Delta neutral strategy involves creating a portfolio where the overall delta, or sensitivity to underlying asset price changes, is zero, effectively minimizing directional risk. Market making focuses on providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk. Explore these strategies in detail to understand how they optimize risk management and profitability in trading.
Why it is important
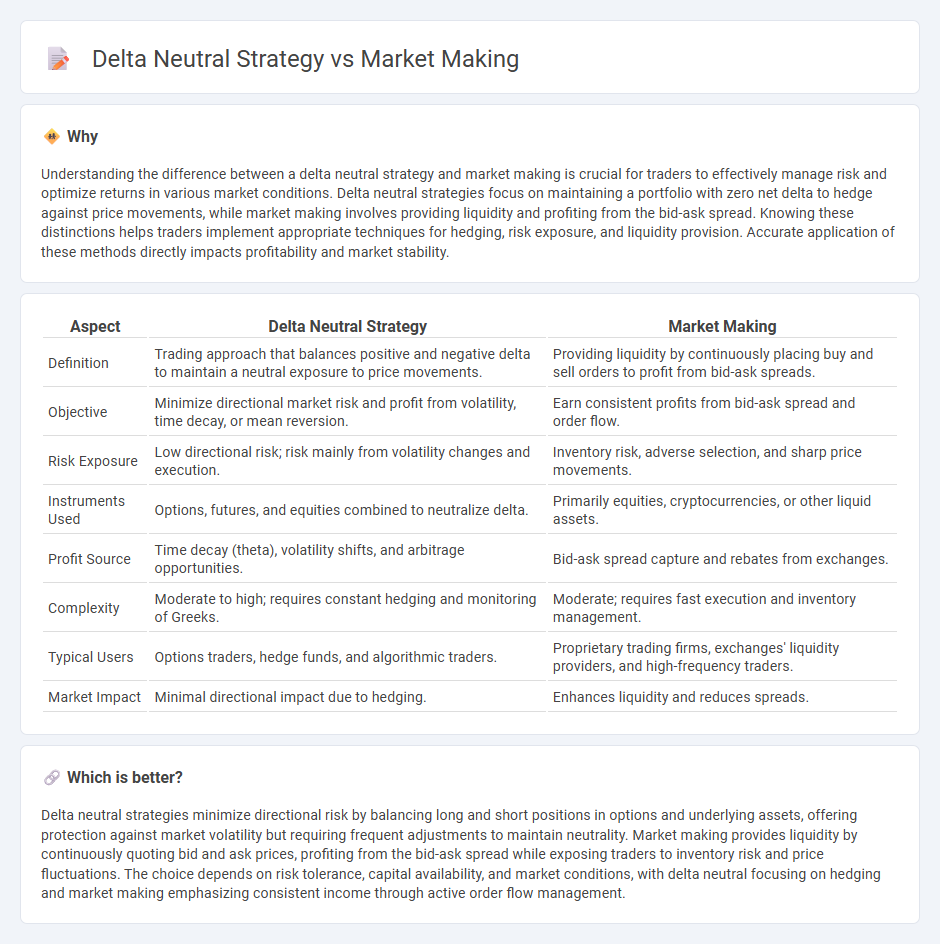
Understanding the difference between a delta neutral strategy and market making is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize returns in various market conditions. Delta neutral strategies focus on maintaining a portfolio with zero net delta to hedge against price movements, while market making involves providing liquidity and profiting from the bid-ask spread. Knowing these distinctions helps traders implement appropriate techniques for hedging, risk exposure, and liquidity provision. Accurate application of these methods directly impacts profitability and market stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Neutral Strategy | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach that balances positive and negative delta to maintain a neutral exposure to price movements. | Providing liquidity by continuously placing buy and sell orders to profit from bid-ask spreads. |
| Objective | Minimize directional market risk and profit from volatility, time decay, or mean reversion. | Earn consistent profits from bid-ask spread and order flow. |
| Risk Exposure | Low directional risk; risk mainly from volatility changes and execution. | Inventory risk, adverse selection, and sharp price movements. |
| Instruments Used | Options, futures, and equities combined to neutralize delta. | Primarily equities, cryptocurrencies, or other liquid assets. |
| Profit Source | Time decay (theta), volatility shifts, and arbitrage opportunities. | Bid-ask spread capture and rebates from exchanges. |
| Complexity | Moderate to high; requires constant hedging and monitoring of Greeks. | Moderate; requires fast execution and inventory management. |
| Typical Users | Options traders, hedge funds, and algorithmic traders. | Proprietary trading firms, exchanges' liquidity providers, and high-frequency traders. |
| Market Impact | Minimal directional impact due to hedging. | Enhances liquidity and reduces spreads. |
Which is better?
Delta neutral strategies minimize directional risk by balancing long and short positions in options and underlying assets, offering protection against market volatility but requiring frequent adjustments to maintain neutrality. Market making provides liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread while exposing traders to inventory risk and price fluctuations. The choice depends on risk tolerance, capital availability, and market conditions, with delta neutral focusing on hedging and market making emphasizing consistent income through active order flow management.
Connection
Delta neutral strategy and market making are interconnected through their shared goal of minimizing directional market risk by maintaining a balanced portfolio of long and short positions. Market makers continuously adjust their bid and ask prices to capture the spread while using delta neutral hedging techniques to offset price movements of underlying assets, ensuring limited exposure to market volatility. This synergy enables market makers to provide liquidity and earn profits regardless of market direction.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Market making involves continuously placing both buy and sell orders to profit from the bid-ask spread by capturing the difference between buying and selling prices. Delta neutral strategies aim to hedge against directional market risk by balancing positions to maintain a net-zero delta, often reducing exposure to price movements but not specifically targeting the bid-ask spread. Explore these approaches in detail to understand their risk management and profit optimization mechanisms.
Hedging
Market making involves quoting both buy and sell prices to capture the bid-ask spread while maintaining balanced inventory risk through continuous hedging to remain delta neutral. Delta neutral strategies specifically target hedging directional risk by adjusting positions in the underlying asset and derivatives to maintain a portfolio with zero net delta exposure. Explore in-depth techniques and benefits of both market making and delta neutral hedging to optimize trading performance.
Inventory Risk
Market making strategies actively provide liquidity by posting bid and ask quotes, exposing traders to inventory risk due to fluctuating asset prices and order flow imbalances. Delta neutral strategies aim to hedge directional market risk by maintaining a portfolio balanced to price movements, often minimizing inventory exposure but still requiring dynamic adjustments to stay neutral. Explore detailed insights on managing inventory risk in market making and delta neutral approaches for enhanced trading performance.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy | EPAM SolutionsHub - A market maker profits mainly through the bid-ask spread, managing inventory to buy low and sell high, and analyzing order flows to anticipate movements, all while maintaining market liquidity under regulatory rules.
Market maker: What it is, importance, benefits & examples - StoneX - Market making involves continuously quoting buy and sell prices to provide liquidity and earn profits from the bid-ask spread, managing inventory and risk with sophisticated strategies in both liquid and less liquid markets.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - Market makers supply bids and asks to enable immediate trading, profiting from the bid-ask spread and managing risks from holding securities, and can trade on their own account or for others in various markets including real estate.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com