Proprietary trading firm challenges require traders to demonstrate consistent profitability under strict risk management to secure capital allocation, emphasizing skill development and discipline. Hedge funds manage large pools of investor money, focusing on diverse strategies to generate returns while balancing risk and regulatory compliance. Explore the differences in trading approaches, capital structures, and career opportunities between prop firms and hedge funds.
Why it is important
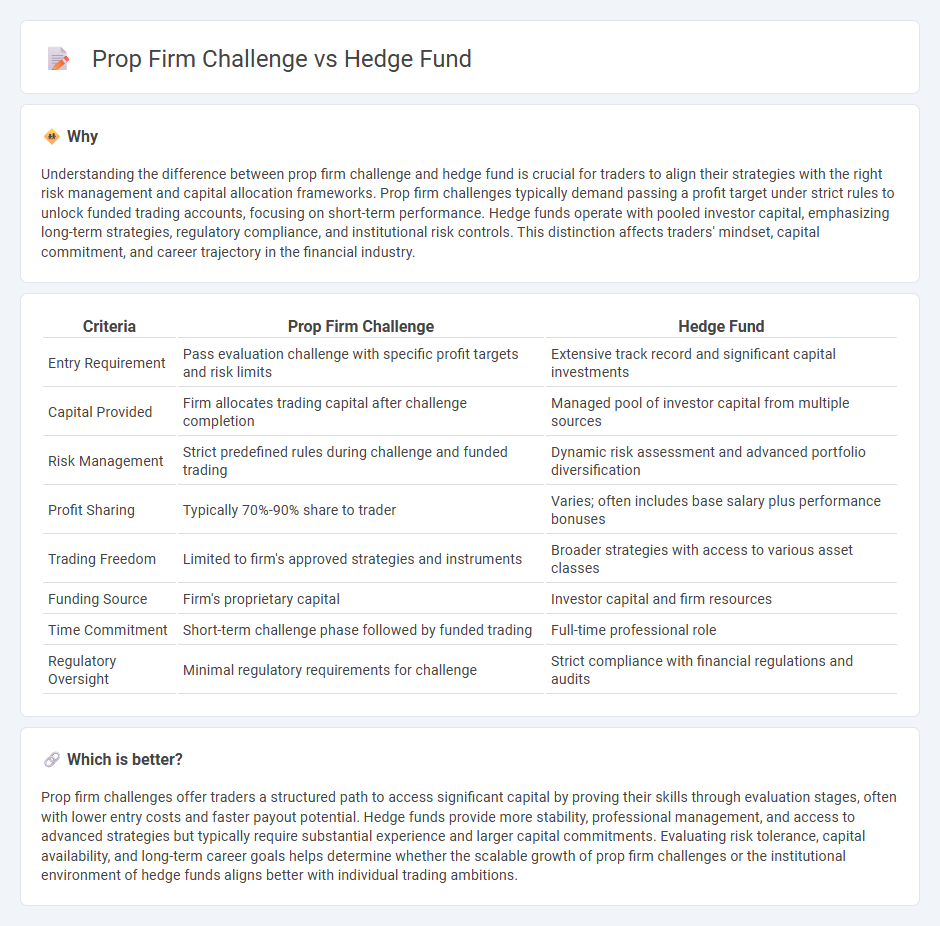
Understanding the difference between prop firm challenge and hedge fund is crucial for traders to align their strategies with the right risk management and capital allocation frameworks. Prop firm challenges typically demand passing a profit target under strict rules to unlock funded trading accounts, focusing on short-term performance. Hedge funds operate with pooled investor capital, emphasizing long-term strategies, regulatory compliance, and institutional risk controls. This distinction affects traders' mindset, capital commitment, and career trajectory in the financial industry.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Prop Firm Challenge | Hedge Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Entry Requirement | Pass evaluation challenge with specific profit targets and risk limits | Extensive track record and significant capital investments |
| Capital Provided | Firm allocates trading capital after challenge completion | Managed pool of investor capital from multiple sources |
| Risk Management | Strict predefined rules during challenge and funded trading | Dynamic risk assessment and advanced portfolio diversification |
| Profit Sharing | Typically 70%-90% share to trader | Varies; often includes base salary plus performance bonuses |
| Trading Freedom | Limited to firm's approved strategies and instruments | Broader strategies with access to various asset classes |
| Funding Source | Firm's proprietary capital | Investor capital and firm resources |
| Time Commitment | Short-term challenge phase followed by funded trading | Full-time professional role |
| Regulatory Oversight | Minimal regulatory requirements for challenge | Strict compliance with financial regulations and audits |
Which is better?
Prop firm challenges offer traders a structured path to access significant capital by proving their skills through evaluation stages, often with lower entry costs and faster payout potential. Hedge funds provide more stability, professional management, and access to advanced strategies but typically require substantial experience and larger capital commitments. Evaluating risk tolerance, capital availability, and long-term career goals helps determine whether the scalable growth of prop firm challenges or the institutional environment of hedge funds aligns better with individual trading ambitions.
Connection
Proprietary firm challenges serve as a proving ground where traders demonstrate skills using firm capital, similar to the stringent selection processes hedge funds employ to manage large portfolios. Both entities prioritize risk management, advanced trading strategies, and consistent profitability to ensure sustainable returns. Successful prop traders often transition to hedge funds, leveraging experience gained through rigorous challenge phases to navigate complex market conditions.
Key Terms
Capital Allocation
Hedge funds typically allocate capital from multiple investors to diversify risk and optimize returns, relying on sophisticated strategies and extensive market data analysis. Proprietary trading firms use their own capital, enabling faster decision-making and higher risk tolerance but limited by internal resources. Explore our detailed comparison to understand which approach better suits your investment goals.
Risk Management
Hedge funds implement rigorous risk management strategies by diversifying portfolios, utilizing advanced analytics, and adhering to strict regulatory compliance to protect investor capital. Proprietary trading firms emphasize real-time risk controls, rapid position adjustments, and high-frequency trading tactics to optimize profits while mitigating losses. Explore how these distinct risk management approaches shape the competitive edge in hedge fund and prop firm challenges.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics in hedge funds emphasize risk-adjusted returns, Sharpe ratio, and alpha generation to align with investor expectations and regulatory standards. Proprietary trading firms prioritize short-term profitability, win rate, and maximum drawdown during challenge assessments to evaluate trader skill and consistency. Explore deeper insights into how these differing performance criteria impact trading strategies and funding opportunities.
Source and External Links
Hedge Funds: Overview, Recruitment, Careers & Salaries - A hedge fund is an investment firm that raises capital from institutional and accredited investors and invests in financial assets using diverse strategies to achieve absolute returns, often involving short-selling, derivatives, and event-driven investments.
Hedge fund - Wikipedia - Hedge funds are pooled investment funds that use complex trading and risk management techniques, often structured as limited partnerships or offshore entities, with service providers like prime brokers and administrators supporting their operations.
Hedge Funds | SEC.gov - Hedge funds pool investor money to pursue positive returns through flexible, often high-risk strategies including leverage, derivatives, and short-selling, which can magnify both potential gains and losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com