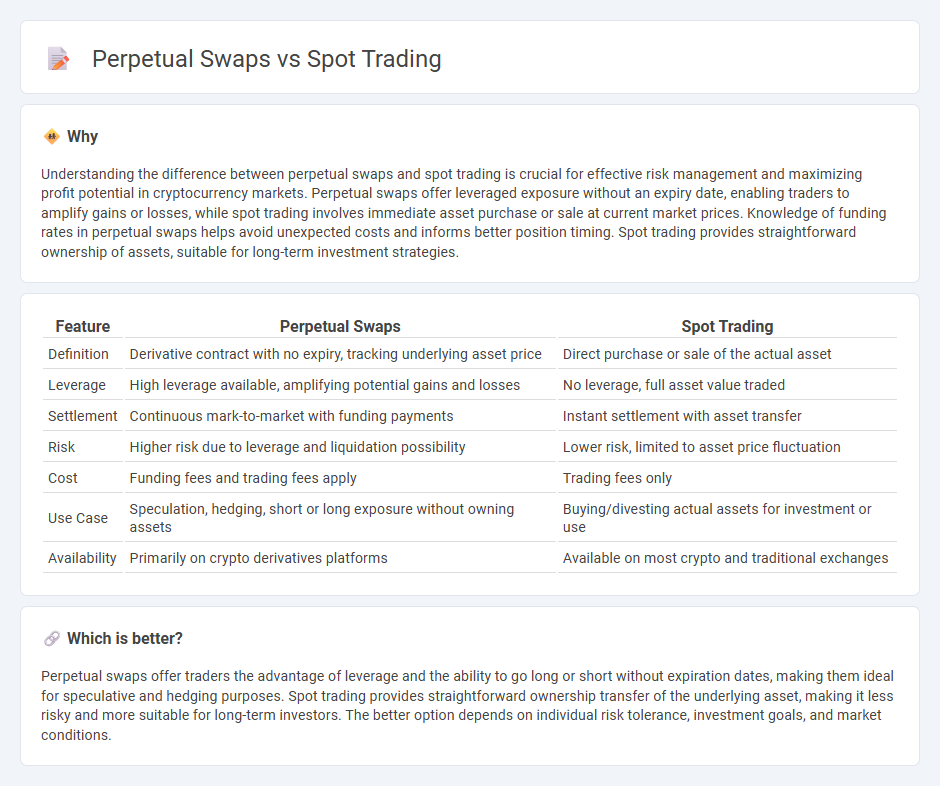
Comparison Table
| Feature | Perpetual Swaps | Spot Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Derivative contract with no expiry, tracking underlying asset price | Direct purchase or sale of the actual asset |
| Leverage | High leverage available, amplifying potential gains and losses | No leverage, full asset value traded |
| Settlement | Continuous mark-to-market with funding payments | Instant settlement with asset transfer |
| Risk | Higher risk due to leverage and liquidation possibility | Lower risk, limited to asset price fluctuation |
| Cost | Funding fees and trading fees apply | Trading fees only |
| Use Case | Speculation, hedging, short or long exposure without owning assets | Buying/divesting actual assets for investment or use |
| Availability | Primarily on crypto derivatives platforms | Available on most crypto and traditional exchanges |
Which is better?
Perpetual swaps offer traders the advantage of leverage and the ability to go long or short without expiration dates, making them ideal for speculative and hedging purposes. Spot trading provides straightforward ownership transfer of the underlying asset, making it less risky and more suitable for long-term investors. The better option depends on individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions.
Connection
Perpetual swaps and spot trading are connected through their reliance on the underlying asset's real-time market price to determine value and settlement. Perpetual swaps enable traders to speculate on price movements without owning the actual asset, while spot trading involves immediate exchange and ownership transfer of the asset. Price convergence mechanisms in perpetual swaps ensure alignment with spot market prices, providing liquidity and arbitrage opportunities for traders.
Key Terms
Settlement
Spot trading involves immediate settlement of assets, where the buyer pays and receives the underlying cryptocurrency instantly, ensuring ownership transfer occurs on the transaction date. Perpetual swaps, on the other hand, do not have a fixed settlement date; they use daily or periodic funding rates to anchor the contract price to the spot price, enabling continuous open positions without expiration. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how settlement mechanisms impact trading strategies and risk management.
Leverage
Spot trading involves buying or selling cryptocurrencies for immediate settlement without leverage, limiting risk exposure to your initial investment. Perpetual swaps enable traders to use leverage, often ranging from 1x to 100x, amplifying both potential gains and losses by borrowing funds to increase position size. Discover how leverage impacts your trading strategy by exploring detailed comparisons and risk management techniques.
Expiry
Spot trading involves the immediate exchange of assets with ownership transfer occurring instantly, whereas perpetual swaps are derivative contracts without an expiry date, allowing continuous trading. The absence of an expiry in perpetual swaps eliminates the need for contract rollover, contrasting sharply with traditional futures that require settlement or renewal at specific intervals. Explore detailed insights into the mechanics and risks of both to enhance your trading strategy.
Source and External Links
What is a Spot Trade? - Spot Trade Definition - FOREX.com US - Spot trading is the immediate purchase or sale of a financial instrument such as forex, commodities, and securities at the current market price, involving transactions that settle "on the spot" as market orders or specific triggered orders, with the price referred to as the spot price distinct from futures prices which are for future delivery.
Differences of Spot Trading vs. Day Trading - Nasdaq - Spot trading involves the immediate exchange of assets, settled typically within two business days at the prevailing market price, making it suitable for traders seeking quick transactions and short-term gains through active market participation.
What is spot trading in crypto and how does it work? - Coinbase - In cryptocurrency markets, spot trading means buying and selling digital currencies at their current market prices, allowing traders to own the assets instantaneously, with trades executed when matching orders are found on the platform's order book.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com