Market microstructure studies the mechanisms and processes behind asset trading, focusing on price formation, order types, and information flow within exchanges. Dark pools are private trading venues that allow large orders to be executed anonymously, reducing market impact and price slippage. Explore how market microstructure theories explain the rise and effects of dark pools in modern trading environments.
Why it is important
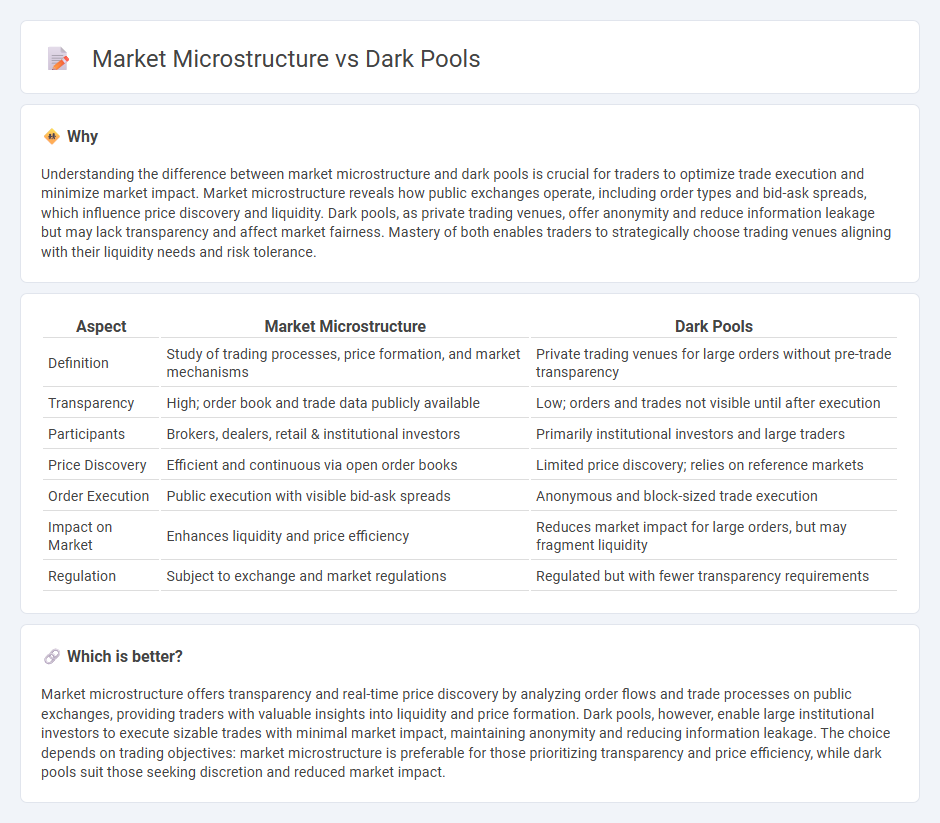
Understanding the difference between market microstructure and dark pools is crucial for traders to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Market microstructure reveals how public exchanges operate, including order types and bid-ask spreads, which influence price discovery and liquidity. Dark pools, as private trading venues, offer anonymity and reduce information leakage but may lack transparency and affect market fairness. Mastery of both enables traders to strategically choose trading venues aligning with their liquidity needs and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Microstructure | Dark Pools |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of trading processes, price formation, and market mechanisms | Private trading venues for large orders without pre-trade transparency |
| Transparency | High; order book and trade data publicly available | Low; orders and trades not visible until after execution |
| Participants | Brokers, dealers, retail & institutional investors | Primarily institutional investors and large traders |
| Price Discovery | Efficient and continuous via open order books | Limited price discovery; relies on reference markets |
| Order Execution | Public execution with visible bid-ask spreads | Anonymous and block-sized trade execution |
| Impact on Market | Enhances liquidity and price efficiency | Reduces market impact for large orders, but may fragment liquidity |
| Regulation | Subject to exchange and market regulations | Regulated but with fewer transparency requirements |
Which is better?
Market microstructure offers transparency and real-time price discovery by analyzing order flows and trade processes on public exchanges, providing traders with valuable insights into liquidity and price formation. Dark pools, however, enable large institutional investors to execute sizable trades with minimal market impact, maintaining anonymity and reducing information leakage. The choice depends on trading objectives: market microstructure is preferable for those prioritizing transparency and price efficiency, while dark pools suit those seeking discretion and reduced market impact.
Connection
Market microstructure examines the processes and rules shaping the trading of financial assets, focusing on order flow, price formation, and liquidity. Dark pools are private trading venues that operate within this framework, providing anonymity and reducing market impact for large orders. The interaction between market microstructure and dark pools influences price discovery and liquidity distribution across public and private markets.
Key Terms
Transparency
Dark pools are private trading venues where large orders are executed anonymously, reducing market transparency compared to traditional public exchanges. Market microstructure studies the mechanisms and processes of trading, emphasizing the importance of transparency to ensure price discovery and fair market conditions. Discover how transparency impacts market efficiency and trader behavior in both dark pools and broader market microstructure.
Order Flow
Dark pools represent private trading venues where large orders are executed anonymously, significantly impacting order flow by reducing visible market liquidity and price discovery. Market microstructure examines these trading processes, including the impact of hidden orders on bid-ask spreads, volatility, and overall market efficiency. Explore the intricate dynamics of order flow in dark pools to better understand their role in modern market microstructure.
Price Discovery
Dark pools impact price discovery by reducing transparency, as trades occur away from public exchanges, limiting available information for market participants. Market microstructure, involving the mechanisms and processes of trade execution, enhances price discovery through order book transparency and liquidity provision. Explore how these factors interact to influence asset pricing and trading efficiency.
Source and External Links
Dark trading: what is it and how does it affect financial markets? - Dark pools are opaque trading venues that allow financial asset orders to be executed anonymously without pre-trade transparency, raising concerns about market fairness and pricing but expanding market access.
Can You Swim in a Dark Pool? | FINRA.org - Dark pools are private trading systems designed for large institutional investors to trade big blocks of shares anonymously to reduce market impact and price swings, though they do not show pre-trade data publicly.
A Beginner's Guide to Dark Pool Trading - Nasdaq - Dark pools are alternative trading systems that let institutional investors execute large trades discreetly to avoid market impact, and their usage has grown significantly since their emergence in the 1980s and regulatory changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com