Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated assets to capitalize on price divergences, leveraging statistical arbitrage techniques for market-neutral strategies. Momentum trading focuses on identifying and riding trends by purchasing assets exhibiting strong recent performance while selling those showing weakness, relying on market sentiment and price momentum indicators. Explore detailed analyses and strategies to master both pair trading and momentum trading approaches.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between pair trading and momentum trading is crucial because pair trading involves exploiting price divergences between two correlated assets, minimizing market risk, while momentum trading capitalizes on the continuation of existing price trends for potential rapid gains. Pair trading strategies focus on relative value and statistical arbitrage, making them market-neutral and less influenced by overall market direction. Momentum trading requires understanding trend strength and timing entry and exit points effectively to maximize profits. Mastering these distinctions allows traders to select strategies best suited to market conditions and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
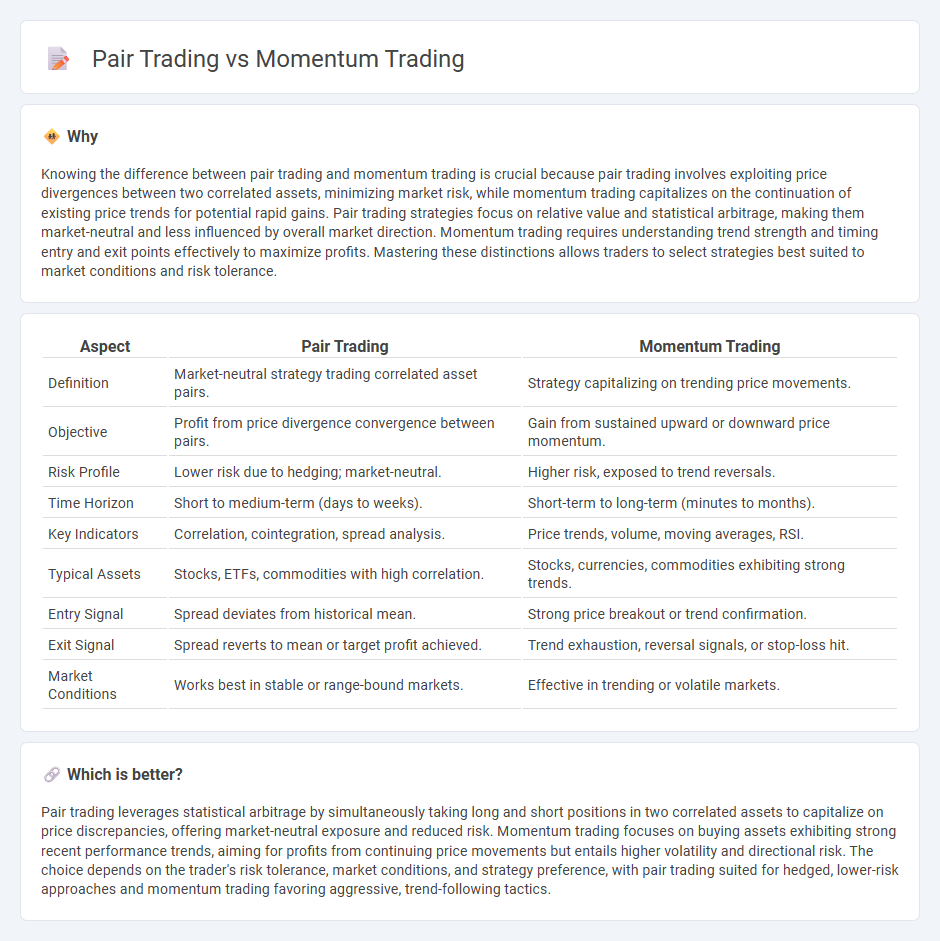
| Aspect | Pair Trading | Momentum Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-neutral strategy trading correlated asset pairs. | Strategy capitalizing on trending price movements. |
| Objective | Profit from price divergence convergence between pairs. | Gain from sustained upward or downward price momentum. |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk due to hedging; market-neutral. | Higher risk, exposed to trend reversals. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term (days to weeks). | Short-term to long-term (minutes to months). |
| Key Indicators | Correlation, cointegration, spread analysis. | Price trends, volume, moving averages, RSI. |
| Typical Assets | Stocks, ETFs, commodities with high correlation. | Stocks, currencies, commodities exhibiting strong trends. |
| Entry Signal | Spread deviates from historical mean. | Strong price breakout or trend confirmation. |
| Exit Signal | Spread reverts to mean or target profit achieved. | Trend exhaustion, reversal signals, or stop-loss hit. |
| Market Conditions | Works best in stable or range-bound markets. | Effective in trending or volatile markets. |
Which is better?
Pair trading leverages statistical arbitrage by simultaneously taking long and short positions in two correlated assets to capitalize on price discrepancies, offering market-neutral exposure and reduced risk. Momentum trading focuses on buying assets exhibiting strong recent performance trends, aiming for profits from continuing price movements but entails higher volatility and directional risk. The choice depends on the trader's risk tolerance, market conditions, and strategy preference, with pair trading suited for hedged, lower-risk approaches and momentum trading favoring aggressive, trend-following tactics.
Connection
Pair trading and momentum trading are connected through their reliance on price movements and statistical relationships between assets. Pair trading exploits mean reversion by identifying two correlated securities, while momentum trading capitalizes on the continuation of existing price trends within those securities. Both strategies use quantitative analysis to inform trade decisions, often within market-neutral frameworks.
Key Terms
**Momentum Trading:**
Momentum trading capitalizes on the continuation of existing market trends by buying assets that demonstrate strong upward price movement and selling those showing downward momentum. This strategy relies heavily on technical indicators such as moving averages and relative strength index (RSI) to identify and confirm trends. Explore more about how momentum trading can optimize your portfolio performance.
Trend
Momentum trading capitalizes on the continuation of existing price trends by buying assets showing strong upward momentum and selling those with downward momentum. Pair trading involves simultaneously taking long and short positions in two correlated assets to exploit relative price movements while minimizing market risk. Explore in-depth strategies and examples to master trend-focused trading techniques.
Volume
Momentum trading leverages high trading volume to identify stocks with strong price trends, capitalizing on continued market movement driven by investor interest. Pair trading, however, focuses on the relative volume and price relationship between two correlated assets to exploit temporary divergences without market direction exposure. Explore the dynamics of volume in both strategies to optimize your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Momentum Trading: Types, Strategies and More - Part I - Momentum trading involves buying or selling assets based on recent price trends, with two main types: time-series momentum (buying assets that have performed well over a set period) and cross-sectional momentum (selecting top performers relative to other assets in the same universe).
Momentum Trading for Beginners (What They Don't Teach You) - This video explains how momentum trading focuses on riding strong price moves by following trends, using indicators like RSI and MACD, and emphasizes risk management and trade confirmation for success in fast-moving markets.
Momentum investing - Wikipedia - Momentum investing is a strategy of buying securities that have had high returns over the past 3 to 12 months and selling those with poor returns, relying partly on behavioral finance explanations and sometimes viewed as a market anomaly difficult to explain fully by efficient market theory.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com