Funding rate arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between perpetual futures contracts and spot markets by capitalizing on the periodic payments made between long and short positions, whereas options arbitrage involves strategies that take advantage of mispriced options relative to their underlying assets or other derivatives. Both approaches leverage market inefficiencies to generate profit but require thorough understanding of market mechanics, risk management, and timing. Explore the nuances and strategies behind these arbitrage techniques to enhance your trading effectiveness.
Why it is important
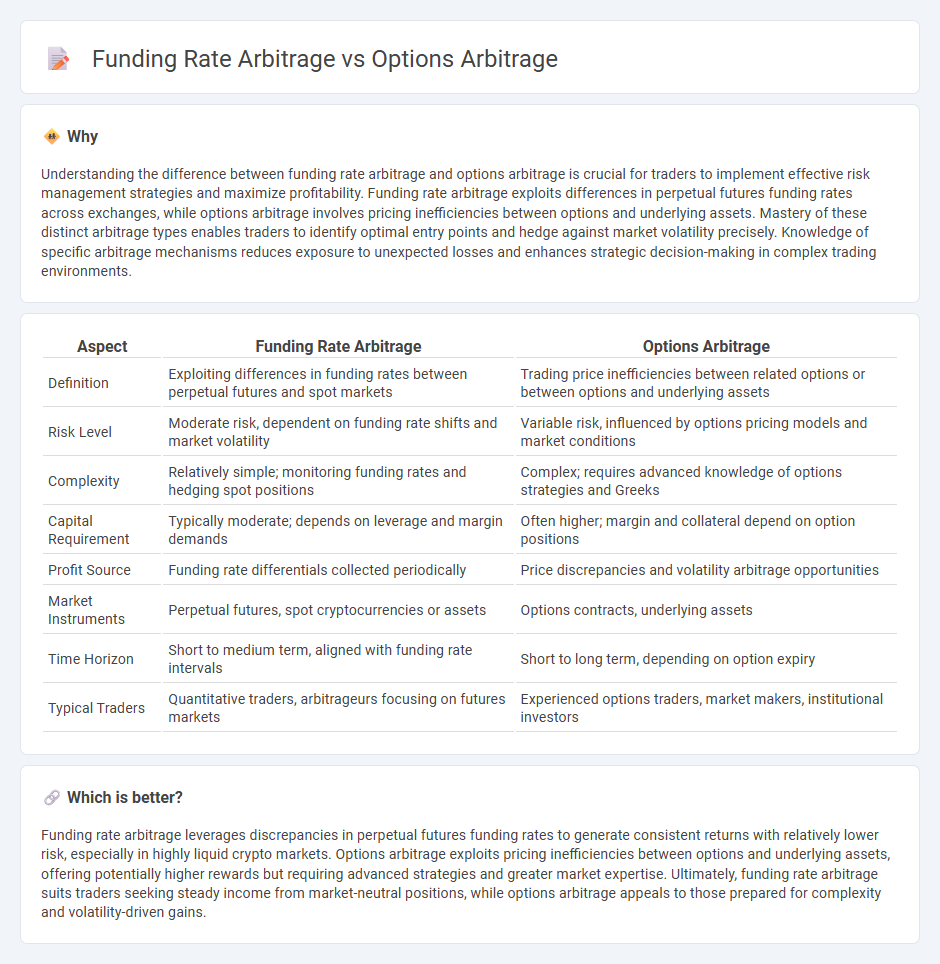
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and options arbitrage is crucial for traders to implement effective risk management strategies and maximize profitability. Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in perpetual futures funding rates across exchanges, while options arbitrage involves pricing inefficiencies between options and underlying assets. Mastery of these distinct arbitrage types enables traders to identify optimal entry points and hedge against market volatility precisely. Knowledge of specific arbitrage mechanisms reduces exposure to unexpected losses and enhances strategic decision-making in complex trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Options Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting differences in funding rates between perpetual futures and spot markets | Trading price inefficiencies between related options or between options and underlying assets |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk, dependent on funding rate shifts and market volatility | Variable risk, influenced by options pricing models and market conditions |
| Complexity | Relatively simple; monitoring funding rates and hedging spot positions | Complex; requires advanced knowledge of options strategies and Greeks |
| Capital Requirement | Typically moderate; depends on leverage and margin demands | Often higher; margin and collateral depend on option positions |
| Profit Source | Funding rate differentials collected periodically | Price discrepancies and volatility arbitrage opportunities |
| Market Instruments | Perpetual futures, spot cryptocurrencies or assets | Options contracts, underlying assets |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, aligned with funding rate intervals | Short to long term, depending on option expiry |
| Typical Traders | Quantitative traders, arbitrageurs focusing on futures markets | Experienced options traders, market makers, institutional investors |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage leverages discrepancies in perpetual futures funding rates to generate consistent returns with relatively lower risk, especially in highly liquid crypto markets. Options arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between options and underlying assets, offering potentially higher rewards but requiring advanced strategies and greater market expertise. Ultimately, funding rate arbitrage suits traders seeking steady income from market-neutral positions, while options arbitrage appeals to those prepared for complexity and volatility-driven gains.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage exploits discrepancies between perpetual futures funding rates and spot prices, while options arbitrage leverages mispricings between options premiums and underlying assets. Both strategies rely on identifying and capitalizing on price inefficiencies in derivative markets to generate risk-adjusted returns. This connection highlights how traders use derivative instruments to achieve market-neutral profits via systematic exploitation of relative value differences.
Key Terms
**Options Arbitrage:**
Options arbitrage exploits price discrepancies between options and their underlying assets, enabling traders to lock in risk-free profits by simultaneously buying and selling related contracts. This strategy relies heavily on market inefficiencies, volatility differences, and mispriced Greeks such as delta, gamma, and theta. Explore detailed methodologies and examples of options arbitrage to enhance your trading precision and profitability.
Put-Call Parity
Options arbitrage exploits price discrepancies related to Put-Call Parity, ensuring the theoretical equivalence between call and put options with the same strike price and expiration, allowing traders to profit from mispriced options. Funding rate arbitrage leverages differences in borrowing costs between perpetual futures contracts and spot prices, capturing risk-free gains through margin financing. Explore deeper insights into how Put-Call Parity impacts arbitrage strategies and enhances trading efficiency.
Strike Price
Options arbitrage focuses on exploiting price inefficiencies between an option's strike price and the underlying asset's spot price to secure risk-free profits. Funding rate arbitrage, on the other hand, capitalizes on discrepancies between perpetual futures' funding rates and spot market prices, which do not directly involve the strike price. Explore the nuanced impacts of strike price selection in options arbitrage to enhance your trading strategy.
Source and External Links
Options Arbitrage Strategies Explained (Low-Risk Trading Insights) - Options arbitrage involves exploiting price inefficiencies by simultaneously buying and selling related options contracts in the same market to earn risk-free or very low-risk profits independent of market direction, relying on pricing gaps caused by factors like volatility and liquidity.
Options arbitrage - Wikipedia - This strategy includes specific positions such as conversions (short call, long put, long underlying) and reversals (long call, short put, short underlying) designed to create delta-neutral, low-risk portfolios that exploit mispricings between options and the underlying asset.
How do you find option arbitrage opportunities? - Quantcha - Tools like option screeners help detect arbitrage opportunities, but traders must consider factors like dividends, early assignment risk, liquidity, and interest rate changes before executing these strategies to avoid hidden risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com