Market microstructure examines the mechanisms and processes that facilitate trading, including order types, price formation, and information flow within markets. Liquidity refers to the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without causing significant price changes, driven by factors like bid-ask spreads and market depth. Explore how understanding market microstructure enhances liquidity analysis and trading strategies for better investment outcomes.
Why it is important
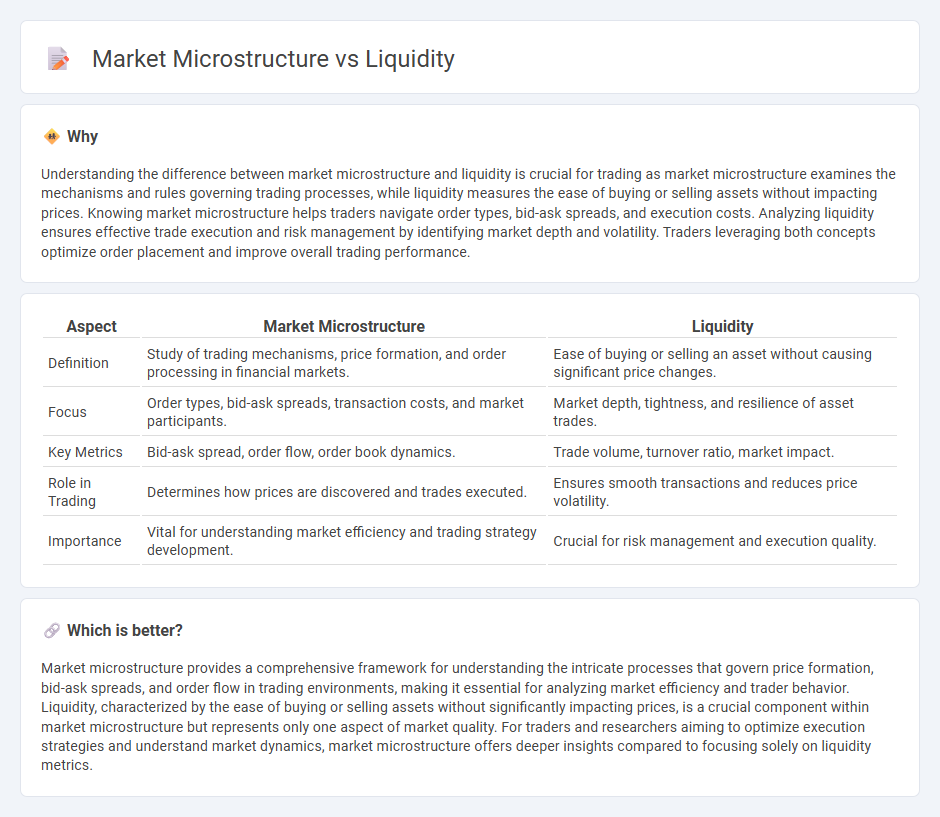
Understanding the difference between market microstructure and liquidity is crucial for trading as market microstructure examines the mechanisms and rules governing trading processes, while liquidity measures the ease of buying or selling assets without impacting prices. Knowing market microstructure helps traders navigate order types, bid-ask spreads, and execution costs. Analyzing liquidity ensures effective trade execution and risk management by identifying market depth and volatility. Traders leveraging both concepts optimize order placement and improve overall trading performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Microstructure | Liquidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of trading mechanisms, price formation, and order processing in financial markets. | Ease of buying or selling an asset without causing significant price changes. |
| Focus | Order types, bid-ask spreads, transaction costs, and market participants. | Market depth, tightness, and resilience of asset trades. |
| Key Metrics | Bid-ask spread, order flow, order book dynamics. | Trade volume, turnover ratio, market impact. |
| Role in Trading | Determines how prices are discovered and trades executed. | Ensures smooth transactions and reduces price volatility. |
| Importance | Vital for understanding market efficiency and trading strategy development. | Crucial for risk management and execution quality. |
Which is better?
Market microstructure provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the intricate processes that govern price formation, bid-ask spreads, and order flow in trading environments, making it essential for analyzing market efficiency and trader behavior. Liquidity, characterized by the ease of buying or selling assets without significantly impacting prices, is a crucial component within market microstructure but represents only one aspect of market quality. For traders and researchers aiming to optimize execution strategies and understand market dynamics, market microstructure offers deeper insights compared to focusing solely on liquidity metrics.
Connection
Market microstructure directly influences liquidity by shaping the mechanisms through which buyers and sellers interact, determining the speed and cost of executing trades. High transparency, efficient order matching systems, and low transaction costs enhance liquidity by attracting more participants and increasing trade volumes. Variations in microstructure, such as different trading protocols and information asymmetries, can lead to fluctuations in bid-ask spreads and market depth, impacting overall market liquidity.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Bid-ask spread is a crucial indicator in both liquidity assessment and market microstructure analysis, reflecting the cost of executing trades and the efficiency of price formation. Narrow spreads typically signify high liquidity and competitive markets where buying and selling prices are closely aligned, whereas wider spreads indicate lower liquidity and greater transaction costs. Explore the intricate relationship between liquidity and bid-ask spreads to understand market dynamics more deeply.
Order Book
Order book dynamics are central to understanding market microstructure and liquidity, as they concisely display real-time supply and demand through limit orders with specified prices and volumes. The depth, spread, and order flow within the order book influence price discovery and market liquidity by determining how efficiently assets can be bought or sold without significant price impact. Explore further to uncover how order book intricacies shape market behavior and trading strategies.
Market Depth
Market depth, a fundamental aspect of liquidity in market microstructure, refers to the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels within the order book, indicating the market's ability to absorb large transactions without significant price changes. High market depth signals strong liquidity, minimizing price volatility and enhancing trade execution efficiency for investors. Explore further to understand how market depth influences trading strategies and price discovery.
Source and External Links
Liquidity: A Look into Finance's Most Essential Concept - Liquidity in finance refers to how quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash, with key measures including the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio that assess a company's ability to meet short-term obligations by converting assets to cash.
What is liquidity? | BDC.ca - Liquidity is a business's ability to convert assets into cash quickly to pay short-term liabilities, emphasizing the importance of tracking liquid assets like cash and marketable securities for sound financial planning.
Market liquidity - Wikipedia - Market liquidity describes how easily assets can be bought or sold in the market without affecting their price significantly, with cash being the most liquid asset due to its immediate usability for transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com