Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate returns by systematically buying low and selling high, focusing on short-term price movements. Value investing targets undervalued assets based on fundamental analysis, aiming for long-term capital appreciation through market corrections. Explore the nuances and strategies behind volatility harvesting and value investing to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
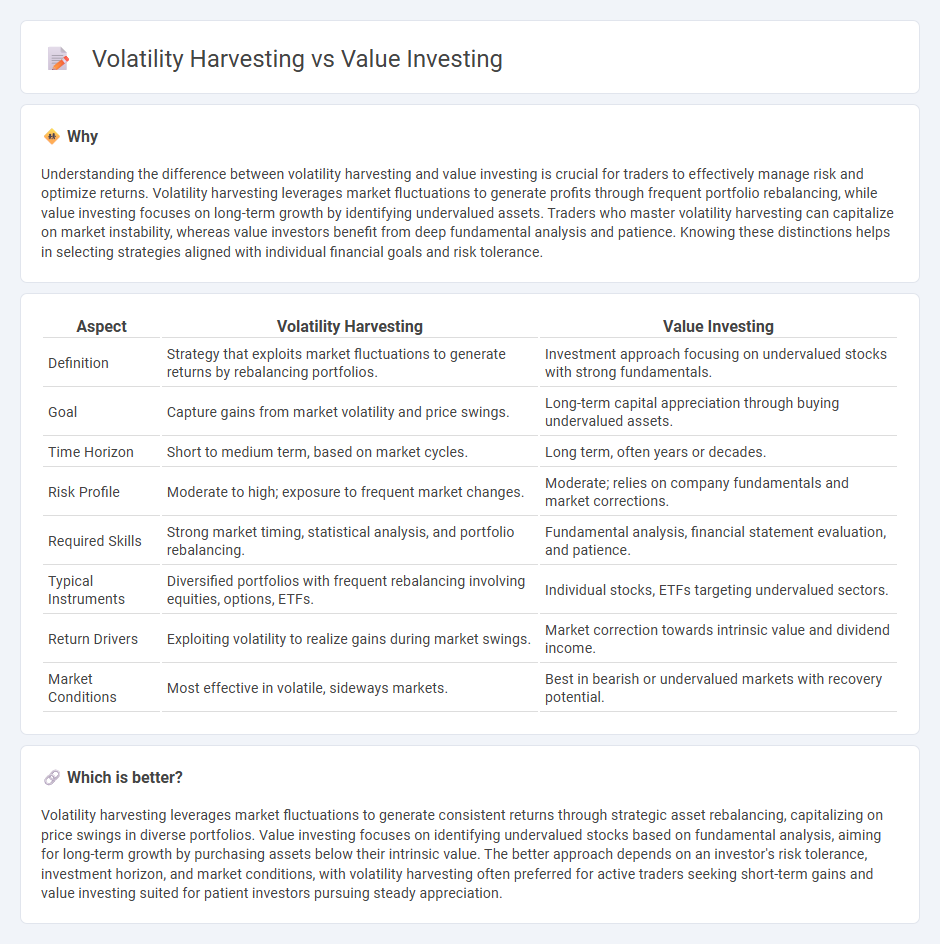
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and value investing is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize returns. Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate profits through frequent portfolio rebalancing, while value investing focuses on long-term growth by identifying undervalued assets. Traders who master volatility harvesting can capitalize on market instability, whereas value investors benefit from deep fundamental analysis and patience. Knowing these distinctions helps in selecting strategies aligned with individual financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Value Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy that exploits market fluctuations to generate returns by rebalancing portfolios. | Investment approach focusing on undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. |
| Goal | Capture gains from market volatility and price swings. | Long-term capital appreciation through buying undervalued assets. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, based on market cycles. | Long term, often years or decades. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high; exposure to frequent market changes. | Moderate; relies on company fundamentals and market corrections. |
| Required Skills | Strong market timing, statistical analysis, and portfolio rebalancing. | Fundamental analysis, financial statement evaluation, and patience. |
| Typical Instruments | Diversified portfolios with frequent rebalancing involving equities, options, ETFs. | Individual stocks, ETFs targeting undervalued sectors. |
| Return Drivers | Exploiting volatility to realize gains during market swings. | Market correction towards intrinsic value and dividend income. |
| Market Conditions | Most effective in volatile, sideways markets. | Best in bearish or undervalued markets with recovery potential. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate consistent returns through strategic asset rebalancing, capitalizing on price swings in diverse portfolios. Value investing focuses on identifying undervalued stocks based on fundamental analysis, aiming for long-term growth by purchasing assets below their intrinsic value. The better approach depends on an investor's risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market conditions, with volatility harvesting often preferred for active traders seeking short-term gains and value investing suited for patient investors pursuing steady appreciation.
Connection
Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing portfolios, while value investing focuses on identifying undervalued assets with strong fundamentals. Both strategies capitalize on market inefficiencies and price divergences, using volatility as an opportunity rather than a threat. Combining volatility harvesting with value investing can enhance long-term portfolio performance by balancing risk and optimizing asset allocation under varying market conditions.
Key Terms
**Value Investing:**
Value investing involves selecting stocks that appear undervalued based on fundamental analysis, emphasizing metrics such as low price-to-earnings ratios and strong dividend yields. This strategy seeks to capitalize on market inefficiencies by investing in companies with solid financial health and growth potential that are temporarily overlooked. Explore more to understand how value investing can build long-term wealth through disciplined stock selection.
Intrinsic Value
Value investing prioritizes identifying stocks trading below their intrinsic value, aiming for long-term capital appreciation by capitalizing on market inefficiencies. Volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations through frequent trading to generate returns independent of market direction, often focusing less on fundamental metrics like intrinsic value. Explore how intrinsic value assessment can enhance your investment strategy by delving deeper into the principles behind value investing and volatility harvesting.
Margin of Safety
Value investing emphasizes a margin of safety by purchasing undervalued assets with a significant discount to intrinsic value, minimizing the risk of permanent capital loss. Volatility harvesting exploits market fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing portfolios, but it relies less directly on a margin of safety concept. Explore how integrating margin of safety principles enhances both strategies for more resilient investment outcomes.
Source and External Links
Value investing - Wikipedia - Value investing is an investment paradigm focused on buying securities that appear underpriced based on fundamental analysis, originally developed by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd, emphasizing a "margin of safety" by purchasing stocks below their intrinsic value.
What is value investing? | iShares - BlackRock - Value investing targets companies cheap relative to their peers using metrics like Price to Book and Price to Earnings ratios, now accessible through low-cost ETFs for broad market exposure.
Value Investing History | Columbia Business School - Developed in the 1920s by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd, value investing involves estimating a stock's intrinsic value to find securities trading below that value rather than speculating on price movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com