Front running exploits prior knowledge of pending orders to gain an unfair advantage, while spoofing involves placing fake orders to manipulate market prices and mislead other traders. Both practices are illegal and can distort market integrity, leading to losses for genuine investors. Explore the differences and regulatory implications of front running versus spoofing to enhance your understanding of trading ethics.
Why it is important
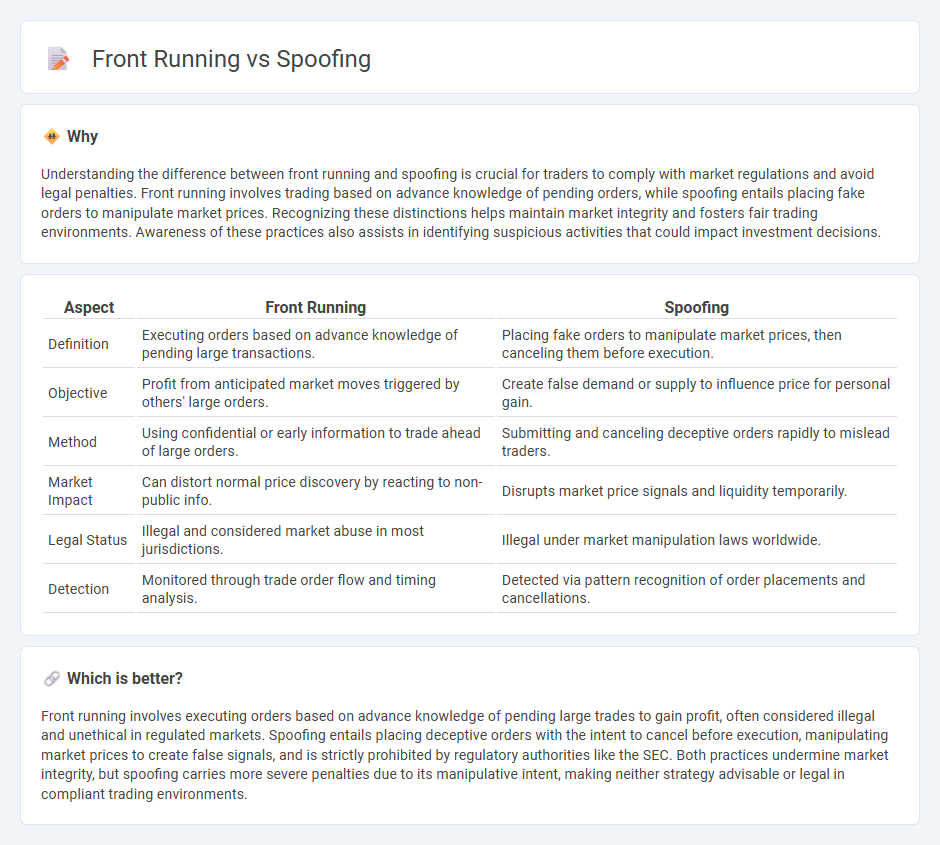
Understanding the difference between front running and spoofing is crucial for traders to comply with market regulations and avoid legal penalties. Front running involves trading based on advance knowledge of pending orders, while spoofing entails placing fake orders to manipulate market prices. Recognizing these distinctions helps maintain market integrity and fosters fair trading environments. Awareness of these practices also assists in identifying suspicious activities that could impact investment decisions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Front Running | Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large transactions. | Placing fake orders to manipulate market prices, then canceling them before execution. |
| Objective | Profit from anticipated market moves triggered by others' large orders. | Create false demand or supply to influence price for personal gain. |
| Method | Using confidential or early information to trade ahead of large orders. | Submitting and canceling deceptive orders rapidly to mislead traders. |
| Market Impact | Can distort normal price discovery by reacting to non-public info. | Disrupts market price signals and liquidity temporarily. |
| Legal Status | Illegal and considered market abuse in most jurisdictions. | Illegal under market manipulation laws worldwide. |
| Detection | Monitored through trade order flow and timing analysis. | Detected via pattern recognition of order placements and cancellations. |
Which is better?
Front running involves executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades to gain profit, often considered illegal and unethical in regulated markets. Spoofing entails placing deceptive orders with the intent to cancel before execution, manipulating market prices to create false signals, and is strictly prohibited by regulatory authorities like the SEC. Both practices undermine market integrity, but spoofing carries more severe penalties due to its manipulative intent, making neither strategy advisable or legal in compliant trading environments.
Connection
Front running and spoofing are both illegal trading practices that manipulate market behavior to benefit the trader at the expense of others. Front running involves executing orders based on advance knowledge of pending large trades, while spoofing entails placing fake orders to create a false impression of demand or supply, influencing prices. Both tactics undermine market integrity and are closely monitored by regulatory bodies like the SEC and CFTC.
Key Terms
Order Book Manipulation
Spoofing involves placing large orders in the order book with no intention of executing them, aiming to create false market signals and manipulate prices. Front running exploits prior knowledge of large pending orders by entering trades ahead to profit from the expected price movements caused by those orders. Explore deeper insights into Order Book Manipulation techniques to understand their impact on market integrity and trading strategies.
Priority Access
Priority access plays a crucial role in both spoofing and front running, where traders leverage early information to manipulate market prices. Spoofing involves placing deceptive orders with priority access to create false demand or supply signals, while front running exploits priority access by executing trades ahead of large pending orders to gain profit. Discover how understanding priority access nuances can help detect and prevent these manipulative trading strategies.
Market Integrity
Spoofing involves placing fake orders to manipulate market prices and deceive other traders, compromising market integrity by creating false demand or supply signals. Front running refers to unethical trading where brokers execute orders for their own accounts ahead of client orders, exploiting non-public information and undermining fair market practices. Learn more about how these manipulative tactics threaten market integrity and the regulatory measures in place to combat them.
Source and External Links
What is Spoofing & How to Prevent it - Kaspersky - Spoofing is a cybercrime where attackers impersonate trusted entities to trick victims into actions like transferring money or giving sensitive information, often leading to data breaches or malware infections.
Spoofing | Spoof Calls | What is a Spoofing Attack - Malwarebytes - Spoofing involves pretending to be someone else to gain trust, steal data, money, or spread malware through methods like email, caller ID, website, GPS, or IP spoofing.
What Is Spoofing? Definition, Types & More | Proofpoint US - Spoofing is a tactic used by threat actors to disguise communication or data sources as trusted ones, resulting in breaches, financial loss, and malware spread; prevention includes using authentication protocols and security training.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com