Penny Jump and Order Book represent crucial concepts in trading, where Penny Jump refers to the smallest price increment a stock can move, influencing bid-ask spreads and market liquidity. The Order Book displays real-time buy and sell orders, providing transparency into market depth and price levels. Explore the detailed mechanics and strategic implications of Penny Jump versus Order Book to enhance your trading insight.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between penny jump and order book is crucial for traders to execute precise entry and exit strategies, optimize trade timing, and minimize slippage. Penny jump refers to a small price increase affecting order execution, while the order book displays real-time buy and sell orders, revealing market depth and liquidity. Mastering these concepts enables traders to anticipate price movements and enhance order placement efficiency. Accurate interpretation of order book dynamics can significantly improve short-term trading performance and risk management.
Comparison Table
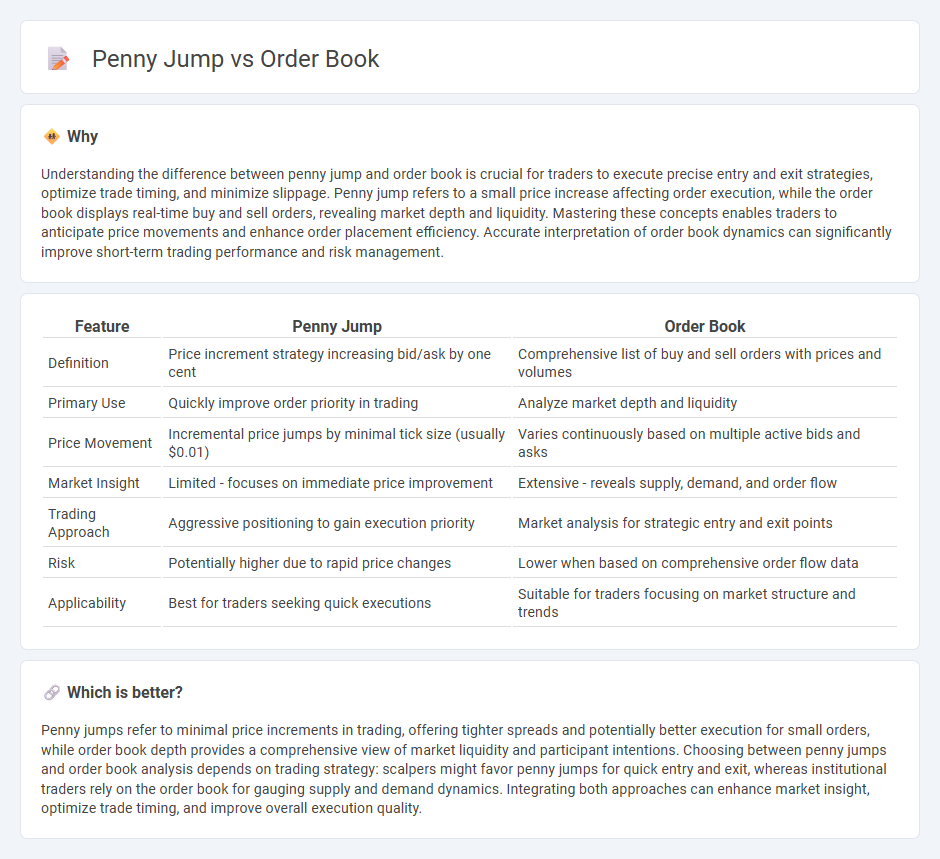
| Feature | Penny Jump | Order Book |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price increment strategy increasing bid/ask by one cent | Comprehensive list of buy and sell orders with prices and volumes |
| Primary Use | Quickly improve order priority in trading | Analyze market depth and liquidity |
| Price Movement | Incremental price jumps by minimal tick size (usually $0.01) | Varies continuously based on multiple active bids and asks |
| Market Insight | Limited - focuses on immediate price improvement | Extensive - reveals supply, demand, and order flow |
| Trading Approach | Aggressive positioning to gain execution priority | Market analysis for strategic entry and exit points |
| Risk | Potentially higher due to rapid price changes | Lower when based on comprehensive order flow data |
| Applicability | Best for traders seeking quick executions | Suitable for traders focusing on market structure and trends |
Which is better?
Penny jumps refer to minimal price increments in trading, offering tighter spreads and potentially better execution for small orders, while order book depth provides a comprehensive view of market liquidity and participant intentions. Choosing between penny jumps and order book analysis depends on trading strategy: scalpers might favor penny jumps for quick entry and exit, whereas institutional traders rely on the order book for gauging supply and demand dynamics. Integrating both approaches can enhance market insight, optimize trade timing, and improve overall execution quality.
Connection
Penny jumps occur when the price of a security increases by the minimum tick size, often one cent, directly influenced by the order book's bid and ask levels. The order book displays real-time buy and sell orders, and a concentrated volume at a specific price can trigger a penny jump as trades execute at the next highest or lowest tick. Market participants monitor order book depth to anticipate penny jumps, optimizing entry and exit points in high-frequency and algorithmic trading strategies.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
The order book displays real-time bid-ask spreads, revealing liquidity and price levels, while penny jumps represent minimal price increments used to narrow the spread and enhance market efficiency. Bid-ask spreads influence trading strategies by indicating market depth and potential transaction costs. Explore how managing bid-ask spreads can optimize trading outcomes through deeper insights.
Market Depth
Market Depth reveals the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels within the Order Book, offering traders insights into potential price movements. Penny Jump refers to small, incremental price changes that can be anticipated by analyzing these depth levels for liquidity and order concentration. Explore more to understand how mastering Market Depth can enhance trading strategies and execution.
Order Types
Order book dynamics play a crucial role in determining the execution of various order types, such as market, limit, and stop orders, which directly affect price movements and liquidity. Penny jumps, or minimal price increments, reflect the granularity with which orders are placed, exposing the microstructure of the order book and influencing bid-ask spreads. Explore deeper insights into how diverse order types interact within the order book to optimize trading strategies and price discovery.
Source and External Links
Order Book - Definition, Components, How It Works - An order book is a list of current buy and sell orders for a specific security, showing prices and volumes that market participants are willing to trade at, originally used in stock exchanges and now also common in cryptocurrency markets.
What is an order book? - Coinbase - An order book is a dynamic electronic list displaying all current buy orders ("bids") and sell orders ("asks") for an asset, including the quantities and prices at which traders want to transact, providing transparency about market supply and demand.
Order Book overview - TT Help Library - Trading Technologies - The Order Book widget shows working orders in real time, allowing traders to view, cancel, modify, or sort orders, and access detailed order information including trade reference IDs and historical activity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com