Penny jump refers to the smallest possible price improvement by one cent in trading, allowing traders to gain priority in order execution without significantly raising the bid or ask price. Slippage occurs when a trade is executed at a price different from the expected price, often due to market volatility or low liquidity, resulting in a cost to the trader. Explore the nuances of penny jump and slippage to optimize your trading strategies and minimize costs.
Why it is important
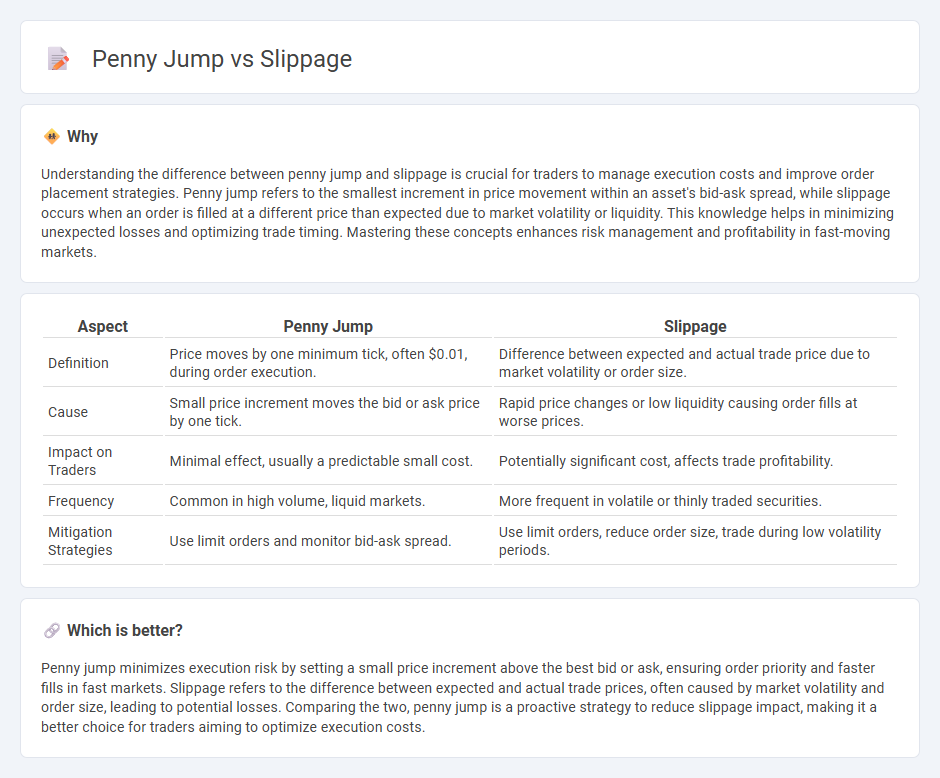
Understanding the difference between penny jump and slippage is crucial for traders to manage execution costs and improve order placement strategies. Penny jump refers to the smallest increment in price movement within an asset's bid-ask spread, while slippage occurs when an order is filled at a different price than expected due to market volatility or liquidity. This knowledge helps in minimizing unexpected losses and optimizing trade timing. Mastering these concepts enhances risk management and profitability in fast-moving markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Penny Jump | Slippage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price moves by one minimum tick, often $0.01, during order execution. | Difference between expected and actual trade price due to market volatility or order size. |
| Cause | Small price increment moves the bid or ask price by one tick. | Rapid price changes or low liquidity causing order fills at worse prices. |
| Impact on Traders | Minimal effect, usually a predictable small cost. | Potentially significant cost, affects trade profitability. |
| Frequency | Common in high volume, liquid markets. | More frequent in volatile or thinly traded securities. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Use limit orders and monitor bid-ask spread. | Use limit orders, reduce order size, trade during low volatility periods. |
Which is better?
Penny jump minimizes execution risk by setting a small price increment above the best bid or ask, ensuring order priority and faster fills in fast markets. Slippage refers to the difference between expected and actual trade prices, often caused by market volatility and order size, leading to potential losses. Comparing the two, penny jump is a proactive strategy to reduce slippage impact, making it a better choice for traders aiming to optimize execution costs.
Connection
Penny jump and slippage both relate to price movements during trade execution, with penny jump referring to the minimum price increment in securities and slippage representing the difference between expected and actual trade prices. During volatile markets, penny jumps can cause increased slippage as rapid price changes prevent orders from filling at intended levels. Traders must understand that penny jumps influence market liquidity and price gaps, directly impacting the slippage experienced in order executions.
Key Terms
Execution price
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected execution price and the actual price at which a trade is executed, often caused by market volatility or order size. Penny jump focuses on the discrete price increments, typically one cent, highlighting the minimum price improvement during order execution. Explore more to understand how these factors impact trading strategies and execution efficiency.
Order size
Order size significantly impacts slippage, as larger orders often face greater price deviations due to market liquidity constraints. In contrast, penny jumps typically involve minimal price changes seen with smaller, more frequent order sizes in highly liquid markets. Explore further to understand how order size influences execution costs and market impact.
Liquidity
Slippage occurs when an order executes at a price different from the expected one due to insufficient liquidity, causing a price gap. Penny jumps refer to minimal price changes that can still impact execution costs in highly liquid markets by pushing prices up or down by a single cent. Explore deeper insights into how liquidity influences trading costs and execution quality.
Source and External Links
Slippage - Definition, Why It Happens, How To Minimize - Slippage happens when a trade executes at a price different from the requested price, often due to market volatility or low liquidity causing price changes between order placement and execution.
What is slippage? Understanding Slippage in Trading - Slippage is a common feature of fast-moving markets where orders are executed at the next best available price if sufficient volume at the requested price is lacking, especially during high volatility or low liquidity periods.
What is slippage in crypto and how to minimize its impact? - Coinbase - In crypto, slippage is the difference between the expected and actual trade execution price caused by rapid price fluctuations and low liquidity, and it can be managed using limit orders or setting slippage tolerance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com