Quantitative signals in trading rely on numerical data and statistical models to identify patterns and predict market movements, using metrics like price trends, volume, and moving averages. Sentiment analysis evaluates market sentiment by analyzing news, social media, and trader behavior to gauge emotions and crowd psychology that influence asset prices. Explore further to understand how combining quantitative signals and sentiment analysis can enhance trading strategies.
Why it is important
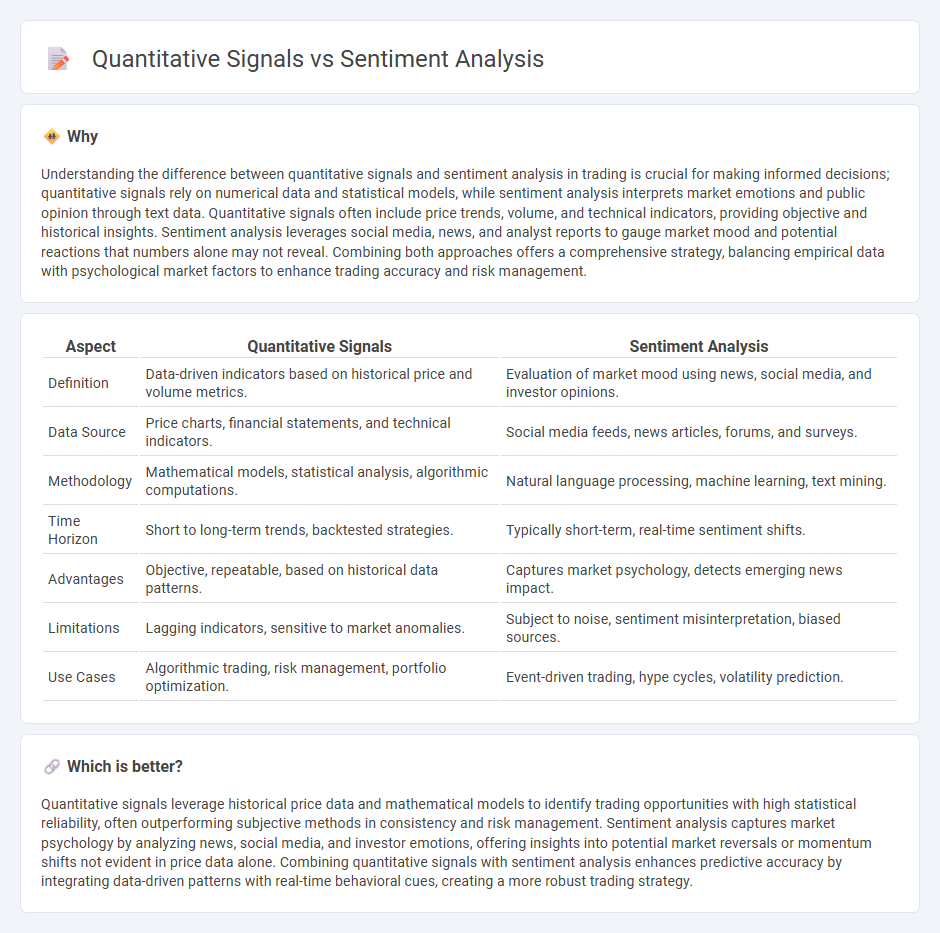
Understanding the difference between quantitative signals and sentiment analysis in trading is crucial for making informed decisions; quantitative signals rely on numerical data and statistical models, while sentiment analysis interprets market emotions and public opinion through text data. Quantitative signals often include price trends, volume, and technical indicators, providing objective and historical insights. Sentiment analysis leverages social media, news, and analyst reports to gauge market mood and potential reactions that numbers alone may not reveal. Combining both approaches offers a comprehensive strategy, balancing empirical data with psychological market factors to enhance trading accuracy and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Signals | Sentiment Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven indicators based on historical price and volume metrics. | Evaluation of market mood using news, social media, and investor opinions. |
| Data Source | Price charts, financial statements, and technical indicators. | Social media feeds, news articles, forums, and surveys. |
| Methodology | Mathematical models, statistical analysis, algorithmic computations. | Natural language processing, machine learning, text mining. |
| Time Horizon | Short to long-term trends, backtested strategies. | Typically short-term, real-time sentiment shifts. |
| Advantages | Objective, repeatable, based on historical data patterns. | Captures market psychology, detects emerging news impact. |
| Limitations | Lagging indicators, sensitive to market anomalies. | Subject to noise, sentiment misinterpretation, biased sources. |
| Use Cases | Algorithmic trading, risk management, portfolio optimization. | Event-driven trading, hype cycles, volatility prediction. |
Which is better?
Quantitative signals leverage historical price data and mathematical models to identify trading opportunities with high statistical reliability, often outperforming subjective methods in consistency and risk management. Sentiment analysis captures market psychology by analyzing news, social media, and investor emotions, offering insights into potential market reversals or momentum shifts not evident in price data alone. Combining quantitative signals with sentiment analysis enhances predictive accuracy by integrating data-driven patterns with real-time behavioral cues, creating a more robust trading strategy.
Connection
Quantitative signals and sentiment analysis intersect in trading by providing complementary data sources to predict market movements. Quantitative signals rely on numerical data such as price patterns and volume metrics, while sentiment analysis interprets textual data from news, social media, and financial reports to gauge trader emotions and market mood. Integrating these methods enhances algorithmic trading strategies, enabling more accurate forecasting and risk management.
Key Terms
**Sentiment Analysis:**
Sentiment analysis involves evaluating textual data from sources such as social media, reviews, and news articles to gauge the emotional tone behind the information, providing valuable insights into public opinion and market trends. This qualitative approach complements quantitative signals like trading volume or price movements by offering context-rich data that can predict market sentiment shifts ahead of numerical indicators. Explore more about how sentiment analysis can enhance your strategic decisions and market understanding.
News Sentiment
News sentiment analysis evaluates the emotional tone of news articles to gauge market sentiment, while quantitative signals rely on numerical data such as price trends and volume. Integrating news sentiment with quantitative indicators enhances predictive accuracy in financial forecasting. Explore our detailed guide to understand how combining these approaches can improve investment strategies.
Social Media Buzz
Sentiment analysis evaluates the emotional tone behind social media posts, offering qualitative insights into user opinions and brand perception. Quantitative signals measure metrics such as share counts, likes, comments, and engagement rates, providing numerical data on content popularity and reach. Explore how combining sentiment analysis with quantitative signals can enhance your understanding of social media buzz and drive strategic marketing decisions.
Source and External Links
Sentiment Analysis and How to Leverage It - Qualtrics - Sentiment analysis identifies and interprets qualitative data to understand emotions about a topic and includes types like fine-grained, aspect-based, and intent-based sentiment analysis.
What is Sentiment Analysis? | Definition from TechTarget - Sentiment analysis, or opinion mining, uses NLP, ML, and AI to categorize text's emotional tone as positive, negative, or neutral, providing insights on customer sentiment and brand reputation from various text sources.
What is Sentiment Analysis? - AWS - Sentiment analysis analyzes digital text to determine emotional tone and includes types such as fine-grained scoring, aspect-based sentiment, intent-based and emotional detection to understand customer feelings in depth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com