Liquidity sweep involves quickly buying or selling large volumes of assets to capitalize on available liquidity, often impacting market prices and order book dynamics. Spoofing is a manipulative trading tactic where false orders are placed to create deceptive market signals, misleading other traders about supply or demand. Explore how these strategies influence market behavior and regulatory responses to better understand their impact on trading environments.
Why it is important
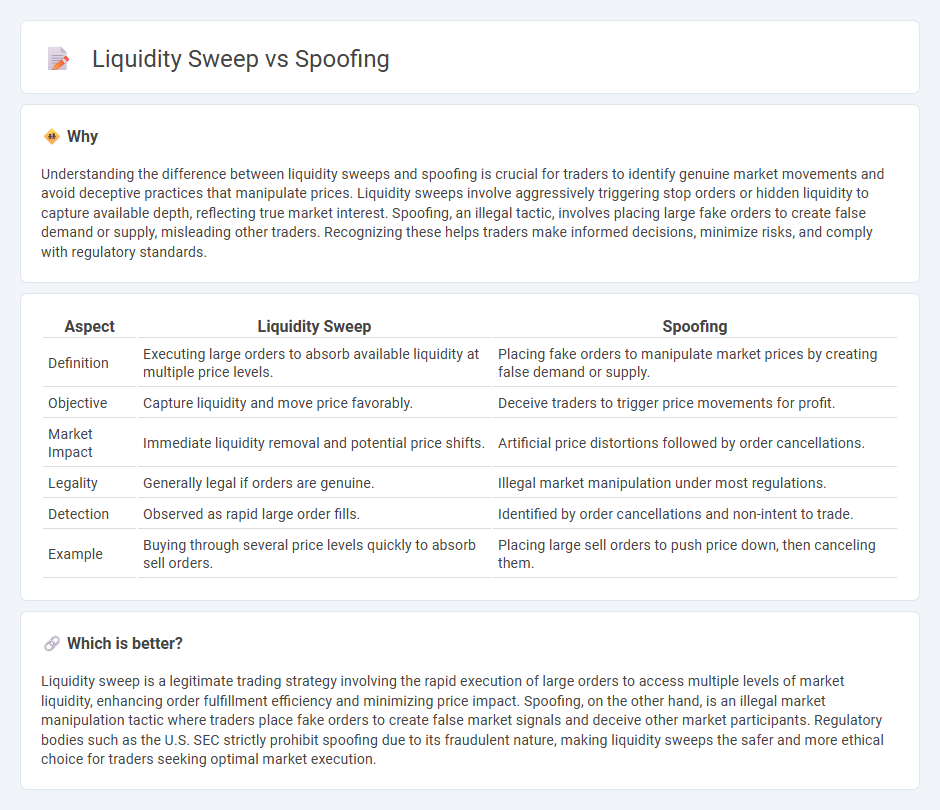
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweeps and spoofing is crucial for traders to identify genuine market movements and avoid deceptive practices that manipulate prices. Liquidity sweeps involve aggressively triggering stop orders or hidden liquidity to capture available depth, reflecting true market interest. Spoofing, an illegal tactic, involves placing large fake orders to create false demand or supply, misleading other traders. Recognizing these helps traders make informed decisions, minimize risks, and comply with regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweep | Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing large orders to absorb available liquidity at multiple price levels. | Placing fake orders to manipulate market prices by creating false demand or supply. |
| Objective | Capture liquidity and move price favorably. | Deceive traders to trigger price movements for profit. |
| Market Impact | Immediate liquidity removal and potential price shifts. | Artificial price distortions followed by order cancellations. |
| Legality | Generally legal if orders are genuine. | Illegal market manipulation under most regulations. |
| Detection | Observed as rapid large order fills. | Identified by order cancellations and non-intent to trade. |
| Example | Buying through several price levels quickly to absorb sell orders. | Placing large sell orders to push price down, then canceling them. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweep is a legitimate trading strategy involving the rapid execution of large orders to access multiple levels of market liquidity, enhancing order fulfillment efficiency and minimizing price impact. Spoofing, on the other hand, is an illegal market manipulation tactic where traders place fake orders to create false market signals and deceive other market participants. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. SEC strictly prohibit spoofing due to its fraudulent nature, making liquidity sweeps the safer and more ethical choice for traders seeking optimal market execution.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps and spoofing are connected through market manipulation tactics that mislead traders about true supply and demand. Spoofing involves placing large fake orders to create an illusion of liquidity, which triggers liquidity sweeps as traders' stop-loss or market orders are executed on this false volume. Both practices disrupt market transparency and can lead to increased volatility and unfair trading advantages.
Key Terms
Order Book
Spoofing manipulates the order book by placing large fake orders to create false market sentiment, which are quickly canceled before execution to mislead traders. In contrast, liquidity sweeps aggressively consume available orders across price levels to capture liquidity and reveal genuine supply or demand, often signaling strong market moves. Explore further to understand how these tactics impact price dynamics and trading strategies.
Market Depth
Spoofing involves placing large fake orders on market depth to create false demand or supply signals, misleading traders into reacting to non-existent liquidity. A liquidity sweep targets hidden or iceberg orders by aggressively executing trades through multiple price levels in the order book, revealing true market depth and liquidity. Explore how these tactics influence order book dynamics and impact trading strategies.
Execution Speed
Spoofing manipulates market perception by placing and canceling orders rapidly, exploiting execution speed to create false demand or supply signals. Liquidity sweeps aggressively execute large orders across multiple price levels, leveraging high-speed trading to capture fleeting liquidity pockets instantaneously. Explore advanced trading strategies to understand how execution speed impacts market dynamics and order execution efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Spoofing & How to Prevent it - Spoofing is a cybercrime where attackers impersonate a trusted entity or device, often by faking emails or websites, to manipulate victims into actions like transferring money or disclosing personal information, potentially leading to data breaches or ransomware attacks.
Spoofing | Spoof Calls | What is a Spoofing Attack - Spoofing in cybersecurity involves pretending to be something else, such as a trusted organization, to gain confidence and steal data or money, with common forms including email, caller ID, website, and GPS spoofing.
What Is Spoofing? Definition, Types & More - Spoofing is a tactic where threat actors disguise unauthorized communications as trusted sources via channels like emails and phone calls, leading to potential financial loss, data breaches, and reputational damage, with prevention relying on authentication protocols and security training.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com