Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated assets to exploit pricing inefficiencies and reduce market risk, while swing trading focuses on capturing short- to medium-term price movements within trending markets using technical analysis. Pair trading leverages statistical arbitrage and mean-reversion strategies, whereas swing trading relies on identifying momentum and chart patterns to time entry and exit points. Discover more about how these trading strategies can optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
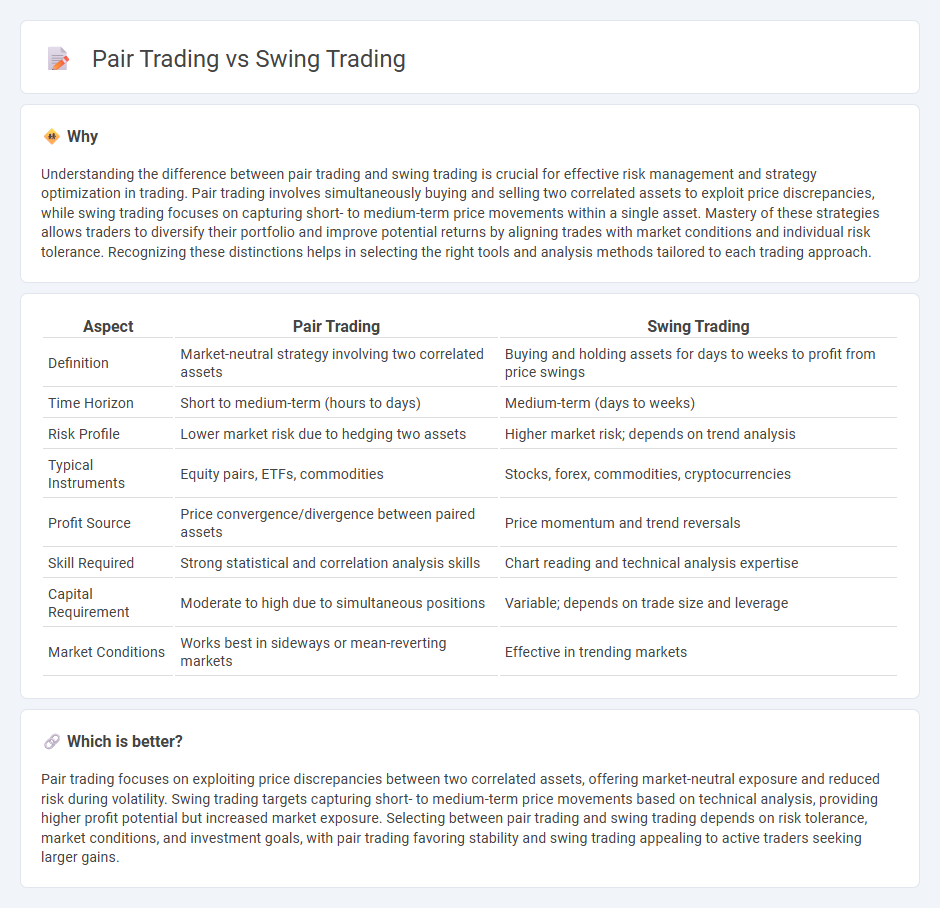
Understanding the difference between pair trading and swing trading is crucial for effective risk management and strategy optimization in trading. Pair trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated assets to exploit price discrepancies, while swing trading focuses on capturing short- to medium-term price movements within a single asset. Mastery of these strategies allows traders to diversify their portfolio and improve potential returns by aligning trades with market conditions and individual risk tolerance. Recognizing these distinctions helps in selecting the right tools and analysis methods tailored to each trading approach.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Pair Trading | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market-neutral strategy involving two correlated assets | Buying and holding assets for days to weeks to profit from price swings |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term (hours to days) | Medium-term (days to weeks) |
| Risk Profile | Lower market risk due to hedging two assets | Higher market risk; depends on trend analysis |
| Typical Instruments | Equity pairs, ETFs, commodities | Stocks, forex, commodities, cryptocurrencies |
| Profit Source | Price convergence/divergence between paired assets | Price momentum and trend reversals |
| Skill Required | Strong statistical and correlation analysis skills | Chart reading and technical analysis expertise |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high due to simultaneous positions | Variable; depends on trade size and leverage |
| Market Conditions | Works best in sideways or mean-reverting markets | Effective in trending markets |
Which is better?
Pair trading focuses on exploiting price discrepancies between two correlated assets, offering market-neutral exposure and reduced risk during volatility. Swing trading targets capturing short- to medium-term price movements based on technical analysis, providing higher profit potential but increased market exposure. Selecting between pair trading and swing trading depends on risk tolerance, market conditions, and investment goals, with pair trading favoring stability and swing trading appealing to active traders seeking larger gains.
Connection
Pair trading and swing trading both capitalize on market inefficiencies but differ in approach and timeframe; pair trading exploits price divergences between correlated assets, aiming for mean reversion, while swing trading focuses on capturing short- to medium-term price movements in individual securities. Integrating pair trading strategies within swing trading techniques enhances risk management by hedging directional exposure and allows traders to profit from relative value fluctuations. This synergy leverages statistical arbitrage principles alongside momentum and trend analysis for diversified trading opportunities.
Key Terms
**Swing Trading:**
Swing trading targets capturing short- to medium-term gains by analyzing market trends and price patterns, typically holding positions from several days to weeks. It relies heavily on technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD to identify entry and exit points within volatile market conditions. Explore further strategies and tools essential for successful swing trading techniques.
Trends
Swing trading captures short- to medium-term price movements by identifying and riding market trends, typically holding positions for several days to weeks. Pair trading involves simultaneously taking long and short positions in two correlated assets to exploit relative price divergences while minimizing market risk. Explore detailed strategies and risk management techniques to master trend-focused swing and pair trading.
Support and Resistance
Swing trading hinges on identifying key support and resistance levels to time market entries and exits within short to medium-term price swings. Pair trading involves monitoring correlated asset pairs where support and resistance levels guide simultaneous long and short positions to exploit relative price movements. Explore detailed strategies and techniques to enhance your trading performance further.
Source and External Links
Swing trading - Wikipedia - Swing trading is a speculative strategy where an asset is held for days or weeks to profit from price swings, using methods like moving averages and algorithms to time entries and exits.
What is swing trading & how does it work? - Saxo Bank - Swing trading aims to capture price movements using strategies such as breakout trading and trend trading, often leveraging technical indicators like moving averages and relative strength index.
Swing trading: A complete guide for investors | TD Direct Investing - Swing trading profits from short-term price changes by buying dips and shorting rises, combining technical and fundamental analysis, with a holding period longer than day trading but shorter than trend investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com