Options flow trading provides real-time insights into large trades and market sentiment by analyzing unusual options activity, enabling traders to anticipate significant price movements. Algorithmic trading employs complex mathematical models and high-frequency data processing to execute trades at optimal speed and efficiency, capitalizing on micro-market opportunities. Explore the differences and advantages of these approaches to enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
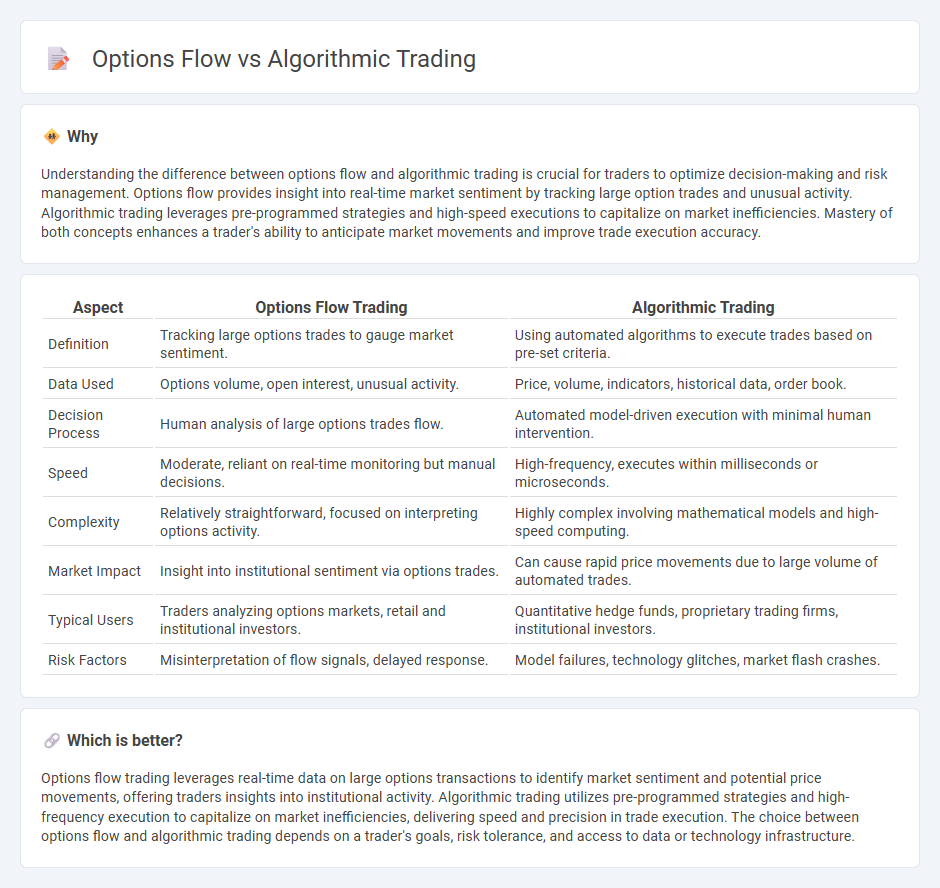
Understanding the difference between options flow and algorithmic trading is crucial for traders to optimize decision-making and risk management. Options flow provides insight into real-time market sentiment by tracking large option trades and unusual activity. Algorithmic trading leverages pre-programmed strategies and high-speed executions to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Mastery of both concepts enhances a trader's ability to anticipate market movements and improve trade execution accuracy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Options Flow Trading | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tracking large options trades to gauge market sentiment. | Using automated algorithms to execute trades based on pre-set criteria. |
| Data Used | Options volume, open interest, unusual activity. | Price, volume, indicators, historical data, order book. |
| Decision Process | Human analysis of large options trades flow. | Automated model-driven execution with minimal human intervention. |
| Speed | Moderate, reliant on real-time monitoring but manual decisions. | High-frequency, executes within milliseconds or microseconds. |
| Complexity | Relatively straightforward, focused on interpreting options activity. | Highly complex involving mathematical models and high-speed computing. |
| Market Impact | Insight into institutional sentiment via options trades. | Can cause rapid price movements due to large volume of automated trades. |
| Typical Users | Traders analyzing options markets, retail and institutional investors. | Quantitative hedge funds, proprietary trading firms, institutional investors. |
| Risk Factors | Misinterpretation of flow signals, delayed response. | Model failures, technology glitches, market flash crashes. |
Which is better?
Options flow trading leverages real-time data on large options transactions to identify market sentiment and potential price movements, offering traders insights into institutional activity. Algorithmic trading utilizes pre-programmed strategies and high-frequency execution to capitalize on market inefficiencies, delivering speed and precision in trade execution. The choice between options flow and algorithmic trading depends on a trader's goals, risk tolerance, and access to data or technology infrastructure.
Connection
Options flow provides real-time data on market participant sentiment and large block trades, which algorithmic trading systems analyze to execute high-frequency, data-driven trades. Algorithms use this flow to identify patterns and predict short-term price movements, enhancing trade accuracy and speed. Integrating options flow into algorithmic models increases market efficiency and improves risk-adjusted returns.
Key Terms
Algorithmic Trading:
Algorithmic trading leverages advanced mathematical models and high-speed computing to execute trades at optimal prices, minimizing human error and maximizing execution efficiency in financial markets. This automated approach uses historical data, real-time market conditions, and predefined criteria to make split-second trading decisions across asset classes like equities, futures, and forex. Discover more about how algorithmic trading transforms modern investment strategies and market dynamics.
Backtesting
Algorithmic trading leverages historical market data and complex mathematical models to execute backtests, allowing traders to evaluate the performance of strategies under various market conditions. Options flow analysis focuses on interpreting real-time options market data to gauge investor sentiment and anticipate price movements, with backtesting emphasizing pattern recognition in options volume and volatility to refine predictive models. Explore advanced backtesting techniques to enhance the integration of algorithmic trading and options flow insights for superior investment decisions.
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms in algorithmic trading utilize pre-programmed instructions to systematically place orders based on market conditions, minimizing market impact and optimizing trade timing. Options flow analysis focuses on real-time monitoring of options market activity to detect large trades or unusual patterns, offering insights into potential price movements and sentiment shifts. Explore how integrating execution algorithms with options flow data can enhance trading strategies and execution precision.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes to open and close trades based on set rules like price movements, employing strategies such as price action, technical analysis, or a combination, often with risk management measures like stops and limits for high-frequency trading.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading consists of pre-programmed rules that execute trades when conditions, like price crossing moving averages, are met, allowing for large trades to be broken down and executed in smaller batches to avoid distorting market prices.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading automates order execution based on variables like time and price, with advancements including machine learning techniques such as deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms that adapt dynamically to volatile market conditions for improved trade timing and profitability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com